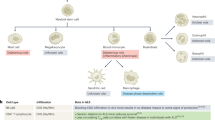
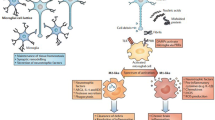
Abstract
Neuroinflammation is now a well-characterised feature of neurodegenerative diseases. Immune dysfunction outside the central nervous system is also increasingly recognised as part of the diseases. Peripheral inflammation has emerged as a modulator of disease progression and neuropathology in several neurodegenerative diseases, making it targetable in new therapeutic approaches. In addition, the easy accessibility of blood immune cells and markers makes them ideal candidates for use as possible biomarkers and a potential model of central immune cells.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clement AM, Nguyen MD, Roberts EA, Garcia ML, Boillée S, Rule M, McMahon AP, Doucette W, Siwek D, Ferrante RJ et al (2003) Wild-type nonneuronal cells extend survival of SOD1 mutant motor neurons in ALS mice. Science 302:113–117
Bradford J, Shin JY, Roberts M, Wang CE, Li XJ, Li S (2009) Expression of mutant huntingtin in mouse brain astrocytes causes age-dependent neurological symptoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:22480–22485
Merad M, Manz MG, Karsunky H, Wagers A, Peters W, Charo I, Weissman IL, Cyster JG, Engleman EG (2002) Langerhans cells renew in the skin throughout life under steady-state conditions. Nat Immunol 3:1135–1141
Ransohoff RM, Perry VH (2009) Microglial physiology: unique stimuli, specialized responses. Annu Rev Immunol 27:119–145
Ajami B, Bennett JL, Krieger C, Tetzlaff W, Rossi FM (2007) Local self-renewal can sustain CNS microglia maintenance and function throughout adult life. Nat Neurosci 10:1538–1543
Sapp E, Kegel KB, Aronin N, Hashikawa T, Uchiyama Y, Tohyama K, Bhide PG, Vonsattel JP, DiFiglia M (2001) Early and progressive accumulation of reactive microglia in the Huntington disease brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:161–172
Vonsattel JP, Myers RH, Stevens TJ, Ferrante RJ, Bird ED, Richardson EP (1985) Neuropathological classification of Huntington’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 44:559–577
Tai YF, Pavese N, Gerhard A, Tabrizi SJ, Barker RA, Brooks DJ, Piccini P (2007) Microglial activation in presymptomatic Huntington’s disease gene carriers. Brain 130:1759–1766
Rogers J, Mastroeni D, Leonard B, Joyce J, Grover A (2007) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: are microglia pathogenic in either disorder? Int Rev Neurobiol 82:235–246
Herrera AJ, Castaño A, Venero JL, Cano J, Machado A (2000) The single intranigral injection of LPS as a new model for studying the selective effects of inflammatory reactions on dopaminergic system. Neurobiol Dis 7:429–447
Wyss-Coray T, Rogers J (2012) Inflammation in Alzheimer disease—a brief review of the basic science and clinical literature. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a006346
Schwab C, McGeer PL (2008) Inflammatory aspects of Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. J Alzheimers Dis 13:359–369
Harold D, Abraham R, Hollingworth P, Sims R, Gerrish A, Hamshere ML, Pahwa JS, Moskvina V, Dowzell K, Williams A et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1088–1093
Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, Campion D, Sleegers K, Hiltunen M, Combarros O, Zelenika D, Bullido MJ, Tavernier B et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1094–1099
Guerreiro R, Wojtas A, Bras J, Carrasquillo M, Rogaeva E, Majounie E, Cruchaga C, Sassi C, Kauwe JS, Younkin S et al (2013) TREM2 variants in Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 368:117–127
Wahner AD, Sinsheimer JS, Bronstein JM, Ritz B (2007) Inflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms and increased risk of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 64:836–840
Hamza TH, Zabetian CP, Tenesa A, Laederach A, Montimurro J, Yearout D, Kay DM, Doheny KF, Paschall J, Pugh E et al (2010) Common genetic variation in the HLA region is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 42:781–785
