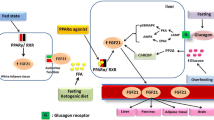
Abstract
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has a significant role in the regulation of energy metabolism, e.g., in the control of systemic glucose and lipid metabolism. For instance, FGF21 enhances insulin sensitivity, increases glucose uptake, and thus can decrease serum hyperglycemia, while it also increases lipid oxidation and inhibits lipogenesis. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a tissue energy sensor involved in maintaining the energy balance and tissue integrity. It is known that AMPK signaling generates an energy metabolic profile which displays a remarkable overlap with that of FGF21. There is convincing evidence that endocrine FGF21 signaling activates the AMPK pathway, either directly through FGFR1/β-klotho signaling or indirectly by stimulating the secretion of adiponectin and corticosteroids, which consequently can activate AMPK signaling in their target tissues. By activating AMPK, FGF21 can promote a healthy aging process and thus extend mammalian lifespan. We will examine the signaling mechanisms through which FGF21 can activate the AMPK pathway and then discuss the significance of the close connection between FGF21 and AMPK signaling in the control of metabolic disorders and the aging process.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beenken A, Mohammadi M (2009) The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:235–253
Turner N, Grose R (2010) Fibroblast growth factor signalling: from development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10:116–129
Ornitz DM, Itoh N (2015) The fibroblast growth factor signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 4:215–266
Kuro-o M (2008) Endocrine FGFs and Klothos: emerging concepts. Trends Endocrinol Metab 19:239–245
Hu MC, Shiizaki K, Kuro-o M, Moe OW (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and Klotho: physiology and pathophysiology of an endocrine network of mineral metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 75:503–533
Markan KR, Potthoff MJ (2016) Metabolic fibroblast growth factors (FGFs): mediators of energy homeostasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 53:85–93
Ding X, Boney-Montoya J, Owen BM, Bookout AL, Coate KC, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2012) βKlotho is required for fibroblast growth factor 21 effects on growth and metabolism. Cell Metab 16:387–393
Kuro-o M (2009) Klotho and aging. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790:1049–1058
Gallego-Escuredo JM, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Catalan V, Domingo P, Giralt M, Frühbeck G, Villarroya F (2015) Opposite alterations in FGF21 and FGF19 levels and disturbed expression of the receptor machinery for endocrine FGFs in obese patients. Int J Obes (Lond) 39:121–129
Lage R, Dieguez C, Vidal-Puig A, Lopez M (2008) AMPK: a metabolic gauge regulating whole-body energy homeostasis. Trends Mol Med 14:539–549
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA (2012) AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:251–262
Chau MD, Gao J, Yang Q, Wu Z, Gromada J (2010) Fibroblast growth factor 21 regulates energy metabolism by activating the AMPK-SIRT1-PGC-1α pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:12553–12558
Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N (2000) Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 1492:203–206
Zhang X, Yeung DC, Karpisek M, Stejskal D, Zhou ZG, Liu F, Wong RL, Chow WS, Tso AW, Lam KS et al (2008) Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetes 57:1246–1253
Suomalainen A, Elo JM, Pietiläinen KH, Hakonen AH, Sevastianova K, Korpela M, Isohanni P, Marjavaara SK, Tyni T, Kiuru-Enari S et al (2011) FGF-21 as a biomarker for muscle-manifesting mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies: a diagnostic study. Lancet Neurol 10:806–818
Keipert S, Ost M, Johann K, Imber F, Jastroch M, van Schothorst EM, Keijer J, Klaus S (2014) Skeletal muscle mitochondrial uncoupling drives endocrine cross-talk through the induction of FGF21 as a myokine. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 306:E469–E482
