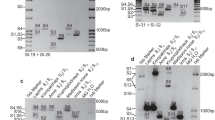
Abstract
Gametophytic self-incompatibility (GSI) in sweet cherry is determined by a locus S with multiple alleles. In the style, the S-locus codifies for an allele-specific ribonuclease (S-RNase) that is involved in the rejection of pollen that carries the same S allele. In this work we report the cloning and genomic DNA sequence analysis including the 5′ flanking regions of four S-RNases of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L., Rosaceae). DNA from the cultivars Ferrovia, Pico Colorado, Taleguera Brillante and Vittoria was amplified through PCR using primers designed in the conserved sequences of sweet cherry S-RNases. Two alleles were amplified for each cultivar and three of them correspond to three new S-alleles named S 23 , S 24 and S 25 present in 'Pico Colorado', 'Vittoria' and 'Taleguera Brillante' respectively. To confirm the identity of the amplified fragments, the genomic DNA of these three putative S-RNases and the allele S 12 amplified in the cultivar Ferrovia were cloned and sequenced. The nucleotide and deduced amino-acid sequences obtained contained the structural features of rosaceous S-RNases. The isolation of the 5′-flanking sequences of these four S-RNases revealed a conserved putative TATA box and high similarity among them downstream from that sequence. However, similarity was low compared with the 5′-flanking regions of S-RNases from the Maloideae. S 6 - and S 24 -RNase sequences are highly similar, and most amino-acid substitutions among these two RNases occur outside the rosaceous hypervariable region (RHV), but within another highly variable region. The confirmation of the different specificity of these two S-RNases would help elucidate which regions of the S-RNase sequences play a role in S-pollen specific recognition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bošković R, Tobutt KR (2001) Genotyping cherry cultivars assigned to incompatibility groups, by analysing stylar ribonucleases. Theor Appl Genet 103:475–485
Broothaerts W, Janssens GA, Proost P, Broekaert F (1995) cDNA cloning and molecular analysis of two self-incompatibility alleles from apple. Plant Mol Biol 27:499–511
De Nettancourt D (2001) Incompatibility and incongruity in wild and cultivated plants, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Ficker M, Kirch HH, Eijlander R, Jacobsen E, Thompson RD (1998) Multiple elements of the S 2 -RNase promoter from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) are required for cell type-specific expression in transgenic potato and tobacco. Mol Gen Genet 257:132–142
Hauck N, Iezzoni AF, Yamane H, Tao R (2001) Revising the S-allele nomenclature in sweet cherry (Prunus avium) using RFLP probes. J Am Soc Hort Sci 126:654–660
Hormaza JI (2002) Molecular characterization and similarity relationships among apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) genotypes using simple sequence repeats. Theor Appl Genet 104:321–328
Huang S, Lee HS, Karunanandaa B, Kao TH (1994) Ribonuclease activity of Petunia inflata S-proteins is essential for rejection of self-pollen. Plant Cell 6:1021–1028
Iorger TR, Gohlke JR, Xu B, Kao TH (1991) Primary structural features of the self-incompatibility proteins in the Solanaceae. Sex Plant Reprod 4:81–87
Ishimizu T, Shinkawa T, Sakiyama F, Norioka S (1998) Primary structural features of rosaceous S-RNases with gametophytic self-incompatibility. Plant Mol Biol 37:931–941
Janssens GA, Goderis IJ, Broekaert F, Broothaerts W (1995) A molecular method for S-allele identification in apple based on allele-specific PCR. Theor Appl Genet 91:691–698
Kaufmann H, Salamini F, Thompson RD (1991) Sequence variability and gene structure at the self-incompatibility locus of Solanum tuberosum. Mol Gen Genet 226:457–466
Kheyr-Pour A, Bintrim SB, Ioerger TR, Remy R, Hammond SA, Kao TH (1990) Sequence diversity of pistil S-proteins associated with gametophytic self-incompatibility in Nicotiana alata. Sex Plant Reprod 3:88–97
Lee HS, Huang S, Kao TH (1994) S-proteins control rejection of incompatible pollen in Petunia inflata. Nature 367:560–563
Ma RC, Oliveira MM (2001) Molecular cloning of the self-incompatibility genes S1 and S3 from almond (Prunus dulcis cv Ferragnès). Sex Plant Reprod 14:163–167
Ma RC, Oliveira MM (2002) Evolutionary analysis of S-RNase genes from Rosaceae species. Mol Gen Genomics 267:71–78
Matton DP, Maes O, Laublin G, Xike Q, Bertrand C, Morse D, Capadoccia M (1997) Hypervariable domains of self-incompatibility RNases mediate allele-specific pollen recognition. Plant Cell 9:1757–1766
McClure BA, Haring V, Ebert PR, Anderson MA, Simpson RJ, Sakiyama F, Clarke AE (1989) Style self-incompatibility gene products of Nicotiana alata are ribonucleases. Nature 342:955–957
Murfett J, Atherton T, Mou B, Gasser C, McClure BA (1994) S-RNase expressed in transgenic Nicotiana causes S-allele-specific pollen rejection. Nature 367:563–566
Norioka N, Katayama H, Matsuki T, Ishimizu T, Takasaki T, Nakanishi T, Norioka S (2001) Sequence comparison of the 5′ flanking regions of Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia) S-RNases associated with gametophytic self-incompatibility. Sex Plant Reprod 13:289–291
Sassa H, Hirano H, Ikeshashi H (1992) Self-incompatibility related RNases in styles of Japanese pear (Pyrus serotina Rehd.). Plant Cell Physiol 33:811–814
Sassa H, Hirano H, Ikeshashi H (1993) Identification and characterization of stylar glycoproteins associated with self-incompatibility of Japanese pear, Pyrus serotina Rehd. Mol Gen Genet 241:17–25
