Abstract
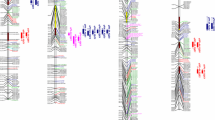
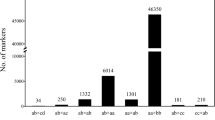
DNA marker maps based on single populations are the basis for gene, loci and genomic analyses. Individual maps can be integrated to produce composite maps with higher marker densities if shared marker orders are consistent. However, estimates of marker order in composite maps must include sets of markers that were not polymorphic in multiple populations. Often some of the pooled markers were not codominant, or were not correctly scored. The soybean composite map was composed of data from five separate populations based on northern US germplasm but does not yet include ‘Essex’ by ‘Forrest’ recombinant inbred line (RIL) population (E × F) or any southern US soybean cultivars. The objectives were, to update the E × F map with codominant markers, to compare marker orders among this map, the Forrest physical map and the composite soybean map and to compare QTL identified by composite interval maps to the earlier interval maps. Two hundred and thirty seven markers were used to construct the core of the E × F map. The majority of marker orders were consistent between the maps. However, 19 putative marker inversions were detected on 12 of 20 linkage groups (LG). Eleven marker distance compressions were also found. The number of inverted markers ranged from 1 to 2 per LG. Thus, marker order inversions may be common in southern compared to northern US germplasm. A total of 61 QTL among 37 measures of six traits were detected by composite interval maps, interval maps and single point analysis. Seventeen of the QTL found in composite intervals had previously been detected among the 29 QTL found in simple interval maps. The genomic locations of the known QTL were more closely delimited. A genome sequencing project to compare Southern and Northern US soybean cultivars would catalog and delimit inverted regions and the associated QTL. Gene introgression in cultivar development programs would be accelerated.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahana VS, GL Graef JE Specht JR Steadman KM Eskridge (2001) Identification of QTL for resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in soybean. Crop Sci 41:180–188
Areshchenkova T, Ganal MW (1999) Long tomato microsatellites are predominately associated with centromeric regions. Genome 42:536–544
Ashfield T, Bocian A, Held D, Henk A, Marek L, Danesh D, Penuela S, Meksem K, Lightfoot DA, Young N, Shoemaker R, Innes R (2003) Genetic and physical mapping of the soybean Rpg1-b disease resistance gene reveals a complex locus containing several tightly linked families of NBS/LRR genes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:817–826
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng Z (2001) QTL Cartographer Version 2.0. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA
Blanc G, Wolfe KH (2004) Widespread paleopolyploidy in model plant species inferred from age distributions of duplicate genes. Plant Cell 16:1667–1678
Broum P, Tanksley SD (1996) Characterization and genetic mapping of simple repeat sequences in the tomato genome. Mol Gen Genet 250:39–49
Chang SJC, Doubler TW, Kilo V, Suttner RJ, Klein JH, Schmidt ME, Gibson PT, Lightfoot DA (1996) Two additional loci underlying durable field resistance to soybean sudden-death syndrome (SDS). Crop Sci 36:1624–1628
Chang SJC, Doubler TW, Kilo V, Suttner V, Schmidt ME, Gibson PT, Lightfoot DA (1997) Association of field resistance to soybean sudden-death syndrome (SDS) and cyst nematode (SCN). Crop Sci 37:965–971
cho Y, Njiti VN, Chen X, Kassem MA, Meksem K, Lightfoot DA, Wood AJ (2002) Quantitative trait loci (QTL) associated with foliar trigonelline accumulation in Glycine max (L. Merr.). Phytochemistry 52:1235–1238
Concibido VC, Diers BW, Prakash R, Arelli PR (2004) A decade of QTL mapping for cyst nematode resistance in soybean. Crop Sci 44:1121–1131
Cregan PB, Jarvik T, Bush AL, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Kahler AL, Kaya N, VanToai TT, Lohnes DG, Chung J, Specht JE (1999) An integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean genome. Crop Sci 39:1464–1490