Brahma MK, Adam RC, Pollak NM, Jaeger D, Zierler KA, Pöcher N, Schreiber R, Romauch M, Moustafa T, Eder S et al (2014) Fibroblast growth factor 21 is induced upon cardiac stress and alters cardiac lipid homeostasis. J Lipid Res 55:2229–2241
Inagaki T, Dutchak P, Zhao G, Ding X, Gautron L, Parameswara V, Li Y, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Esser V et al (2007) Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARα-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab 5:415–425
Muise ES, Azzolina B, Kuo DW, El-Sherbeini M, Tan Y, Yuan X, Mu J, Thompson JR, Berger JP, Wong KK (2008) Adipose fibroblast growth factor 21 is up-regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and altered metabolic states. Mol Pharmacol 74:403–412
Berglund ED, Kang L, Lee-Young RS, Hasenour CM, Lustig DG, Lynes SE, Donahue EP, Swift LL, Charron MJ, Wasserman DH (2010) Glucagon and lipid interactions in the regulation of hepatic AMPK signaling and expression of PPARα and FGF21 transcripts in vivo. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299:E607–E614
Li Y, Wong K, Giles A, Jiang J, Lee JW, Adams AC, Kharitonenkov A, Yang Q, Gao B, Guarente L et al (2014) Hepatic SIRT1 attenuates hepatic steatosis and controls energy balance in mice by inducing fibroblast growth factor 21. Gastroenterology 146:539–549
Min AK, Bae KH, Jung YA, Choi YK, Kim MJ, Kim JH, Jeon JH, Kim JG, Lee IK, Park KG (2014) Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 mediates fasting-induced hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 expression. Endocrinology 155:2924–2931
Fazeli PK, Lun M, Kim SM, Bredella MA, Wright S, Zhang Y, Lee H, Catana C, Klibanski A, Patwari P et al (2015) FGF21 and the late adaptive response to starvation in humans. J Clin Invest 125:4601–4611
Kim KH, Jeong YT, Oh H, Kim SH, Cho JM, Kim YN, Kim SS, Kim do H, Hur KY, Kim HK et al (2013) Autophagy deficiency leads to protection from obesity and insulin resistance by inducing Fgf21 as a mitokine. Nat Med 19:83–92
Jiang S, Yan C, Fang QC, Shao ML, Zhang YL, Liu Y, Deng YP, Shan B, Liu JQ, Li HT et al (2014) Fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by the IRE1α-XBP1 branch of the unfolded protein response and counteracts endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced hepatic steatosis. J Biol Chem 289:29751–29765
Woo YC, Xu A, Wang Y, Lam KS (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 21 as an emerging metabolic regulator: clinical perspectives. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 78:489–496
Giralt M, Gavalda-Navarro A, Villarroya F (2015) Fibroblast growth factor-21, energy balance and obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 418:66–73
Kharitonenkov A, DiMarchi R (2015) FGF21 revolutions: recent advances illuminating FGF21 biology and medicinal properties. Trends Endocrinol Metab 26:608–617
Fisher FM, Maratos-Flier E (2016) Understanding the physiology of FGF21. Annu Rev Physiol 78:223–241
Xu J, Lloyd DJ, Hale C, Stanislaus S, Chen M, Sivits G, Vonderfecht S, Hecht R, Li YS, Lindberg RA et al (2009) Fibroblast growth factor 21 reverses hepatic steatosis, increases energy expenditure, and improves insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes 58:250–259
Jin L, Lin Z, Xu A (2016) Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against atherosclerosis via fine-tuning the multiorgan crosstalk. Diabetes Metab J 40:22–31
Gaich G, Chien JY, Fu H, Glass LC, Deeg MA, Holland WL, Kharitonenkov A, Bumol T, Schilske HK, Moller DE (2013) The effects of LY2405319, an FGF21 analog, in obese human subjects with type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab 18:333–340
Fisher FM, Chui PC, Antonellis PJ, Bina HA, Kharitonenkov A, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E (2010) Obesity is a fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21)-resistant state. Diabetes 59:2781–2789
Camporez JP, Jornayvaz FR, Petersen MC, Pesta D, Guigni BA, Serr J, Zhang D, Kahn M, Samuel VT, Jurczak MJ et al (2013) Cellular mechanisms by which FGF21 improves insulin sensitivity in male mice. Endocrinology 154:3099–3109
