Abstract
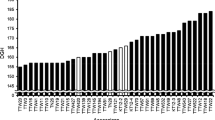
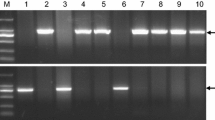
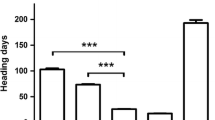
Natural variation in wheat requirement of long exposures to cold temperatures to accelerate flowering (vernalization) is mainly controlled by the Vrn-1, Vrn-2, Vrn-3, and Vrn-4 loci. The first three loci have been well characterized, but limited information is available for Vrn-4. So far, natural variation for Vrn-4 has been detected only in the D genome (Vrn-D4), and genetic stocks for this gene are available in Triple Dirk (TDF, hereafter). We detected heterogeneity in the Vrn-1 alleles present in different TDF stocks, which may explain inconsistencies among previous studies. A correct TDF seed stock from Japan carrying recessive vrn-A1, vrn-B1, and vrn-D1 alleles was crossed with three different winter cultivars to generate F2 mapping populations. Most of the variation in flowering time in these three populations was controlled by a single locus, Vrn-D4, which was mapped within a 1.8 cM interval flanked by markers Xcfd78 and Xbarc205 in the centromeric region of chromosome 5D. A factorial ANOVA for heading time using Vrn-D4 alleles and vernalization as factors showed a significant interaction (P < 0.0001), which confirmed that the Vrn-D4 effect on flowering time is modulated by vernalization. Comparison of the different Triple Dirk stocks revealed that Vrn-B1, Vrn-D1, and Vrn-D4 all have a small residual response to vernalization, but Vrn-D4 differs from the other two in its response to short vernalization periods. The precise mapping and characterization of Vrn-D4 presented here represent a first step toward the positional cloning of this gene.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry GJ, Salisbury PA, Halloran GM (1980) Expression of vernalization genes in near-isogenic wheat lines—duration of vernalization period. Ann Bot 46:235–241
Bonnin I, Rousset M, Madur D, Sourdille P, Dupuits C, Brunel D, Goldringer I (2008) FT genome A and D polymorphisms are associated with the variation of earliness components in hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 116:383–394
Corbesier L, Vincent C, Jang SH, Fornara F, Fan QZ, Searle I, Giakountis A, Farrona S, Gissot L, Turnbull C, Coupland G (2007) FT protein movement contributes to long-distance signaling in floral induction of Arabidopsis. Science 316:1030–1033
Distelfeld A, Li C, Dubcovsky J (2009a) Regulation of flowering in temperate cereals. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:178–184
Distelfeld A, Tranquilli G, Li C, Yan L, Dubcovsky J (2009b) Genetic and molecular characterization of the VRN2 loci in tetraploid wheat. Plant Physiol 149:245–257
Dubcovsky J, Chen C, Yan L (2005) Molecular characterization of the allelic variation at the VRN-H2 vernalization locus in barley. Mol Breed 15:395–407
Dvorak J (1988) Cytogenetical and molecular inferences about the evolution of wheat. In: Miller TE, Koebner RMD (eds) Proceedings of 7th international wheat genetics symposium, Cambridge, pp 187–192
Dvorak J, McGuire PE (1981) Nonstructural chromosome differentiation among wheat cultivars with special reference to differentiation of chromosomes in related species. Genetics 97:391–414
Endo TR, Gill BS (1996) The deletion stocks of common wheat. J Hered 87:295–307
Flood RG, Halloran GM (1986) Genetics and physiology of vernalization response in wheat. Adv Agron 39:87–125
Fu D, Szűcs P, Yan L, Helguera M, Skinner J, Hayes P, Dubcovsky J (2005) Large deletions in the first intron of the VRN-1 vernalization gene are associated with spring growth habit in barley and polyploid wheat. Mol Genet Genomics 273:54–65
Fu D, Dunbar M, Dubcovsky J (2007) Wheat VIN3-like PHD finger genes are up-regulated by vernalization. Mol Genet Genomics 277:301–313
Goncharov NP (1998) Genetic resources of wheat related species: the Vrn genes controlling growth habit (spring vs. winter). Euphytica 100:371–376
Goncharov NP (2003) Genetics of growth habit (spring vs. winter) in common wheat: confirmation of the existence of dominant gene Vrn4. Theor Appl Genet 107:768–772
Gotoh T (1979) Genetic studies on growth habit of some important spring wheat cultivars in Japan, with special reference to the identification of the spring genes involved. Japan J Breed 29:133–145
Hemming MN, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES, Trevaskis B (2008) Low-temperature and daylength cues are integrated to regulate FLOWERING LOCUS T in barley. Plant Physiol 147:355–366
Hemming MN, Fieg S, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES, Trevaskis B (2009) Regions associated with repression of the barley (Hordeum vulgare) VERNALIZATION1 gene are not required for cold induction. Mol Genet Genomics 282:107–117
Iqbal M, Navabi A, Yang RC, Salmon DF, Spaner D (2007) Molecular characterization of vernalization response genes in Canadian spring wheat. Genome 50:511–516
Iwaki K, Nakagawa K, Kuno H, Kato K (2000) Ecogeographical differentiation in East Asian wheat, revealed from the geographical variation of growth habit and Vrn genotype. Euphytica 111:137–143
Iwaki K, Haruna S, Niwa T, Kato K (2001) Adaptation and ecological differentiation in wheat with special reference to geographical variation of growth habit and Vrn genotype. Pl Breed 120:107–114
Kato K, Yamagata H (1988) Method for evaluation of chilling requirement and narrow-sense earliness of wheat cultivars. Japan J Breed 38:172–186
Kato K, Nakagawa K, Kuno H (1993) Chromosomal location of the vernalization response, Vrn2 and Vrn4, in common wheat, Triticum aestivum L. Wheat Inform Serv 76:53
Kato K, Yamashita M, Ishimoto K, Yoshino H, Fujita M (2003) Genetic analysis of two genes for vernalization response, the former Vrn2 and Vrn4, using PCR based molecular markers. In: Pogna NE, Romano N, Pogna EA, Galterio G (eds) Proceeding of 10th international wheat genetics symposium. Inst Sperimentale per la Cerealcolture, Paestum, Italy, pp 971–973
Kerber ER (1964) Wheat—reconstitution of tetraploid component (AABB) of hexaploids. Science 143:253–255
Knott DR (1959) The inheritance of rust resistance. IV. Monosomic analysis of rust resistance and some other characters in six varieties of wheat including Gabo and Kenya Farmer. Can J Plant Sci 39:215–228
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Li C, Dubcovsky J (2008) Wheat FT protein regulates VRN1 transcription through interactions with FDL2. Plant J 55:543–554
Lin MK, Belanger H, Lee YJ, Varkonyi-Gasic E, Taoka KI, Miura E, Xoconostle-Cazares B, Gendler K, Jorgensene RA, Phinney B, Lough TJ, Lucas WJ (2007) FLOWERING LOCUS T protein may act as the long-distance florigenic signal in the cucurbits. Plant Cell 19:1488–1506
Linkiewicz AM, Qi LL, Gill BS, Ratnasiri A, Echalier B, Chao S, Lazo GR, Hummel DD, Anderson OD, Akhunov ED, Dvorak J, Pathan MS, Nguyen HT, Peng JH, Lapitan NLV, Miftahudin, Gustafson JP, La Rota CM, Sorrells ME, Hossain KG, Kalavacharla V, Kianian SF, Sandhu D, Bondareva SN, Gill KS, Conley EJ, Anderson JA, Fenton RD, Close TJ, McGuire PE, Qualset CO, Dubcovsky J (2004) A 2500-locus bin map of wheat homoeologous group 5 provides insights on gene distribution and colinearity with rice. Genetics 168:665–676
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lupton FGH (1987) Wheat breeding in Australia. In: Lupton FGH (ed) Wheat breeding. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 63–64
Maystrenko OI (1980) Cytogenetic study of the growth habit and ear emergence time in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). In: Balyae DK (ed) Proceedings of 14th international congress of genetics, MIR Publishers, Moscow, pp 267–282
McIntosh RA, Yamazaki Y, Devos KM, Dubcovsky J, Rogers WJ, Appels R (2003) Catalogue of Gene Symbols for Wheat. In: Pogna NE, Romano M, Pogna E, Galterio G (eds) Proceedings of 10th international wheat genetics symposium. Inst Sperimentale per la Cerealicoltura, Rome, Paestum, Italy. http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/ggpages/wgc/2000upd.html
Mei HW, Luo LJ, Ying CS, Wang YP, Yu XQ, Guo LB, Paterson AH, Li ZK (2003) Gene actions of QTLs affecting several agronomic traits resolved in a recombinant inbred rice population and two testcross populations. Theor Appl Genet 107:89–101
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nagata K, Shimizu H, Terao T (2002) Quantitative trait loci for non-structural carbohydrate accumulation in leaf sheaths and culms of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and their effects on grain filling. Breed Sci 52:275–283
O’Brien L, Morell M, Wrigley C, Appels R (2001) Genetic pool of Australian wheats. In: Bonjean AP, Angus WJ (eds) The world wheat book. Lavoisier, Paris, pp 611–648
Oliver SN, Finnegan EJ, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ, Trevaskis B (2009) Vernalization-induced flowering in cereals is associated with changes in histone methylation at the VERNALIZATION1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:8386–8391
Pugsley AT (1972) Additional genes inhibiting winter habit in wheat. Euphytica 21:547–552
SAS Institute Inc. (2006) SAS user’s guide, version 9.1. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary
Sears EM, Steintz-Sears LM (1978) The telocentric chromosomes of common wheat. In: Ramanujam S (ed) Proceedings of 5th international wheat genetics symposium, New Delhi, India, pp 389–407
Seki MO, Matsunaka S, Hatta H, Fujita K, Hatano M, Kiribuchi Otobe T, Kawada C, Kato N (2007) Growth and yield of near-isogenic wheat (Triticum aestivum) lines carrying different vernalization response genes. Breed Res 9:125–133
Septiningsih EM, Prasetiyono J, Lubis E, Tai TH, Tjubaryat T, Moeljopawiro S, McCouch SR (2003) Identification of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 107:1419–1432
Shitsukawa N, Ikari C, Shimada S, Kitagawa S, Sakamoto K, Saito H, Ryuto H, Fukunishi N, Abe T, Takumi S, Nasuda S, Murai K (2007) The einkorn wheat (Triticum monococcum) mutant, maintained vegetative phase, is caused by a deletion in the VRN1 gene. Genes Genet Syst 82:167–170
Stelmakh AF (1987a) Genetic effects of the Vrn 1–3 loci and specific action of the dominant Vrn-D1 allele in common bread wheat. Physiol Genet 21:278–286
Stelmakh AF (1987b) Growth habit in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L EM. Thell. Euphytica 36:513–519
Stelmakh AF (1998) Genetic systems regulating flowering response in wheat. Euphytica 100:359–369
Tamaki S, Matsuo S, Wong HL, Yokoi S, Shimamoto K (2007) Hd3a protein is a mobile flowering signal in rice. Science 316:1033–1036
Trevaskis B, Hemming MN, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ (2007) The molecular basis of vernalization-induced flowering in cereals. Trends Plant Sci 12:352–357
Uga Y, Nonoue Y, Liang ZW, Lin HX, Yamamoto S, Yamanouchi U, Yano M (2007) Accumulation of additive effects generates a strong photoperiod sensitivity in the extremely late-heading rice cultivar ‘Nona Bokra’. Theor Appl Genet 114:1457–1466
Worland AJ, Gale MD, Law CN (1987) Wheat genetics. In: Lupton FGH (ed) Wheat breeding. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 129–171
Yan L, Loukoianov A, Tranquilli G, Helguera M, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J (2003) Positional cloning of wheat vernalization gene VRN1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6263–6268
Yan L, Helguera M, Kato K, Fukuyama S, Sherman J, Dubcovsky J (2004a) Allelic variation at the VRN-1 promoter region in polyploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 109:1677–1686
Yan L, Loukoianov A, Blechl A, Tranquilli G, Ramakrishna W, SanMiguel P, Bennetzen JL, Echenique V, Dubcovsky J (2004b) The wheat VRN2 gene is a flowering repressor down-regulated by vernalization. Science 303:1640–1644
Yan L, Fu D, Li C, Blechl A, Tranquilli G, Bonafede M, Sanchez A, Valarik M, Dubcovsky J (2006) The wheat and barley vernalization gene VRN3 is an orthologue of FT. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:19581–19586
Zhang XK, Xia XC, Xiao YG, Dubcovsky J, He ZH (2008) Allelic variation at the vernalization genes Vrn-A1, Vrn-B1, Vrn-D1 and Vrn-B3 in Chinese common wheat cultivars and their association with growth habit. Crop Sci 48:458–470
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the United States Department of Agriculture Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Services National Research Initiative competitive grants 2007-35301-17737 and 2007-35301-18188 and Grant-in-Aids for Research Programs of Wheat and Barley Production from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan and for Young Scientists (B) (20780002) from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Langridge.
T. Yoshida and H. Nishida contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, T., Nishida, H., Zhu, J. et al. Vrn-D4 is a vernalization gene located on the centromeric region of chromosome 5D in hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 120, 543–552 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1174-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1174-3