DeWan AT, Parrado AR, Matise TC, Leal SM (2002) Map error reduction: using genetic and sequence-based physical maps to order closely linked markers. Hum Hered 54:34–44
Dong YS, Zhao LM, Liu B, Wang ZW, Jin ZQ, Sun H (2004) The genetic diversity of cultivated soybean grown in China. Theor Appl Genet 108:931–936
Ekstrom CT (2003) Detecting low-quality markers using map expanders. Genet Epidemiol 25:214–224
Ferreira AR, Foutz KR, Keim P (2000) Soybean genetic map of RAPD markers assigned to an existing scaffold RFLP map. J Hered 91:392–396
Gizlice Z, Carter TE, Gerig TM, Burton JW (1996) Genetic diversity patterns in North American public soybean cultivars based on coefficient of parentage. Crop Sci 36:753–765
Gonzales MD, Archuleta E, Farmer A, Gajendran K, Grant D, Shoemaker R, Beavis WD, Waugh ME (2005) The Legume Information System (LIS): an integrated information resource for comparative legume biology. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D660–D665
Hauge, BM, Wang ML, Parsons JD, Parnell LD (2001) Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with soybean cyst nematode resistance. WO 01/51627 PCT/US01/00552 Patent # 20030005491
Hnetkovsky N, Chang SJC, Doubler TW, Gibson PT, Lightfoot DA (1996) Genetic mapping of loci underlying field resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome (SDS). Crop Sci 36:393–400
Hoeck JA, Fehr WR, Shoemaker RC, Welke GA, Johnson SL, Cianzio SR (2003) Molecular marker analysis of seed size in soybean. Crop Sci 43:68–74
Hyten DL, Pantalone VR, Sams CE, Saxton AM, Landau-Ellis D, Stefaniak TR, Schmidt ME (2004) Seed quality QTL in a prominent soybean population. Theor Appl Genet 109:552–561
Iqbal MJ, Meksem K, Njiti VN, Kassem My A, Lightfoot DA (2001) Microsatellite markers identity three additional quantitative trait loci for resistance to soybean sudden-death syndrome (SDS) in Essex x Forrest RILs. Theor Appl Genet 102:187–192
Iqbal MJ, Yaegashi S, Ahsan R, Shopinski KL, Lightfoot DA (2005) Root response to Fusarium solani f. sp . glycines temporal accumulation of transcripts in partially resistant and susceptible soybean. Theor Appl Genet 110:1429–1438
Jansen RC, Stam P (1994) High resolution of quantitative traits into multiple loci via interval mapping. Genetics 136: 1447–1455
Kassem MA (2003) Whole genome linkage map and QTL mapping in soybean. Ph.D. dissertation. Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL, USA
Kassem MA, Meksem K, Iqbal MJ, Wood AJ, Lightfoot DA (2004a) Definition of soybean genomic regions that control seed phytoestrogen amounts. J Biomed Biotech 1:52–60
Kassem MA, Meksem K, Kang CH, Njiti VN, Kilo V, Wood AJ, Lightfoot DA (2004b) Loci underlying resistance to manganese toxicity mapped in a recombinant inbred line population of ‘Essex’ × ‘Forrest’. Plant Soil 260:197–204
Kazi S, Bashir R. Shultz JL, Lavu N, Lightfoot DA (2005) Map locations for an additional 1,053 BES derived microsatellite markers for soybean. PAG XIII
Kazi S, Shultz J, Bashir R, Afzal J, Njiti V, Lightfoot DA (2006) Identification of loci underlying resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome in ‘Hartwig’ by ‘Flyer’. Theor Appl Genet (linked manuscript)
Kearsey AG, Farquhar L (1997) QTL analysis in plants; where are we now? Heredity 80:137–142
Keim P, Diers BW, Olson TC, Shoemaker RC (1990a) RFLP mapping in soybean: association between marker loci and variation in quantitative traits. Genetics 126:735–742
Keim P, Diers BW, Shoemaker RC (1990b) Genetic analysis of soybean hard seededness with molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 79(4):465–469
Keim P, Beavis W, Schupp JM, Freestone R (1992) Evaluation of soybean RFLP marker diversity in adapted germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 85:205–212
Keim P., Schupp JM, Travis SE, Clayton K, Zhu T, Shi L, Ferreira A, Webb DM (1997) A high-density soybean genetic map based on AFLP markers. Crop Sci 37:537–543
Kilo V, Lightfoot DA (1996) Loci underlying resistance to manganese toxicity mapped in soybean recombinant inbred lines. Soyb Genet Newsl 23:155–157
Lander E, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daley M, Lincoln S, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lark KG, Weismann JM, Matthews BF, Palmer R, Chase K, Macalma T (1993) A genetic map of soybean (Glycine max L.) using an intraspecific cross of two cultivars: ‘Minsoy’ and ‘Noir 1’. Theor Appl Genet 86:901–906
