Abstract
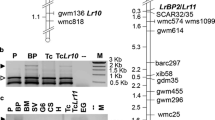
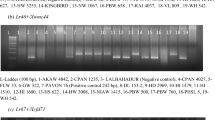
Three dominant resistance genes, Pr3, Pr4, and Pr5, were identified by genetic analysis of resistance to leaf rust in rye (Puccinia recondita f. sp. secalis). Each of the three genes confers resistance to a broad scale of single-pustule isolates (SPIs), but differences could be observed for specific Pr gene/SPI combinations. Resistance conferred by the three genes was effective in both detached-leaf tests carried out on seedlings and in field tests of adult plants. Molecular marker analysis mapped Pr3 to the centromeric region of rye chromosome arm 1RS, whereas Pr4 and Pr5 were assigned to the centromeric region of 1RL. Chromosomal localization and reaction patterns to specific SPIs provide evidence that the three Pr genes represent distinct and novel leaf-rust resistance genes in rye. The contributions of these genes to resistance breeding in rye and wheat are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartoš P, Bareš I (1971) Leaf and stem rust resistance of hexaploid wheat cultivars Salzmünder Bartweizen and Weique. Euphytica 20:435–440
Boyko EV, Gill KS, Mickelson-Young L, Nasuda S, Raupp WJ, Ziegle JN, Singh S, Hassawi DS, Fritz AK, Namuth D, Lapitan NLV, Gill BS (1999) A high-density genetic linkage map of Aegilops tauschii, the D-genome progenitor of bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 99:16–26
Devos KM, Gale MD (2000) Genome relationships: the grass model in current research. Plant Cell 12:637–646
Feuillet C, Schachermayr G, Keller B (1997) Molecular cloning of a new receptor-like kinase gene encoded at the Lr10 disease resistance locus of wheat. Plant J 11:45–52
Frauenstein K (1985) Untersuchungen zur Schadwirkung des Braunrostes, Puccinia recondita Rob. ex Desm., an Winterroggen. Nachrichtenbl Dtsch Pflanzenschutz DDR 39:177–178
Frauenstein K, Reichel A (1978) Zum Erkennen von slow-rusting-Formen bei Roggenbraunrost (Puccinia recondita Rob. ex Desm.). 2. Symposium über Schaderreger in der industriemässigen Getreideproduktion, Martin-Luther-Universität Halle, Wissenschaftliche Beiträge 14 (S11), 403–411
Gale MD, Devos KM (1998a) Comparative mapping in the grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1971–1974
Gale MD, Devos KM (1998b) Plant comparative genetics after 10 years. Science 282:656–659
Hackauf B, Wehling P (2002) Identification of microsatellite polymorphisms in an expressed portion of the rye genome. Plant Breed 121:17–25
Hart GE, Gale MD, McIntosh RA (1993) Linkage maps of Triticum aestivum hexaploid wheat, 2n=42, genomes A, B, and D) and T. tauschii (2n=14, genome D). In: O’Brien SJ (ed) Genetic maps: locus maps of complex genomes. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 6204–6219
Hsam SLK, Mohler V, Hartl L, Wenzel G, Zeller FJ (2000) Mapping of powdery mildew and leaf rust resistance genes on the wheat-rye translocated chromosome T1BL·1RS using molecular and biochemical markers. Plant Breed 119:87–89
Jahn M, Freier B, Kluge E (1995) Zum Einfluss von Klimaveränderungen auf die phytosanitäre Situation im Agrarbereich. In: Weigel HJ, Dämmgen U, Scholz F (eds) Klimawirkungsforschung im Geschäftsbereich des BML. Reihe A: Angewandte Wissenschaft, vol 442. Landwirtschaftsverlag, Münster, pp 81–92
Keller B, Feuillet C (2000) Colinearity and gene density in grass genomes. Trends Plant Sci 5:246–251
Kobylanski VD, Solodukhina OV (1983) Damage of important fungal diseases and methods for resistance breeding of short-straw rye (in Russian). In: Voprosy Sal. I Genetiki zernovych Kult, Moscow, pp 140–147
Kobylanski VD, Solodukhina OV (1996) Genetic bases and practical breeding utilization of heterogenous resistance of rye to brown rust. Vortr Pflanzenzuecht 35:155–163
Korzun V, Malyshev S, Voylokov AV, Börner A (2001) A genetic map of rye (Secale cereale L.) combining RFLP, isozyme, protein, microsatellite and gene loci. Theor Appl Genet 102:709–717
Laurie DA, Devos KM (2002) Trends in comparative genetics and their potential impacts on wheat and barley research. Plant Mol Biol 48:729–740
Madsen LH, Collins NC, Rakwalska M, Backes G, Sandal N, Krusell L, Jensen J, Waterman EH, Jahoor A, Ayliffe M, Pryor AJ, Langridge P, Schulze-Lefert P, Stougaard J (2003) Barley disease resistance gene analogs of the NBS-LRR class: identification and mapping. Mol Genet Genomics 269:150–161
Mettin D, Blüthner WD, Schlegel R (1973) Additional evidence on spontaneous 1B/1R wheat-rye substitutions and translocations. In: Sears ER, Sears LMS (eds) Proc 4th Int Wheat Genet Symp. Mo. Agric Exp Sta, Columbia, Mo., pp 179–184
Miedaner T, Sperling U (1995) Effect of leaf rust on yield components of winter rye hybrids and assessment of quantitative resistance. J Phytopathol 143:725–730
Miedaner T, Gey A-KM, Sperling U, Geiger HH (2002) Quantitative-genetic analysis of leaf-rust resistance in seedling and adult-plant stages of inbred lines and their testcrosses in winter rye. Plant Breed 121:475–479
