Abstract
Key message
qGSN5, a novel quantitative trait locus coordinating grain size and grain number in rice, was fine-mapped to an 85.60-kb region. GS3 may be a suppressor of qGSN5.
Abstract
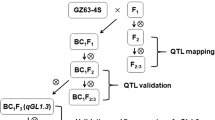
Grain size and grain number are two factors that directly determine rice grain yield; however, the underlying genetic mechanisms are complicated and remain largely unclear. In this study, a chromosome segment substitution line (CSSL), CSSL28, which showed increased grain size and decreased grain number per panicle, was identified in a set of CSSLs derived from a cross between 93-11 (recipient) and Nipponbare (donor). Four substitution segments were identified in CSSL28, and the substitution segment located on chromosome 5 was responsible for the phenotypes of CSSL28. Thus, we defined this quantitative trait locus (QTL) as grain size and grain number 5 (qGSN5). Cytological and quantitative PCR analysis showed that qGSN5 regulates the development of the spikelet hull by affecting cell proliferation. Genetic analysis showed that qGSN5 is a semi-dominant locus regulating grain size and grain number. Through map-based cloning and overlapping substitution segment analysis, qGSN5 was finally delimited to an 85.60-kb region. Based on sequence and quantitative PCR analysis, Os05g47510, which encodes a P-type pentatricopeptide repeat protein, is the most likely candidate gene for qGSN5. Pyramiding analysis showed that the effect of qGSN5 was significantly lower in the presence of a functional GS3 gene, indicating that GS3 may be a suppressor of qGSN5. In addition, we found that qGSN5 could improve the grain shape of hybrid rice. Together, our results lay the foundation for cloning a novel QTL coordinating grain size and grain number in rice and provide a good genetic material for long-grain hybrid rice breeding.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashikari M, Sakakibara H, Lin S, Yamamoto T, Takashi T, Nishimura A, Angeles ER, Qian Q, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2005) Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production. Science 309:741–745
Bai X, Huang Y, Hu Y, Liu H, Zhang B, Smaczniak C, Hu G, Han Z, Xing Y (2017) Duplication of an upstream silencer of FZP increases grain yield in rice. Nat Plants 3:885–893
Che R, Tong H, Shi B, Liu Y, Fang S, Liu D, Xiao Y, Hu B, Liu L, Wang H (2015) Control of grain size and rice yield by GL2-mediated brassinosteroid responses. Nat Plants 2:15195
Duan P, Rao Y, Zeng D, Yang Y, Xu R, Zhang B, Dong G, Qian Q, Li Y (2014) SMALL GRAIN 1, which encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4, influences grain size in rice. Plant J 77:547–557
Duan P, Ni S, Wang J, Zhang B, Xu R, Wang Y, Chen H, Zhu X, Li Y (2015) Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat Plants 2:15203
Duan P, Xu J, Zeng D, Zhang B, Geng M, Zhang G, Huang K, Huang L, Xu R, Ge S, Qian Q, Li Y (2017) Natural variation in the promoter of gse5 contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Mol Plant 10:685–694
Fan Y, Li Y (2019) Molecular, cellular and Yin-Yang regulation of grain size and number in rice. Mol Breed 39:163
Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112:1164–1171
Guo T, Chen K, Dong N-Q, Shi C-L, Ye W-W, Gao J-P, Shan J-X, Lin H-X (2018) GRAIN SIZE AND NUMBER1 Negatively regulates the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMPK6 Cascade to coordinate the trade-off between grain number per panicle and grain size in rice. Plant Cell 30:871–888