Lightfoot DA, Njiti VN, Gibson PT, Kassem MA, Iqbal JM, Meksem K (2005) Registration of the ‘Essex’ by ‘Forrest’ recombinant inbred line mapping population. Crop Sci 45:1678–1681
Mansur LM, Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T, Cregan PB, Lark KG (1996) Genetic mapping of agronomic traits using recombinant inbred lines of soybean. Crop Sci 36:1327–1336
Maughan PJ, Saghai Maroof MA, Buss GR (2000) Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling sucrose content in soybean (Glycine max). Mol Breed 6:105–111
McCouch SR, Teytelmann L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghinrang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:257–279
Meksem K, Doubler TW, Chancharoenchai K, Njiti VN, Chang SJC, Rao-Arelli AP, Cregan PE, Gray LE, Gibson PT, Lightfoot DA (1999) Clustering among loci underlying soybean resistance to Fusarium solani, SDS and SCN in near-isogenic lines. Theor Appl Genet 99:1131–1142
Meksem K, Ruben E, Zobrist K, Zhang H-B, Lightfoot DA (2000) Two large insert libraries for soybean: applications in cyst nematode resistance and genome wide physical mapping. Theor Appl Genet 101:747–755
Meksem K, Njiti VN, Banz WJ, Iqbal MJ, Kassem My A, Hyten DL, Yuang J, Winters TA, Lightfoot DA (2001a) Genomic regions that underlie soybean seed isoflavone content. J Biomed Biotech 1(1):38–45
Meksem K, Pantazopoulos P, Njiti VN, Hyten LD, Arelli PR, Lightfoot DA (2001b) ‘Forrest’ resistance to soybean cyst nematode is bigenic: saturation mapping of the Rhg1 and Rhg4 loci. Theor Appl Genet 103:710–717
Njiti VN, Doubler TW, Suttner RJ, Gray LE, Gibson PT, Lightfoot DA (1998) Resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome and root colonization by Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines in near-isogeneic lines. Crop Sci 38:472–477
Njiti VN, Meksem K, Yuan J, Lightfoot DA, Banz WJ, Winters TA (1999) DNA markers associated with loci underlying seed phytoestrogen content in soybean. J Med Food 2:185–187
Njiti VN, Meksem K, Iqbal MJ, Johnson JE, Kassem MA, Zobrist KF, Kilo VY, Lightfoot DA (2002) Common loci underlie field resistance to soybean sudden death syndrome in Forrest, Pyramid, Essex, and Douglas. Theor Appl Genet 104:294–300
Primomo VS, Poysa V, Ablett GR, Jackson CJ, Rajcan I (2005a) Agronomic Performance of recombinant inbred line populations segregating for isoflavone content in soybean seeds. Crop Sci 45:2203–2211
Primomo VS, Poysa V, Ablett GR, Jackson CJ, Gijzen M, Rajcan I (2005b) Mapping QTL for individual and total isoflavone content in soybean seeds. Crop Sci 45:2454–2464
Reyna N, Sneller CH (2001) Evaluation of marker-assisted introgression of yield QTL alleles into adapted soybean. Crop Sci 41:1317–1321
Ruben EA (2000) Positional cloning of the rhg1 and Rhg4 loci, MS thesis, PSGA, SIUC Carbondale, p 132
Ruben E, Aziz J, Afzal J, Njiti VN, Triwitayakorn K, Iqbal MJ, Yaegashi S, Bashir R, Kazi S, Arelli P, Town CD, Meksem K, Lightfoot DA (2006) Genomic analysis of the rhg1 locus: Candidate genes that underlie soybean resistance to the cyst nematode. Mole Gen Genomics (in review)
Schmidt ME, Suttner RJ, Klein JH, Gibson PT, Lightfoot DA, Myers Jr O (1999) Registration of LS-G96 soybean germplasm resistant to soybean sudden death syndrome (SDS) and soybean cyst nematode race 3. Crop Sci 39(3):598
Searle IR, Men AE, Laniya TS, Buzas DM, Iturbe-Ormaetxe I, Carroll BJ, PM Gresshoff (2003) Long-distance signaling in nodulation directed by a CLAVATA1-like receptor kinase. Science 299:109–112
Shopinski K, Iqbal J, Yuan J, Afzal A, Ahsan R, Shultz J, Meksem K, Lightfoot D (2003) EST integration with the soybean physical map. Agron Abst 102:388
Shopinski K, Iqbal MJ, Shultz JL, Langin C, Lightfoot DA (2006) Establishment of stress and defense related EST landmarks in Glycine max L. [Merr.] cv ‘Forrest’ physical map. Theor Appl Genet (in review)
Shultz J, Meksem K, Lightfoot DA (2003) Evaluating physical maps by clone location comparison. Genome Lett 2:99–107