Mohler V, Hsam SLK, Zeller FJ, Wenzel G (2001) An STS marker distinguishing the rye-derived powdery mildew resistance alleles at the Pm8/Pm17 locus of common wheat. Plant Breed 120:448–450
Musa GLC, Dyck PL, Samborski DJ (1984) The inheritance of resistance in rye to Puccinia recondita f. sp. secalis and f. sp. tritici. Can J Plant Sci 64:511–519
Parlevliet JE (1977) Variation for partial resistance in a cultivar of rye, Secale cereale, to brown rust, Puccinia recondita f. sp. secalis. Cereal Rusts Bull 5:13–16
Parlevliet JE (1989) Identification and evaluation of quantitative resistance. In: Leonard KJ, Fry WE (eds) Plant disease epidemiology: genetics, resistance and management, vol 2. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 215–248
Roux SR, Ruge B, Linz A, Wehling P (2000) Leaf rust resistance in rye—evaluation, genetic analysis and molecular mapping. Acta Phytopathol Entomol Hung 35:65–73
Ruge B, Roux SR, Linz A, Wehling P (1999) Erschließung und molekulare Charakterisierung von Resistenzen gegen Braunrost bei Roggen (Secale cereale L.). Vortr Pflanzenzuecht 46:169–176
Saal B, Wricke G (1999) Development of simple sequence repeat markers in rye (Secale cereale L.). Genome 42:964–972
Sawhney RN, Sharma JB (1999) Novel complementary genes for adult plant leaf rust resistance in a wheat stock carrying the 1BL-1RS translocation. Plant Breed 118:269–271
Shimizu Y, Nasuda S, Endo TR (1997) Detection of the Sec-1 locus of rye by a PCR-based method. Genes Genet Syst 72:197–203
Singh NK, Shepherd KW, McIntosh RA (1990) Linkage mapping of genes for resistance to leaf, stem and stripe rusts and ω-secalins on the short arm of rye chromosome 1R. Theor Appl Genet 80:609–616
Solodukhina OV (1994) Rye resistance to brown rust and powdery mildew: the potential of hereditary variability (in Russian). Genetika 30:616–618
Solodukhina OV (2002) Genetic characterization of rye accessions with regard to leaf rust resistance. Russ J Genet 38:399–407
Sorrells ME, La Rota M, Bermudez-Kandianis CE, Greene RA, Kantety R, Munkvold JD, Miftahudin Mahmoud A, Ma X, Gustafson PJ, Qi LL, Echalier B, Gill BS, Matthews DE, Lazo GR, Chao S, Anderson OD, Edwards H, Linkiewicz AM, Dubcovsky J, Akhunov ED, Dvorak J, Zhang D, Nguyen HT, Peng J, Lapitan NLV, Gonzalez-Hernandez JL, Anderson JA, Hossain K, Kalavacharla V, Kianian SF, Choi DW, Close TJ, Dilbirligi M, Gill KS, Steber C, Walker-Simmons MK, McGuire PE, Qualset CO (2003) Comparative DNA sequence analysis of wheat and rice genomes. Genome Res 13:1818–1827
Stevens WL (1942) Accuracy of mutations rates. J Genet 43:301–307
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap version 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Voylokov AV, Fuong FT, Smirnov VG (1993) Genetic studies on self-fertility in rye (Secale cereale L.). 1. The identification of genotypes of self-fertile lines for the sf-alleles of self-incompatibility genes. Theor Appl Genet 87:616–618
Voylokov AV, Korzun V, Börner A (1998) Mapping of three self-fertility mutations in rye (Secale cereale L.) using RFLP, isozyme and morphological markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:147–153
Wehling P, Wricke G (1985) Linkage between an incompatibility locus and a peroxidase isozyme locus (Prx7) in rye. Theor Appl Genet 71:289–291
Wehling P, Linz A, Hackauf B, Roux SR, Ruge B, Klocke B (2003) Leaf-rust resistance in rye (Secale cereale L.). 1. Genetic analysis and mapping of resistance genes Pr1 and Pr2. Theor Appl Genet 107:432–438
Welz G (1986) Struktur und Dynamik der Virulenz in Populationen von Erysiphe graminis f. sp. hordei. Marchal. PhD thesis, Justus-Liebig-Universität, Giessen, Germany
Zadoks JC, Chang TT, Konzak CF (1974) A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res 41:415–421
Zeller FJ (1973) 1B/1R wheat-rye chromosome substitutions and translocations. In: Proc 4th Int Wheat Genetics Symp. Mo. Agric Exp Sta, Columbia, Mo., pp 209–222
Zeller FJ, Hsam SLK (1983) Broadening the genetic variability of cultivated wheat by utilizing rye chromatin. In: Sakamoto S (ed) Proceedings of 6th international wheat genetics symposium, Kyoto, pp 161–173
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Prof. F. Salamini for the critical reading of the manuscript. This study was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) (Project Grant WE 2079/3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Salamini
The authors dedicate this paper to Prof. Dr. H.H. Geiger, University of Hohenheim, on the occasion of his 65th birthday.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1826-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roux, S.R., Hackauf, B., Linz, A. et al. Leaf-rust resistance in rye (Secale cereale L.). 2. Genetic analysis and mapping of resistance genes Pr3, Pr4, and Pr5. Theor Appl Genet 110, 192–201 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1807-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1807-5