Habegger KM, Stemmer K, Cheng C, Müller TD, Heppner KM, Ottaway N, Holland J, Hembree JL, Smiley D, Gelfanov V et al (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 21 mediates specific glucagon actions. Diabetes 62:1453–1463
Lin Z, Tian H, Lam KS, Lin S, Hoo RC, Konishi M, Itoh N, Wang Y, Bornstein SR, Xu A et al (2013) Adiponectin mediates the metabolic effects of FGF21 on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in mice. Cell Metab 17:779–789
Patel R, Bookout AL, Magomedova L, Owen BM, Consiglio GP, Shimizu M, Zhang Y, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA, Cummins CL (2015) Glucocorticoids regulate the metabolic hormone FGF21 in a feed-forward loop. Mol Endocrinol 29:213–223
Sa-Nguanmoo P, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2016) Potential roles of fibroblast growth factor 21 in the brain. Metab Brain Dis 31:239–248
Douris N, Stevanovic DM, Fisher FM, Cisu TI, Chee MJ, Nguyen NL, Zarebidaki E, Adams AC, Kharitonenkov A, Flier JS et al (2015) Central fibroblast growth factor 21 browns white fat via sympathetic action in male mice. Endocrinology 156:2470–2481
Bookout AL, de Groot MH, Owen BM, Lee S, Gautron L, Lawrence HL, Ding X, Elmquist JK, Takahashi JS, Mangelsdorf DJ et al (2013) FGF21 regulates metabolism and circadian behavior by acting on the nervous system. Nat Med 19:1147–1152
Dailey L, Ambrosetti D, Mansukhani A, Basilico C (2005) Mechanisms underlying differential responses to FGF signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:233–247
Ming AY, Yoo E, Vorontsov EN, Altamentova SM, Kilkenny DM, Rocheleau JV (2012) Dynamics and distribution of Klothoβ (KLB) and fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (FGFR1) in living cells reveal the fibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF21)-induced receptor complex. J Biol Chem 287:19997–20006
Yie J, Wang W, Deng L, Tam LT, Stevens J, Chen MM, Li Y, Xu J, Lindberg R, Hecht R et al (2012) Understanding the physical interactions in the FGF21/FGFR/β-Klotho complex: structural requirements and implications in FGF21 signaling. Chem Biol Drug Des 79:398–410
Fisher FM, Estall JL, Adams AC, Antonellis PJ, Bina HA, Flier JS, Kharitonenkov A, Spiegelman BM, Maratos-Flier E (2011) Integrated regulation of hepatic metabolism by fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) in vivo. Endocrinology 152:2996–3004
Liu SQ, Roberts D, Kharitonenkov A, Zhang B, Hanson SM, Li YC, Zhang LQ, Wu YH (2013) Endocrine protection of ischemic myocardium by FGF21 from the liver and adipose tissue. Sci Rep 3:2767
Salminen A, Hyttinen JM, Kaarniranta K (2011) AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits NF-kB signaling and inflammation: impact on healthspan and lifespan. J Mol Med (Berl) 89:667–676
Yu Y, Li S, Liu Y, Tian G, Yuan Q, Bai F, Wang W, Zhang Z, Ren G, Zhang Y et al (2015) Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis through modulating oxidative stress and suppressing nuclear factor-kB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 25:74–82
Xu P, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Yuan Q, Song L, Liu M, Liu Z, Yang Y, Li J, Li D et al (2016) Fibroblast growth factor 21 attenuates hepatic fibrogenesis through TGF-β/smad2/3 and NF-kB signaling pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 290:43–53
Patel V, Adya R, Chen J, Ramanjaneya M, Bari MF, Bhudia SK, Hillhouse EW, Tan BK, Randeva HS (2014) Novel insights into the cardio-protective effects of FGF21 in lean and obese rat hearts. PLoS One 9:e87102
Wang XM, Song SS, Xiao H, Gao P, Li XJ, Si LY (2014) Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against high glucose induced cellular damage and dysfunction of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase in endothelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 34:658–671
Jiang X, Chen J, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Tan Y, Feng W, Skibba M, Xin Y, Cai L (2015) The protective effect of FGF21 on diabetes-induced male germ cell apoptosis is associated with up-regulated testicular AKT and AMPK/Sirt1/PGC-1α signaling. Endocrinology 156:1156–1170