Björkqvist M, Wild EJ, Tabrizi SJ (2009) Harnessing immune alterations in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron 64:21–24
Lee KS, Chung JH, Choi TK, Suh SY, Oh BH, Hong CH (2009) Peripheral cytokines and chemokines in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 28:281–287
Ferrari CC, Tarelli R (2011) Parkinson's disease and systemic inflammation. Parkinsons Dis 2011:9
Kuhle J, Lindberg RL, Regeniter A, Mehling M, Steck AJ, Kappos L, Czaplinski A (2009) Increased levels of inflammatory chemokines in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 16:771–774
Moreau C, Devos D, Brunaud-Danel V, Defebvre L, Perez T, Destée A, Tonnel AB, Lassalle P, Just N (2005) Elevated IL-6 and TNF-alpha levels in patients with ALS: inflammation or hypoxia? Neurology 65:1958–1960
Björkqvist M, Wild EJ, Thiele J, Silvestroni A, Andre R, Lahiri N, Raibon E, Lee RV, Benn CL, Soulet D et al (2008) A novel pathogenic pathway of immune activation detectable before clinical onset in Huntington’s disease. J Exp Med 205:1869–1877
Wild E, Magnusson A, Lahiri N, Krus U, Orth M, Tabrizi SJ, Björkqvist M (2011) Abnormal peripheral chemokine profile in Huntington's disease. PLoS Curr 3:RRN1231
Dalrymple A, Wild EJ, Joubert R, Sathasivam K, Björkqvist M, Petersén A, Jackson GS, Isaacs JD, Kristiansen M, Bates GP et al (2007) Proteomic profiling of plasma in Huntington’s disease reveals neuroinflammatory activation and biomarker candidates. J Proteome Res 6:2833–2840
Thambisetty M, Simmons A, Velayudhan L, Hye A, Campbell J, Zhang Y, Wahlund LO, Westman E, Kinsey A, Güntert A et al (2010) Association of plasma clusterin concentration with severity, pathology, and progression in Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67:739–748
Reale M, Iarlori C, Thomas A, Gambi D, Perfetti B, Di Nicola M, Onofrj M (2009) Peripheral cytokines profile in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav Immun 23:55–63
Bessler H, Djaldetti R, Salman H, Bergman M, Djaldetti M (1999) IL-1 beta, IL-2, IL-6 and TNF-alpha production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with Parkinson’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 53:141–145
Solerte SB, Cravello L, Ferrari E, Fioravanti M (2000) Overproduction of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha from natural killer (NK) cells is associated with abnormal NK reactivity and cognitive derangement in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 917:331–340
Shalit F, Sredni B, Brodie C, Kott E, Huberman M (1995) T lymphocyte subpopulations and activation markers correlate with severity of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 75:246–250
Lombardi VR, García M, Rey L, Cacabelos R (1999) Characterization of cytokine production, screening of lymphocyte subset patterns and in vitro apoptosis in healthy and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) individuals. J Neuroimmunol 97:163–171
Lucin KM, Wyss-Coray T (2009) Immune activation in brain aging and neurodegeneration: too much or too little? Neuron 64:110–122
Sun YX, Minthon L, Wallmark A, Warkentin S, Blennow K, Janciauskiene S (2003) Inflammatory markers in matched plasma and cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 16:136–144
O’Neill LA, Kaltschmidt C (1997) NF-kappa B: a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends Neurosci 20:252–258
Mattson MP, Meffert MK (2006) Roles for NF-kappaB in nerve cell survival, plasticity, and disease. Cell Death Differ 13:852–860
Teng FY, Tang BL (2010) NF-kappaB signaling in neurite growth and neuronal survival. Rev Neurosci 21:299–313
Kaltschmidt B, Uherek M, Volk B, Baeuerle PA, Kaltschmidt C (1997) Transcription factor NF-kappaB is activated in primary neurons by amyloid beta peptides and in neurons surrounding early plaques from patients with Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:2642–2647