Hu J, Wang Y, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu J, Yu H, Shi Z, Pan J, Zhang D, Kang S, Zhu L, Dong G, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhang G, Xie L, Xiong G, Li J, Qian Q (2015) A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant 8:1455–1465
Huang R, Jiang L, Zheng J, Wang T, Wang H, Huang Y, Hong Z (2013) Genetic bases of rice grain shape: so many genes, so little known. Trends Plant Sci 18:218–226
Huang W, Yu C, Hu J, Wang L, Dan Z, Zhou W, He C, Zeng Y, Yao G, Qi J, Zhang Z, Zhu R, Chen X, Zhu Y (2015) Pentatricopeptide-repeat family protein RF6 functions with hexokinase 6 to rescue rice cytoplasmic male sterility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:14984–14989
Huang K, Wang D, Duan P, Zhang B, Xu R, Li N, Li Y (2017) WIDE AND THICK GRAIN 1, which encodes an otubain-like protease with deubiquitination activity, influences grain size and shape in rice. Plant J 91:849–860
Huo X, Wu S, Zhu Z, Liu F, Fu Y, Cai H, Sun X, Gu P, Xie D, Tan L, Sun C (2017) NOG1 increases grain production in rice. Nat Commun 8:1497
Ishimaru K, Hirotsu N, Madoka Y, Murakami N, Hara N, Onodera H, Kashiwagi T, Ujiie K, Shimizu B, Onishi A, Miyagawa H, Katoh E (2013) Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield. Nat Genet 45:707–711
Kim SR, Yang JI, Moon S, Ryu CH, An K, Kim KM, Yim J, An G (2009) Rice OGR1 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat-DYW protein and is essential for RNA editing in mitochondria. Plant J 59:738–749
Li S, Zhao B, Yuan D, Duan M, Qian Q, Tang L, Wang B, Liu X, Zhang J, Wang J, Sun J, Liu Z, Feng YQ, Yuan L, Li C (2013) Rice zinc finger protein DST enhances grain production through controlling Gn1a/OsCKX2 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:3167–3172
Li N, Xu R, Duan PG, Li YH (2018) Control of grain size in rice. Plant Reprod 31:237–251
Li N, Xu R, Li Y (2019) Molecular networks of seed size control in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70:435–463
Li G, Tang J, Zheng J, Chu C (2021a) Exploration of rice yield potential: Decoding agronomic and physiological traits. Crop J 9:577–589
Li G, Zhang H, Li J, Zhang Z, Li Z (2021b) Genetic control of panicle architecture in rice. Crop J 9:590–597
Liu L, Tong H, Xiao Y, Che R, Xu F, Hu B, Liang C, Chu J, Li J, Chu C (2015a) Activation of Big Grain1 significantly improves grain size by regulating auxin transport in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:11102–11107
Liu S, Hua L, Dong S, Chen H, Zhu X, Jiang J, Zhang F, Li Y, Fang X, Chen F (2015b) OsMAPK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase, influences rice grain size and biomass production. Plant J 84:672–681
Liu J, Chen J, Zheng X, Wu F, Lin Q, Heng Y, Tian P, Cheng Z, Yu X, Zhou K, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Wang H, Wan J (2017) GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signalling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice. Nat Plants 3:17043
Luo J, Liu H, Zhou T, Gu B, Huang X, Shangguan Y, Zhu J, Li Y, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zhao Q, Wang A, Wang Z, Sang T, Wang Z, Han B (2013) An-1 encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein that regulates awn development, grain size, and grain number in rice. Plant Cell 25:3360–3376
Mao H, Sun S, Yao J, Wang C, Yu S, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2010) Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:19579–19584
Qin P, Lu H, Du H, Wang H, Chen W, Chen Z, He Q, Ou S, Zhang H, Li X, Li X, Li Y, Liao Y, Gao Q, Tu B, Yuan H, Ma B, Wang Y, Qian Y, Fan S, Li W, Wang J, He M, Yin J, Li T, Jiang N, Chen X, Liang C, Li S (2021). Pan-genome analysis of 33 genetically diverse rice accessions reveals hidden genomic variations. Cell 184:3542–3558 e3516