Zhang C, Huang Z, Gu J, Yan X, Lu X, Zhou S, Wang S, Shao M, Zhang F, Cheng P et al (2015) Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects the heart from apoptosis in a diabetic mouse model via extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-dependent signalling pathway. Diabetologia 58:1937–1948
Canto C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Feige JN, Lagouge M, Noriega L, Milne JC, Elliott PJ, Puigserver P, Auwerx J (2009) AMPK regulates energy expenditure by modulating NAD+ metabolism and SIRT1 activity. Nature 458:1056–1060
Potthoff MJ, Inagaki T, Satapati S, Ding X, He T, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Finck BN, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA et al (2009) FGF21 induces PGC-1α and regulates carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism during the adaptive starvation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:10853–10858
Mäkelä J, Tselykh TV, Maiorana F, Eriksson O, Do HT, Mudo G, Korhonen LT, Belluardo N, Lindholm D (2014) Fibroblast growth factor-21 enhances mitochondrial functions and increases the activity of PGC-1α in human dopaminergic neurons via Sirtuin-1. SpringerPlus 3:2
Wu AL, Kolumam G, Stawicki S, Chen Y, Li J, Zavala-Solorio J, Phamluong K, Feng B, Li L, Marsters S et al (2011) Amelioration of type 2 diabetes by antibody-mediated activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1. Sci Transl Med 3:113ra126
Markan KR, Naber MC, Ameka MK, Anderegg MD, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA, Mohammadi M, Potthoff MJ (2014) Circulating FGF21 is liver derived and enhances glucose uptake during refeeding and overfeeding. Diabetes 63:4057–4063
Itoh N (2014) FGF21 as a hepatokine, adipokine, and myokine in metabolism and diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 5:107
Kim KH, Lee MS (2014) FGF21 as a stress hormone: the roles of FGF21 in stress adaptation and the treatment of metabolic diseases. Diabetes Metab J 38:245–251
Hui X, Feng T, Liu Q, Gao Y, Xu A (2016) The FGF21-adiponectin axis in controlling energy and vascular homeostasis. J Mol Cell Biol 8:110–119
Liang Q, Zhong L, Zhang J, Wang Y, Bornstein SR, Triggle CR, Ding H, Lam KS, Xu A (2014) FGF21 maintains glucose homeostasis by mediating the cross talk between liver and brain during prolonged fasting. Diabetes 63:4064–4075
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S, Yamashita S, Noda M, Kita S, Ueki K et al (2002) Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med 8:1288–1295
Heiker JT, Kosel D, Beck-Sickinger AG (2010) Molecular mechanisms of signal transduction via adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Biol Chem 391:1005–1018
Thundyil J, Pavlovski D, Sobey CG, Arumugam TV (2012) Adiponectin receptor signalling in the brain. Br J Pharmacol 165:313–327
Combs TP, Marliss EB (2014) Adiponectin signaling in the liver. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 15:137–147
Zhou L, Deepa SS, Etzler JC, Ryu J, Mao X, Fang Q, Liu DD, Torres JM, Jia W, Lechleiter JD et al (2009) Adiponectin activates AMP-activated protein kinase in muscle cells via APPL1/LKB1-dependent and phospholipase C/Ca2+/Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem 284:22426–22435
Fang X, Palanivel R, Cresser J, Schram K, Ganguly R, Thong FS, Tuinei J, Xu A, Abel ED, Sweeney G (2010) An APPL1-AMPK signaling axis mediates beneficial metabolic effects of adiponectin in the heart. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299:E721–E729
Owen BM, Bookout AL, Ding X, Lin VY, Atkin SD, Gautron L, Kliewer SA, Mangelsdorf DJ (2013) FGF21 contributes to neuroendocrine control of female reproduction. Nat Med 19:1153–1156
Owen BM, Ding X, Morgan DA, Coate KC, Bookout AL, Rahmouni K, Kliewer SA, Mangelsdorf DJ (2014) FGF21 acts centrally to induce sympathetic nerve activity, energy expenditure, and weight loss. Cell Metab 20:670–677
Lopez M, Nogueiras R, Tena-Sempere M, Dieguez C (2016) Hypothalamic AMPK: a canonical regulator of whole-body energy balance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 12:421–432
