Abstract
Key message
Four QTL related to haploid male fertility were detected by a segregation distortion method and the key QTL qhmf4 was fine mapped to an interval of ~800 kb.
Abstract
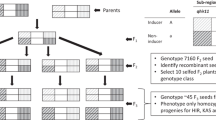
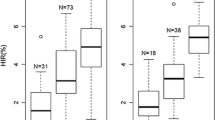
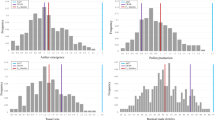
Doubled haploid (DH) technology enables rapid development of homozygous lines in maize breeding programs. However, haploid genome doubling is a bottleneck for the commercialization of DH technology and is limited by haploid male fertility (HMF). This is the first study reporting the quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis of HMF in maize. Four QTL, qhmf1, qhmf2, qhmf3, and qhmf4, controlling HMF have been identified by segregation distortion (SD) loci detection in the selected haploid population derived from ‘Yu87-1/Zheng58’. Three loci, qhmf1, qhmf2, and qhmf4, were also detected in the selected haploid population derived from ‘4F1/Zheng58’. The QTL qhmf4 showed the strongest SD in both haploid populations. Based on the sequence information of ‘Yu87-1’ and ‘Zheng58’, thirteen markers being polymorphic between the two lines were developed to saturate the qhmf4 region. A total of 8168 H1BC2 (haploid backcross generation) plants produced from ‘Yu87-1’ and ‘Zheng58’ were screened for recombinants. All the 48 recombinants were backcrossed to ‘Zheng58’ to develop H1BC3 progeny. The heterozygous H1BC3 individuals were crossed with CAU5 to induce haploids. In each H1BC3 progeny, haploids were genotyped and evaluated for anther emergence score (AES). Significant (or no significant) difference (P < 0.05) between haploids with or without ‘Yu87-1’ donor segment indicated presence or absence of qhmf4 in the donor segment. The analysis of the 48 recombinants narrowed the qhmf4 locus down to an ~800 kb interval flanked by markers IND166 and IND1668.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barret P, Brinkmann M, Beckert M (2008) A major locus expressed in the male gametophyte with incomplete penetrance is responsible for in situ gynogenesis in maize. Theor Appl Genet 117:581–594
Barrett B, Griffiths A, Schreiber M, Ellison N, Mercer C, Bouton J, Ong B, Forster J, Sawbridge T, Spangenberg G, Bryan G, Woodfield D (2004) A microsatellite map of white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:596–608
Chalyk ST (1994) Properties of maternal haploid maize plants and potential application to maize breeding. Euphytica 79:13–18
Chang MT, Coe-Jr EH (2009) Doubled haploids. In: Kriz AL, Larkins BA (eds) Molecular genetic approaches to maize improvement. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 127–142
Chase SS (1952) Selection for parthenogenesis and monoploid fertility in maize. Genetics 37:573–574
Cifuentes M, Rivard M, Pereira L, Chelysheva L, Mercier R (2013) Haploid meiosis in Arabidopsis: double-strand breaks are formed and repaired but without synapsis and crossovers. PLoS One 8:e72431
Coe EH (1959) A line of maize with high haploid frequency. Am Nat 93:381–382
Cui Y, Zhang F, Xu J, Li Z, Xu S (2015) Mapping quantitative trait loci in selected breeding populations: a segregation distortion approach. Heredity 115:538–546
Darvasi A, Soller M (1992) Selective genotyping for determination of linkage between a marker locus and a quantitative trait locus. Theor Appl Genet 85:353–359
Dong X, Xu X, Miao J, Li L, Zhang D, Mi X, Liu C, Tian X, Melchinger AE, Chen S (2013) Fine mapping of qhir1 influencing in vivo haploid induction in maize. Theor Appl Genet 126:1713–1720
Dong X, Xu X, Li L, Liu C, Tian X, Li W, Chen S (2014) Marker-assisted selection and evaluation of high oil in vivo haploid inducers in maize. Mol Breed 34:1147–1158
Dwivedi SL, Britt AB, Tripathi L, Sharma S, Upadhyaya HD, Ortiz R (2015) Haploids: Constraints and opportunities in plant breeding. Biotechnol Adv 33:812–829
Eder J, Chalyk S (2002) In vivo haploid induction in maize. Theor Appl Genet 104:703–708
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics. Addison Wesley Longman, Harlow
Francia E, Tacconi G, Crosatti C, Barabaschi D, Bulgarelli D, Dall’Aglio E, Valè G (2005) Marker assisted selection in crop plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 82:317–342
Geiger HH (2009) Doubled haploids. In: Bennetzen JL, Hake S (eds) Maize handbook. Springer, New York, pp 641–657
Geiger HH, Gordillo GA (2009) Doubled haploids in hybrid maize breeding. Maydica 54:485–499
Geiger HH, Schönleben M (2011) Incidence of male fertility in haploid elite dent maize germplasm. Maize Genet Coop Newsl 85:22–32
Geiger HH, Braun MD, Gordillo GA, Koch S, Jesse J, Krutzfeldt BAE (2006) Variation for female fertility among haploid maize lines. Maize Genet Coop Newsl 80:28–30
Golubovskaya IN, Hamant O, Timofejeva L, Wang CJR, Braun D, Meeley R, Cande WZ (2006) Alleles of afd1 dissect REC8 functions during meiotic prophase I. J Cell Sci 119:3306–3315
Hallauer AR, Carena MJ, Miranda-Filho JB (2010) Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. Springer, New York
Han X, Tang Q, Cao M, Rong T (2006) Study on identifying methods of maize haploids induced by Stock 6. Maize Sci 14:64–66
Häntzschel KR, Weber R (2010) Blockage of mitosis in maize root tips using colchicine-alternatives. Protoplasma 241 (1-4):99–104
Hermisson J, Wagner GP (2004) The population genetic theory of hidden variation and genetic robustness. Genetics 168:2271–2284
Jensen CJ (1974) Chromosome doubling techniques in haploids. In: Kasha KJ (ed) Haploids in higher plants, advances and potential, 1st edn. University of Guelph, Guelph, pp 153–190
Kelliher T, Starr D, Richbourg L, Chintamanani S, Delzer B, Nuccio ML, Green J, Chen Z, McCuiston J, Wang W, Liebler T, Bullock P, Martin B (2017) MATRILINEAL, a sperm-specific phospholipase, triggers maize haploid induction. Nature. doi:10.1038/nature20827
Kitamura S, Akutsu M, Okazaki K (2009) Mechanism of action of nitrous oxide gas applied as a polyploidizing agent during meiosis in lilies. Sex Plant Reprod 22:9–14
Kleiber D, Prigge V, Melchinger AE, Burkard F, San Vicente F, Palomino G, Gordillo GA (2012) Haploid fertility in temperate and tropical maize germplasm. Crop Sci 52:623–630
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lander E, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daley M, Lincoln S, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Li ZK, Fu BY, Gao YM, Xu JL, Ali J, Lafitte HR, Jiang YZ, Domingo-Rey J, Vijayakumar CHM, Maghirang R, Zheng TQ, Zhu LH (2005) Genome-wide introgression lines and their use in genetic and molecular dissection of complex phenotypes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 59:33–52
Li L, Xu XW, Jin WW, Chen SJ (2009) Morphological and molecular evidences for DNA introgression in haploid induction via a high oil inducer CAUHOI in maize. Planta 230:367–376
Liu Z, Song T (2000) Fertility spontaneously restoring of inflorescence and chromosome doubling by chemical treatment in maize haploid. Acta Agron Sin 26:947–952
Liu J, Guo T, Yang P, Wang H, Liu L, Lu Z, Xu X, Hu J, Huang Q, Chen S (2012) Development of automatic nuclear magnetic resonance screening system for haploid kernels in maize. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 28:233–236
Liu C, Li W, Zhong Y, Dong X, Hu H, Tian X, Wang L, Chen B, Chen C, Melchinger AE, Chen S (2015) Fine mapping of qhir8 affecting in vivo haploid induction in maize. Theor Appl Genet 128:2507–2515
Lynch M, Walsh B (1998). Genetics and analysis of quantitative traits. Sunderland, MA
Melchinger AE, Schipprack W, Würschum T, Chen S, Technow F (2013) Rapid and accurate identification of in vivo-induced haploid seeds based on oil content in maize. Sci Rep 3:1–5
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Nanda DK, Chase SS (1966) An embryo marker for detecting monoploids of maize (Zea mays L.). Crop Sci 6:213–215
Navabi A, Mather D, Bernier J, Spaner D, Atlin GN (2009) QTL detection with bidirectional and unidirectional selective genotyping: marker-based and trait-based analyses. Theor Appl Genet 118:347–358
Prasanna BM, Chaikam V, Mahuku G (2012) Doubled haploid (DH) technology in maize breeding: an overview. Doubled haploid technology in maize breeding: theory and practice. CIMMYT, Mexico, 1–8
Prigge V, Sánchez C, Dhillon BS, Schipprack W, Araus JL, Bänziger M, Melchinger AE (2011) Doubled haploids in tropical maize: I. effects of inducers and source germplasm on in vivo haploid induction rates. Crop Sci 51:1498–1506
Prigge V, Xu XW, Li L, Babu R, Chen SJ, Atlin GN, Melchinger AE (2012) New insights into the genetics of in vivo induction of maternal haploids, the backbone of doubled haploid technology in maize. Genetics 190:781–793
Röber FK, Gordillo GA, Geiger HH (2005) In vivo haploid induction in maize: performance of new inducers and significance for doubled haploid lines in hybrid breeding. Maydica 50:275–283
Rotarenco V, Dicu G, Fuia S (2010) New inducers of maternal haploids in maize. Maize Genet Coop Newsl 84:21–22