Qiu T, Zhao X, Feng H, Qi L, Yang J, Peng YL, Zhao W (2021) OsNBL3, a mitochondrion-localized pentatricopeptide repeat protein, is involved in splicing nad5 intron 4 and its disruption causes lesion mimic phenotype with enhanced resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Biotechnol J. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13659
Sadras VO (2007) Evolutionary aspects of the trade-off between seed size and number in crops. Field Crops Res 100:125–138
Seo H, Kim SH, Lee BD, Lim JH, Lee SJ, An G, Paek NC (2020) The rice basic helix-loop-helix 79 (OsbHLH079) determines leaf angle and grain shape. Int J Mol Sci 21:2090
Shi C, Ren Y, Liu L, Wang F, Zhang H, Tian P, Pan T, Wang Y, Jing R, Liu T, Wu F, Lin Q, Lei C, Zhang X, Zhu S, Guo X, Wang J, Zhao Z, Wang J, Zhai H, Cheng Z, Wan J (2019) Ubiquitin specific protease 15 has an important role in regulating grain width and size in rice. Plant Physiol 180:381–391
Si L, Chen J, Huang X, Gong H, Luo J, Hou Q, Zhou T, Lu T, Zhu J, Shangguan Y, Chen E, Gong C, Zhao Q, Jing Y, Zhao Y, Li Y, Cui L, Fan D, Lu Y, Weng Q, Wang Y, Zhan Q, Liu K, Wei X, An K, An G, Han B (2016) OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice. Nat Genet 48:447–456
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630
Su S, Hong J, Chen X, Zhang C, Chen M, Luo Z, Chang S, Bai S, Liang W, Liu Q, Zhang D (2021) Gibberellins orchestrate panicle architecture mediated by DELLA–KNOX signalling in rice. Plant Biotechnol J. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13661
Sun S, Wang L, Mao H, Shao L, Li X, Xiao J, Ouyang Y, Zhang Q (2018) A G-protein pathway determines grain size in rice. Nat Commun 9:851
Tang QY, Zhang CX (2013) Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci 20:254–260
Torres Acosta JA, Fowke LC, Wang H (2011) Analyses of phylogeny, evolution, conserved sequences and genome-wide expression of the ICK/KRP family of plant CDK inhibitors. Ann Bot 107:1141–1157
Wang S, Wu K, Yuan Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Lin X, Zeng R, Zhu H, Dong G, Qian Q, Zhang G, Fu X (2012) Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44:950–954
Wang S, Wu K, Qian Q, Liu Q, Li Q, Pan Y, Ye Y, Liu X, Wang J, Zhang J, Li S, Wu Y, Fu X (2017) Non-canonical regulation of SPL transcription factors by a human OTUB1-like deubiquitinase defines a new plant type rice associated with higher grain yield. Cell Res 27:1142–1156
Wu Y, Wang Y, Mi XF, Shan JX, Li XM, Xu JL, Lin HX (2016) The QTL GNP1 encodes GA20ox1, which increases grain number and yield by increasing cytokinin activity in rice panicle meristems. PLoS Genet 12:e1006386
Wu M, Ren Y, Cai M, Wang Y, Zhu S, Zhu J, Hao Y, Teng X, Zhu X, Jing R, Zhang H, Zhong M, Wang Y, Lei C, Zhang X, Guo X, Cheng Z, Lin Q, Wang J, Jiang L, Bao Y, Wang Y, Wan J (2019) Rice FLOURY ENDOSPERM10 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein that is essential for the trans-splicing of mitochondrial nad1 intron 1 and endosperm development. New Phytol 223:736–750
Xiao HJ, Xu YH, Ni CZ, Zhang QN, Zhong FY, Huang JS, Liu W, Peng LL, Zhu YG, Hu J (2018) A rice dual-localized pentatricopeptide repeat protein is involved in organellar RNA editing together with OsMORFs. J Exp Bot 69:2923–2936
Xiao Y, Liu D, Zhang G, Gao S, Liu L, Xu F, Che R, Wang Y, Tong H, Chu C (2019) Big Grain3, encoding a purine permease, regulates grain size via modulating cytokinin transport in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 61:581–597
Xing Y, Zhang Q (2010) Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:421
Xu R, Duan P, Yu H, Zhou Z, Zhang B, Wang R, Li J, Zhang G, Zhuang S, Lyu J, Li N, Chai T, Tian Z, Yao S, Li Y (2018a) Control of grain size and weight by the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMAPK6 signaling pathway in rice. Mol Plant 11:860–873
Xu R, Yu H, Wang J, Duan P, Zhang B, Li J, Li Y, Xu J, Lyu J, Li N, Chai T, Li Y (2018b) A mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase influences grain size and weight in rice. Plant J 95:937–946
Yang XM, Ren YL, Cai Y, Niu M, Feng ZM, Jing RN, Mou CL, Liu X, Xiao LJ, Zhang X, Wu FQ, Guo XP, Jiang L, Wan JM (2018). Overexpression of OsbHLH107, a member of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family, enhances grain size in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 11:41
Yang W, Wu K, Wang B, Liu H, Guo S, Guo X, Luo W, Sun S, Ouyang Y, Fu X, Chong K, Zhang Q, Xu Y (2021) The RING E3 ligase CLG1 targets GS3 for degradation via the endosome pathway to determine grain size in rice. Mol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.1006.1027
Yin W, Xiao Y, Niu M, Meng W, Li L, Zhang X, Liu D, Zhang G, Qian Y, Sun Z, Huang R, Wang S, Liu CM, Chu C, Tong H (2020) ARGONAUTE2 enhances grain length and salt tolerance by activating big grain3 to modulate cytokinin distribution in rice. Plant Cell 32:2292–2306
Yuan H, Fan S, Huang J, Zhan S, Wang S, Gao P, Chen W, Tu B, Ma B, Wang Y, Qin P, Li S (2017) 08SG2/OsBAK1 regulates grain size and number, and functions differently in Indica and Japonica backgrounds in rice. Rice 10:25
Yuan H, Qin P, Hu L, Zhan S, Wang S, Gao P, Li J, Jin M, Xu Z, Gao Q, Du A, Tu B, Chen W, Ma B, Wang Y, Li S (2019) OsSPL18 controls grain weight and grain number in rice. J Genet Genomics 46:41–51
Zhang L, Qi Y, Wu M, Zhao L, Zhao Z, Lei C, Hao Y, Yu X, Sun Y, Zhang X, Guo X, Ren Y, Wan J (2021) Mitochondrion-targeted PENTATRICOPEPTIDE REPEAT5 is required for cis-splicing of nad4 intron 3 and endosperm development in rice. Crop J 9:282–296
Zheng P, Liu Y, Liu X, Huang Y, Sun F, Wang W, Chen H, Jan M, Zhang C, Yuan Y, Tan BC, Du H, Tu J (2021) OsPPR939, a nad5 splicing factor, is essential for plant growth and pollen development in rice. Theor Appl Genet 134:923–940
Zuo J, Li J (2014) Molecular genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci regulating rice grain size. Annu Rev Genet 48:99–118
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Major Research program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (92535301), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32001489), the Open project of Sichuan Provincial Key Laboratory of Crop Resources and Genetic Improvement, and the Outstanding Young Scientific and Technological Talents Project in Sichuan Province (2020JDJQ0040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY and SL conceived and designed all the experiments. HY, PG, and XH performed most of the experiments and contributed equally to this work. MY, ZX, MJ, WS, and SZ participated in construction of plant materials, agronomic trait investigation, and primary mapping. XZ, BT, TL, and YW performed cytological analysis and fine mapping. BM, PQ, and WC were involved in candidate gene analysis and exploration of breeding utilization. HY wrote the manuscript, and all authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Jiankang Wang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, H., Gao, P., Hu, X. et al. Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of qGSN5, a novel quantitative trait locus coordinating grain size and grain number in rice. Theor Appl Genet 135, 51–64 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03951-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03951-7