Christ-Crain M, Kola B, Lolli F, Fekete C, Seboek D, Wittmann G, Feltrin D, Igreja SC, Ajodha S, Harvey-White J et al (2008) AMP-activated protein kinase mediates glucocorticoid-induced metabolic changes: a novel mechanism in Cushing’s syndrome. FASEB J 22:1672–1683
Zhao Y, Shen J, Su H, Li B, Xing D, Du L (2008) Chronic corticosterone injections induce a decrease of ATP levels and sustained activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in hippocampal tissues of male mice. Brain Res 1191:148–156
Scerif M, Füzesi T, Thomas JD, Kola B, Grossman AB, Fekete C, Korbonits M (2013) CB1 receptor mediates the effects of glucocorticoids on AMPK activity in the hypothalamus. J Endocrinol 219:79–88
Löwenberg M, Tuynman J, Scheffer M, Verhaar A, Vermeulen L, van Deventer S, Hommes D, Peppelenbosch M (2006) Kinome analysis reveals nongenomic glucocorticoid receptor-dependent inhibition of insulin signaling. Endocrinology 147:3555–3562
Bowles NP, Karatsoreos IN, Li X, Vemuri VK, Wood JA, Li Z, Tamashiro KL, Schwartz GJ, Makriyannis AM, Kunos G et al (2015) A peripheral endocannabinoid mechanism contributes to glucocorticoid-mediated metabolic syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:285–290
Kola B, Boscaro M, Rutter GA, Grossman AB, Korbonits M (2006) Expanding role of AMPK in endocrinology. Trends Endocrinol Metab 17:205–215
Liu J, Peng Y, Wang X, Fan Y, Qin C, Shi L, Tang Y, Cao K, Li H, Long J et al (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction launches dexamethasone-induced skeletal muscle atrophy via AMPK/FOXO3 signaling. Mol Pharm 13:73–84
Nader N, Ng SS, Lambrou GI, Pervanidou P, Wang Y, Chrousos GP, Kino T (2010) AMPK regulates metabolic actions of glucocorticoids by phosphorylating the glucocorticoid receptor through p38 MAPK. Mol Endocrinol 24:1748–1764
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X, Jiang B, Park O, Luo Z, Lefai E, Shyy JY et al (2011) AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab 13:376–388
Zhang Y, Lei T, Huang JF, Wang SB, Zhou LL, Yang ZQ, Chen XD (2011) The link between fibroblast growth factor 21 and sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c during lipogenesis in hepatocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 342:41–47
Ruderman NB, Carling D, Prentki M, Cacicedo JM (2013) AMPK, insulin resistance, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 123:2764–2772
Fisher FM, Kleiner S, Douris N, Fox EC, Mepani RJ, Verdeguer F, Wu J, Kharitonenkov A, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E et al (2012) FGF21 regulates PGC-1α and browning of white adipose tissues in adaptive thermogenesis. Genes Dev 26:271–281
Beiroa D, Imbernon M, Gallego R, Senra A, Herranz D, Villarroya F, Serrano M, Ferno J, Salvador J, Escalada J et al (2014) GLP-1 agonism stimulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and browning through hypothalamic AMPK. Diabetes 63:3346–3358
Gimeno RE, Moller DE (2014) FGF21-based pharmacotherapy—potential utility for metabolic disorders. Trends Endocrinol Metab 25:303–311
Srivastava RA, Pinkosky SL, Filippov S, Hanselman JC, Cramer CT, Newton RS (2012) AMP-activated protein kinase: an emerging drug target to regulate imbalances in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism to treat cardio-metabolic diseases. J Lipid Res 53:2490–2514
Kurosu H, Choi M, Ogawa Y, Dickson AS, Goetz R, Eliseenkova AV, Mohammadi M, Rosenblatt KP, Kliewer SA, Kuro-o M (2007) Tissue-specific expression of βKlotho and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor isoforms determines metabolic activity of FGF19 and FGF21. J Biol Chem 282:26687–26695
Kola B, Hubina E, Tucci SA, Kirkham TC, Garcia EA, Mitchell SE, Williams LM, Hawley SA, Hardie DG, Grossman AB et al (2005) Cannabinoids and ghrelin have both central and peripheral metabolic and cardiac effects via AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 280:25196–25201
Brennan-Speranza TC, Henneicke H, Gasparini SJ, Blankenstein KI, Heinevetter U, Cogger VC, Svistounov D, Zhang Y, Cooney GJ, Buttgereit F et al (2012) Osteoblasts mediate the adverse effects of glucocorticoids on fuel metabolism. J Clin Invest 122:4172–4189
Zhang Y, Xie Y, Berglund ED, Coate KC, He TT, Katafuchi T, Xiao G, Potthoff MJ, Wei W, Wan Y et al (2012) The starvation hormone, fibroblast growth factor-21, extends lifespan in mice. Elife 1:e00065
Masoro EJ (2005) Overview of caloric restriction and ageing. Mech Ageing Dev 126:913–922
Mendelsohn AR, Larrick JW (2012) Fibroblast growth factor-21 is a promising dietary restriction mimetic. Rejuvenation Res 15:624–628
Laeger T, Henagan TM, Albarado DC, Redman LM, Bray GA, Noland RC, Münzberg H, Hutson SM, Gettys TW, Schwartz MW et al (2014) FGF21 is an endocrine signal of protein restriction. J Clin Invest 124:3913–3922
Lees EK, Krol E, Grant L, Shearer K, Wyse C, Moncur E, Bykowska AS, Mody N, Gettys TW, Delibegovic M (2014) Methionine restriction restores a younger metabolic phenotype in adult mice with alterations in fibroblast growth factor 21. Aging Cell 13:817–827
Mookerjee SA, Divakaruni AS, Jastroch M, Brand MD (2010) Mitochondrial uncoupling and lifespan. Mech Ageing Dev 131:463–472
Gates AC, Bernal-Mizrachi C, Chinault SL, Feng C, Schneider JG, Coleman T, Malone JP, Townsend RR, Chakravarthy MV, Semenkovich CF (2007) Respiratory uncoupling in skeletal muscle delays death and diminishes age-related disease. Cell Metab 6:497–505
Neschen S, Katterle Y, Richter J, Augustin R, Scherneck S, Mirhashemi F, Schürmann A, Joost HG, Klaus S (2008) Uncoupling protein 1 expression in murine skeletal muscle increases AMPK activation, glucose turnover, and insulin sensitivity in vivo. Physiol Genomics 33:333–340
Curtis R, O’Connor G, DiStefano PS (2006) Aging networks in Caenorhabditis elegans: AMP-activated protein kinase (aak-2) links multiple aging and metabolism pathways. Aging Cell 5:119–126
Martin-Montalvo A, Mercken EM, Mitchell SJ, Palacios HH, Mote PL, Scheibye-Knudsen M, Gomes AP, Ward TM, Minor RK, Blouin MJ et al (2013) Metformin improves healthspan and lifespan in mice. Nat Commun 4:2192
Ulgherait M, Rana A, Rera M, Graniel J, Walker DW (2014) AMPK modulates tissue and organismal aging in a non-cell-autonomous manner. Cell Rep 8:1767–1780
Canto C, Auwerx J (2011) Calorie restriction: Is AMPK a key sensor and effector? Physiology (Bethesda) 26:214–224
Xie Z, Zhang J, Wu J, Viollet B, Zou MH (2008) Upregulation of mitochondrial uncoupling protein-2 by the AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial cells attenuates oxidative stress in diabetes. Diabetes 57:3222–3230
Yamauchi T, Kadowaki T (2013) Adiponectin receptor as a key player in healthy longevity and obesity-related diseases. Cell Metab 17:185–196
Lindberg S, Jensen JS, Bjerre M, Pedersen SH, Frystyk J, Flyvbjerg A, Galatius S, Jeppesen J, Mogelvang R (2015) Adiponectin, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk. Eur J Prev Cardiol 22:276–283
Youm YH, Horvath TL, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA, Dixit VD (2016) Prolongevity hormone FGF21 protects against immune senescence by delaying age-related thymic involution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:1026–1031
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Kauppinen A (2016) Age-related changes in AMPK activation: role for AMPK phosphatases and inhibitory phosphorylation by upstream signaling pathways. Ageing Res Rev 28:15–26
Lee WH, Kim SG (2010) AMPK-dependent metabolic regulation by PPAR agonists. PPAR Res. doi:10.1155/2010/549101
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the grants from the Academy of Finland, the University of Eastern Finland, VTR funding from Kuopio University Hospital, the Finnish Cultural Foundation, the Finnish Eye Foundation, and the Alfred Kordelin Foundation. The authors thank Dr. Ewen MacDonald for checking the language of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salminen, A., Kauppinen, A. & Kaarniranta, K. FGF21 activates AMPK signaling: impact on metabolic regulation and the aging process. J Mol Med 95, 123–131 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1477-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1477-1