Shultz JL, Kurunam D, Shopinski K, Iqbal MJ, Kazi S, Zobrist K, Bashir R, Yaegashi S, Lavu N, Afzal AJ, Yesudas CR, Kassem MA, Wu C, Zhang HB, Town CD, Meksem K, Lightfoot DA (2006a) The Soybean Genome Database (SoyGD): a browser for display of duplicated, polyploid, regions and sequence tagged sites on the integrated physical and genetic maps of Glycine max. Nucl Acids Res 34:D758–D765
Shultz JL, Kazi S, Afzal JA, Bashir R, Lightfoot DA (2006b) The development of BAC-end sequence-based microsatellite markers and placement in the physical and genetic maps of soybean. Theor Appl Genet (linked manuscript)
Singh RJ, Hymowitz T (1998) The genomic relationship between Glycine max L. Merr. and G. soja Seib. and Zucc. as revealed by pachytene chromosome analysis. Theor Appl Genet 76:705–711
Song QJ, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Concibido VC, Delannay X, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2004) A new integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 109:122–128
SoyBase (2005) http://www.soybase.agron.iastate.edu/
Stein LD, Mungall C, Shu S, Caudy M, Mangone M, Day A, Nickerson E, Stajich JE, Harris TW, Arva A, Lewis S (2002) The generic genome browser: a building block for a model organism system database. Genome Res 12:1599–1610
Triwitayakorn K, Njiti VN, Iqbal MJ, Yaegashi S, Town C, Lightfoot DA (2005) Genomic analysis of a region encompassing QRfs1 and QRfs2: genes that underlie soybean resistance to sudden death syndrome. Genome/Génome 48:125–138
Vogl C, Xu S (2000) Multipoint mapping of viability and segregation distorting loci using molecular markers. Genetics 155:1439–1447
Wu C, Sun S, Nimmakayala P, Santos FA, Meksem K, Springman R, Ding K, Lightfoot DA, Zhang HB (2004a) A BAC- and BIBAC-based physical map of the soybean genome. Genome Res 14:319–326
Wu CC, Nimmakayala P, Santos FA, Springman R, Scheuring C, Meksem K, Lightfoot DA, Zhang HB (2004b) Construction and characterization of a soybean bacterial artificial chromosome library and use of multiple complementary libraries for genome physical mapping. Theor Appl Genet 109:1041–1050
Yamanaka N, Ninomiya S, Hoshi M, Tsubokura Y, Yano M, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T, Harada K (2001) An informative linkage map of soybean reveals QTL for flowering time, leaflet morphology and regions of segregation distortion. DNA Res 8:61–72
Yuan J, Njiti VN, Meksem K, Iqbal MJ, Triwitayakorn K, Kassem MA, Davis GT, Schmidt ME, Lightfoot DA (2002) Quantitative trait loci in two soybean recombinant inbred line populations segregating for yield and disease resistance. Crop Sci 42:271–277
Zeng ZB (1993) Theoretical basis of separation of multiple linked gene effects on mapping quantitative trait loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10972–10976
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Zhang WK, Wang YJ, Luo GZ, Zhang JS, He CY, Wu XL, Gai JY, Chen SY (2004) QTL mapping of ten agronomic traits on the soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) genetic map and their association with EST markers. Theor Appl Genet 108:1131–1139
Zhu YL, Song QJ, Hyten DL, Van Tansell CP, Matukumalli LK, Grimm DR, Hyatt SM, Fickus EW, Young ND, Cregan PB (2003) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in soybean. Genetics 163:1123–1134
Acknowledgments
This research was funded over the past 11 years in part by grants from the NSF 9872635, ISA 95-122-04; 98-122-02 and 02-127-03 and USB 2228-6228. The integrated genetic and physical map was based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant no. 9872635. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation. The continued support of SIUC, College of Agriculture and Office of the Vice Chancellor for Research to MJI and DAL is appreciated. The authors thank Drs. P. Gibson, O. Myers Jr. and M. Schmidt for assistance with germplasm development and maintenance from 1991 to 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. J. Muehlbauer.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kassem, M.A., Shultz, J., Meksem, K. et al. An updated ‘Essex’ by ‘Forrest’ linkage map and first composite interval map of QTL underlying six soybean traits. Theor Appl Genet 113, 1015–1026 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0361-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0361-8