Hunot S, Brugg B, Ricard D, Michel PP, Muriel MP, Ruberg M, Faucheux BA, Agid Y, Hirsch EC (1997) Nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB is increased in dopaminergic neurons of patients with Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:7531–7536
Khoshnan A, Ko J, Watkin EE, Paige LA, Reinhart PH, Patterson PH (2004) Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex and nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to mutant huntingtin neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 24:7999–8008
Gordon S, Taylor PR (2005) Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol 5:953–964
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F (2005) Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 308:1314–1318
Blennow K, Hampel H, Weiner M, Zetterberg H (2010) Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:131–144
Blum-Degen D, Müller T, Kuhn W, Gerlach M, Przuntek H, Riederer P (1995) Interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 are elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s and de novo Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurosci Lett 202:17–20
Turner MR, Kiernan MC, Leigh PN, Talbot K (2009) Biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 8:94–109
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8:382–397
Ray S, Britschgi M, Herbert C, Takeda-Uchimura Y, Boxer A, Blennow K, Friedman LF, Galasko DR, Jutel M, Karydas A et al (2007) Classification and prediction of clinical Alzheimer’s diagnosis based on plasma signaling proteins. Nat Med 13:1359–1362
Villeda SA, Luo J, Mosher KI, Zou B, Britschgi M, Bieri G, Stan TM, Fainberg N, Ding Z, Eggel A et al (2011) The ageing systemic milieu negatively regulates neurogenesis and cognitive function. Nature 477:90–94
Baron P, Bussini S, Cardin V, Corbo M, Conti G, Galimberti D, Scarpini E, Bresolin N, Wharton SB, Shaw PJ et al (2005) Production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 32:541–544
Choi C, Jeong JH, Jang JS, Choi K, Lee J, Kwon J, Choi KG, Lee JS, Kang SW (2008) Multiplex analysis of cytokines in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease by color-coded bead technology. J Clin Neurol 4:84–88
Kwan W, Magnusson A, Chou A, Adame A, Carson MJ, Kohsaka S, Masliah E, Möller T, Ransohoff R, Tabrizi SJ et al (2012) Bone marrow transplantation confers modest benefits in mouse models of Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci 32:133–142
Simard AR, Soulet D, Gowing G, Julien JP, Rivest S (2006) Bone marrow-derived microglia play a critical role in restricting senile plaque formation in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 49:489–502
Mildner A, Schmidt H, Nitsche M, Merkler D, Hanisch UK, Mack M, Heikenwalder M, Brück W, Priller J, Prinz M (2007) Microglia in the adult brain arise from Ly-6ChiCCR2+ monocytes only under defined host conditions. Nat Neurosci 10:1544–1553
Diserbo M, Agin A, Lamproglou I, Mauris J, Staali F, Multon E, Amourette C (2002) Blood–brain barrier permeability after gamma whole-body irradiation: an in vivo microdialysis study. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 80:670–678
Holmes C, Cunningham C, Zotova E, Woolford J, Dean C, Kerr S, Culliford D, Perry VH (2009) Systemic inflammation and disease progression in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 73:768–774
Holmes C, Cunningham C, Zotova E, Culliford D, Perry VH (2011) Proinflammatory cytokines, sickness behavior, and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 77:212–218
Harris MA, Tsui JK, Marion SA, Shen H, Teschke K (2012) Association of Parkinson’s disease with infections and occupational exposure to possible vectors. Mov Disord 27:1111–1117
D’Amelio M, Ragonese P, Morgante L, Reggio A, Callari G, Salemi G, Savettieri G (2006) Long-term survival of Parkinson’s disease: a population-based study. J Neurol 253:33–37
Cunningham C, Campion S, Lunnon K, Murray CL, Woods JF, Deacon RM, Rawlins JN, Perry VH (2009) