Abstract
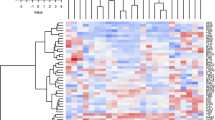
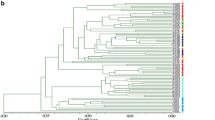
In the present study we have analyzed the genetic diversity pattern in a sample of 54 Italian maize landraces, using morphological traits and molecular markers. Although the 54 landraces surveyed in this study were restricted to Lombardy, the core region of maize production in Italy, our data revealed a large genetic heterogeneity for both morphological and molecular traits in the accessions analyzed. Additionally, our data confirm that the AFLP markers produced a high frequency of polymorphic bands and were able to unequivocally fingerprint each of the landraces considered. Cluster analysis based on AFLP markers displayed a clearer separation of the accessions in comparison to morphological data. Different populations were divided into four major clusters reflecting the geographical origin and seasonal employment of the landraces analyzed. Molecular analysis of variance showed significant (P < 0.01) differences among groups, among populations within groups, and among individuals within populations. Approximately 74% of the total variance could be attributed to differences within populations. Conversely, a lower level of differentiation was detected among groups (~4%). Regarding population structures, the genetic distance between populations (F ST = 0.25 ± 0.3) and the degree of inbreeding within groups (F SC = 0.22 ± 0.2), did not diverge significantly, while both significantly differed from the degree of relatedness between markers within groups (F CT = 0.04 ± 0.03). Results are discussed in relation to a suitable conservation method.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmone Marsan P, Castiglioni P, Fusari F, Kuiper M, Motto M (1998) Genetic diversity and its relationship to hybrid performance in maize as revealed by RFLP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 96:219–227
Ajmone Marsan P, Gorni C, Chittò A, Redaelli R, Van Vijk R, Stam P, Motto M (2001) Identification of QTLs for grain yield and grain-related traits of maize (Zea mays L.) using an AFLP map, different testers, and cofactor analysis. Theor Appl Genet 102:230–243
Boland CR (1996) Setting microsatellites free. Nat Med 2:972–974
Bonin A, Ehrich D, Manel S (2007) Statistical analysis of amplified fragment length polymorphism data: a toolbox for molecular ecologists and evolutionists. Mol Ecol 16:3737–3758
Brandolini A (1969) European races of maize. Annu Corn Sorghum Res Conf Proc 24:36–48
Brandolini A, Brandolini A (2001) Classification of Italian maize (Zea mays L.) germplasm. Plant Gen Res Newslett 126:1–11
Bretting PK, Wildrlechner MP (1995) Genetic markers and plant genetic resource management. In: Janick J (ed) Plant breeding reviews, vol 13. Wiley, New York, pp 11–71
Buckler ES, Gaut BS, McMullen MD (2006) Molecular and functional diversity of maize. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:172–176
Burstin J, Charcosset A (1997) Relationship between phenotypic and marker distances: theoretical and experimental investigations. Heredity 79:477–483
Castiglioni P, Ajmone-Marsan P, Van Wijk R, Motto M (1999) AFLP markers in a molecular linkage map of maize: codominant scoring and linkage group distribution. Theor Appl Genet 99:425–431
Chittò A, Bertolini M, Hartings H, Verderio A, Motto M (2000) AFLP-based genetic relationships among maize inbred lines selected in a climatically temperate location. Maydica 45:257–266
Crossa J, Hernandez CM, Bretting P, Eberhart SA, Taba S (1993) Statistical considerations for maintaining germplasm collections. Theor Appl Genet 86:673–678
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin ver. 3.0: An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolut Bioinf Online 1:47–50
Gauthier P, Gouesnard B, Dallard J, Redaelli R, Rebourg C, Charcosset A, Boyat A (2002) RFLP diversity within and among European traditional maize populations. Theor Appl Genet 105:91–99
Gepts P (1993) The use of molecular and biochemical markers in crop evolution studies. Evol Biol 27:51–94
Gilliland TJ, Coll R, Calsyn E, de Loose M, van Eijk MJT, Roldan-Ruiz I (2000) Estimating genetic conformity between related ryegrass (Lolium) varieties. I. Morphology and biochemical characterisation. Mol Breed 6:569–580
Goodman MM, Bird RMcK (1977) The races of maize IV: tentative grouping of 219 Latin American races. Econ Bot 31:204–221
Gouesnard B, Dallard J, Bertin P, Boyat A, Charcosset A (2005) European maize landraces: genetic diversity, core collection definition and methodology of use. Maydica 50:225–234
Hammer K, Diederichsen A, Spahillari M (1999) Basic studies toward strategies for conservation of plant genetic resources. In: Serwinski J, Feberová I (eds) Proceedings of technical meeting on the methodology of the FAO World Information and Early Warning System on Plant Genetic Resources, Prague
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis Palaeontologia Electronica, vol 4, issue 1, art 4
Hartl DL, Clark AG (1997) Principles of population genetics. Sinauer Associates, Inc, Sunderland
Kresovich S, Williams JGK, McFerson JR, Routman EJ, Schaal BA (1992) Characterization of genetic identities and relationships of Brassica oleracea L. via a random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. Theor Appl Genet 85:190–196
Krauss SL (2000) Accurate gene diversity estimates from amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers. Mol Ecol 9:1241–1245
Le Clerc V, Cadot V, Canadas M, Lallemand D, Guèrin D, Boulineau F (2006) Indicators to assess temporal genetic diversity in the French Catalogue: no losses for maize and peas. Theor Appl Genet 113:1197–1209
Lübberstedt T, Melchinger AE, Dussle C, Vuylsteke M, Kuiper M (2000) Relationship among early European maize inbreds. IV. Genetic diversity revealed with AFLP markers and comparison with RFLP, RAPD, and pedigree data. Crop Sci 40:783–791
Métais I, Hamon B, Jalouzot R, Peltier D (2002) Structure and level of genetic diversity in various bean types evidenced with microsatellite markers isolated from a genomic enriched library. Theor Appl Genet 104:1346–1352
McDermott JM, McDonald BA (1993) Gene flow in plant pathosystems. Annu Rev Phytopathol 31:353–373
Motto M, Lorenzoni C, Gentinetta E, Maggiore T, Salamini F (1978) Expected genetic gain for protein related traits and al location of resources in a modified opaque-2 synthetic. Maydica 23:35–44
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Pollack LM (2003) The history and success of the public-private project on germplasm enhancement of maize (GEM). Adv Agron 78:45–87
Rebourg C, Gouesnard B, Welcker C, Dubreuil P, Chastanet M, Charcosset A (2003) Maize introduction into Europe: the history reviewed in the light of molecular data. Theor Appl Genet 106:895–903
Reif JC, Hamrit S, Heckenberger M, Shipprack W, Maurer HP, Bohn M, Melchinger AE (2005) Genetic structure and diversity of European flint maize populations determined with SSR analysis of individuals and bulks. Theor Appl Genet 111:906–913
Revilla P, Soengas P, Malvar RA, Cartea ME, Ordas A (1998) Isozyme variation and historical relationships among the maize races of Spain. Maydica 43:175–182
Rohlf FJ (1993) NTSYS-PC numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. version 1.8. State Univ, New York
Singh SP, Gutiérrez JJA, Molina A, Urrea C, Gepts P (1991) Genetic diversity in cultivated common bean. II. Marker-based analysis of morphological and agronomic traits. Crop Sci 31:23–29
Smith JSC, Chin ECL, Shu H, Smith OS, Wall SJ, Senior ML, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Ziegle J (1997) An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L.) comparisons with data from RFLPs and pedigree. Theor Appl Genet 95:163–173
Tommasini L, Batley J, Arnold GM, Cooke RJ, Donini P, Lee D, Law JR, Lowe C, Moule C, Trick M, Edwards KJ (2003) The development of multiplex simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers to complement distinctness, uniformity and stability testing of rape (Brassica napus L.) varieties. Theor Appl Genet 106:1091–1101
Vaz Patto MC, Satovic Z, Pêgo S, Fevereiro P (2004) Assessing the genetic diversity of Portuguese maize germplasm using microsatellite markers. Euphytica 137:63–72
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Weir BS, Cockerham CC (1984) Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 38:1358–1370
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ministero delle Politiche Agricole, Alimentari e Forestali, Roma, Italy: special grant “Risorse genetiche vegetali-FAO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Charcosset.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartings, H., Berardo, N., Mazzinelli, G.F. et al. Assessment of genetic diversity and relationships among maize (Zea mays L.) Italian landraces by morphological traits and AFLP profiling. Theor Appl Genet 117, 831–842 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0823-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0823-2