Sassa H, Mase N, Hirano H, Ikeshashi H (1994) Identification of self-incompatibility related glycoproteins in styles of apple (Malus x domestica). Theor Appl Genet 89:201–205
Sassa H, Nishio T, Kowyama Y, Hirano H, Koba T, Ikeshashi H (1996) Self-incompatibility (S) alleles of Rosaceae encode members of a distinct class of the T2/S ribonuclease superfamily. Mol Gen Genet 250:547–557
Simpson GG, Filipowitcz W (1996) Splicing precursors to mRNA in higher plants: mechanisms, regulation and sub-nuclear organisation of the spliceosomal machinery. Plant Mol Biol 32:1–41
Sonneveld T, Robbins TP, Bošković R, Tobutt KR (2001) Cloning six cherry self-incompatibility alleles and development of allele-specific PCR detection. Theor Appl Genet 102:1046–1055
Tamura M, Ushijama K, Sassa H, Hirano H, Tao R, Gradziel TM, Dandekar AM (2000) Identification of self-incompatibility genotypes of almond by allele-specific PCR analysis. Theor Appl Genet 101:344–349
Tao R, Yamane H, Sassa H, Mori H, Gradziel TM, Dandekar AM, Sugiura A (1997) Identification of stylar RNases associated with gametophytic self-incompatibility in almond (Prunus dulcis). Plant Cell Physiol 38:304–311
Tao R, Yamane H, Sugiura A, Murayama H, Sassa H, Mori H (1999a) Molecular typing of S-alleles through identification, characterization and cDNA cloning for S-RNases in sweet cherry. J Am Soc Hort Sci 124:224–233
Tao R, Yamane H, Akira H (1999b) Cloning and nucleotide sequences of cDNA encoding S1- and S4-RNases (Accessions Nos. AB028153 and AB028154) from sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Plant Physiol 120:1207
Tao R, Yamane H, Akira H (1999c) Cloning of genomic DNA sequences encoding S1-, S3-, S4- and S6-RNases (Accessions Nos. AB031815, AB031816, AB031817, AB031818) from sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Plant Physiol 121:1057
Tao R, Habu T, Yamane H, Sugiura A (2002) Characterization and cDNA cloning for Sf-RNase, a molecular marker for self-compatibility, in Japanese apricot (Prunus mume). J Jpn Soc Hort Sci 71:595–600
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for sequence multiple alignment aided with quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tobutt KR, Sonneveld T, Bošković R (2001) Cherry (in)compatibility genotypes-harmonization of recent results from UK, Canada, Japan and USA. Eucarpia Fruit Breeding Section Newslett 5:41–46
Tsai DS, Lee HS, Post LC, Kreiling KM, Kao TH (1992) Sequence of an S-protein of Lycopersicon peruvianum and comparison with other solanaceous S-proteins. Sex Plant Reprod 5:256–263
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R, Yamane H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Hirano H (1998a) Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding S-RNases from almond (Prunus dulcis): primary structural features and sequence diversity of the S-RNases in Rosaceae. Mol Gen Genet 260:261–268
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Hirano H (1998b) Characterization of the flanking regions of the S-RNase genes of Japanese pear (Pyrus serotina) and apple (Malus x domestica). Gene 211:159–167
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Tao R, Hirano H (2003) Structural and transcriptional analysis of the self-incompatibility locus of almond: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with haplotype-specific polymorphism. Plant Cell 15:771–781
Verica JA, McCubbin AG, Kao TH (1998) Are the hypervariable regions of S-RNases sufficient for allele-specific recognition pollen? Plant Cell 10:314–316
Wiersma PA, Wu Z, Zhou L, Hampson C, Kappel F (2001) Identification of self-incompatibility alleles in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) and clarification of incompatibility groups by PCR and sequencing analysis. Theor Appl Genet 102:700–708
Wünsch A, Hormaza JI (in press) Molecular evaluation of genetic diversity and S-allele composition of Spanish local sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars. Genet Resour Crop Evol
Yaegaki H, Shimada T, Moriguchi T, Hayama H, Haji T, Yamaguchi M (2001) Molecular characterization of S-RNase genes and S-genotypes in the Japanese apricot (Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc.). Sex Plant Reprod 13:251–257
Yamane H, Tao R, Murayama H (2000) Determining the S-genotypes of several sweet cherry cultivars based on PCR-RFLP analysis. J Hortic Sci Biotech 75:562–567
Yamane H, Tao R, Sugiura A, Hauck NR, Iezzoni AF (2001) Identification and characterization of S-RNases in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus) J Am Soc Hort Sci 126:661–667
Zuccherelli S, Tassinari P, Broothaerts W, Tartarini S, Dondini L, Sansavini S (2002) S-Allele characterization in self-incompatible pear (Pyrus communis L.) Sex Plant Reprod 15:153–158
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank M.A. Aranda and C. Fernández-Marco for help during the cloning experiments and M. Herrero for her helpful comments on this manuscript. A.W. was supported by a SIA-DGA fellowship and financial support for this work was provided by MCYT (Project Grant AGL2001-2414).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.F. Linskens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wünsch, A., Hormaza, J.I. Cloning and characterization of genomic DNA sequences of four self-incompatibility alleles in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor Appl Genet 108, 299–305 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1418-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1418-6