Sandler L, Hiraizumi Y, Sandler I (1959) Meiotic drive in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. I. The cytogenetic basis of segregation-distortion. Genetics 44(2):233–250
Schmidt W (2003) Hybrid maize breeding at KWS SAAT AG (in German). In: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Austrian Seed Association, Gumpenstein, 25–27 November 2003, pp 1–6
Seitz G (2005) The use of doubled haploids in corn breeding. In: Proceedings of the 41st Annual Illinois Corn Breeders’ School 2005, University of Illinois, Urbana–Champaign, 7–8 March 2005, pp 1–7
Smith JSC, Hussain T, Jones ES, Graham G, Podlich D, Wall S, Williams M (2008) Use of doubled haploids in maize breeding: implications for intellectual property protection and genetic diversity in hybrid crops. Mol Breed 22:51–59
Sugihara N, Higashigawa T, Aramoto D, Kato A (2013) Haploid plants carrying a sodium azide-induced mutation (fdr1) produce fertile pollen grains due to first division restitution (FDR) in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 126:2931–2941
Testillano P, Georgiev S, Mogensen HL, Dumas C, Risueno MC, MatthysRochon E (2004) Spontaneous chromosome doubling results from nuclear fusion during in vitro maize induced microspore embryogenesis. Chromosoma 112:342–349
Vanous AE (2011) Optimization of doubled haploid production in maize (Zea mays L.). Dissertation, Iowa state University
Venuprasad R, Bool ME, Dalid CO, Bernier J, Kumar A, Atlin GN (2009) Genetic loci responding to two cycles of divergent selection for grain yield under drought stress in a rice breeding population. Euphytica 167:261–269
Wan Y, Petolino JF, Widholm JM (1989) Efficient production of doubled haploid plants through colchicine treatment of anther-derived maize callus. Theor Appl Genet 77:889–892
Wang H, Liu J, Xu X, Huang QM, Chen SS, Yang PQ, Chen SJ, Song YQ (2016) Fully-Automated High-Throughput NMR System for Screening of Haploid Kernels of Maize (Corn) by Measurement of Oil Content. PloS one 11:e0159444
Wei J, Chen M (2006) Primary study on the natural fertility of maize haploids. Maize Sci 14:24–26
Weng J, Xie C, Hao Z, Wang J, Liu C, Li M, Zhang D, Bai L, Zhang S, Li X (2011) Genome-wide association study identifies candidate genes that affect plant height in Chinese elite maize (Zea mays L.) inbred lines. PLoS One 6:e29229
Wu P, Ren J, Li L, Chen S (2014) Early spontaneous diploidization of maternal maize haploids generated by in vivo haploid induction. Euphytica 200:127–138
Wu P, Ren J, Tian X, Lübberstedt T, Li W, Li G, Li X, Chen J (2017) New Insights into the Genetics of Haploid Male Fertility in Maize. Crop Sci. doi:10.2135/cropsci2016.01.0017
Xu X, Li L, Dong X, Jin W, Melchinger AE, Chen SJ (2013) Gametophytic and zygotic selection leads to segregation distortion through in vivo induction of a maternal haploid in maize. J Exp Bot 64:1083–1096
Yang Q, Yin GM, Guo YL, Zhang DF, Chen SJ, Xu ML (2010) A major QTL for resistance to Gibberella stalk rot in maize. Theor Appl Genet 121:673–687
Zhan H, Xu S (2011) Generalized linear mixed model for segregation distortion analysis. BMC Genet 12:97
Zhang D, Liu Y, Guo Y, Yang Q, Ye J, Chen S, Xu M (2012) Fine-mapping of qRfg2, a QTL for resistance to Gibberella stalk rot in maize. Theor Appl Genet 124:585–596
Zhang F, Ma X, Gao Y, Hao X, Li Z (2014) Genome-wide response to selection and genetic basis of cold tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Genet 15:55
Zhou W, Tang Z, Hou J, Hu N, Yin T (2015) Genetic map construction and detection of genetic loci underlying segregation distortion in an intraspecific cross of Populus deltoides. PloS one 10:e0126077
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Lai for providing the sequence information of ‘Yu87-1’ and ‘Zheng58’. This work was supported by funds from the National Key Research and Development Plan (2016YFD0101200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31560392), the National Maize Industrial Technology System (CARS-02-09), and Chinese Postdoctoral Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Communicated by Chris Carolin Schön.
J. Ren and P. Wu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., Wu, P., Tian, X. et al. QTL mapping for haploid male fertility by a segregation distortion method and fine mapping of a key QTL qhmf4 in maize. Theor Appl Genet 130, 1349–1359 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2892-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2892-6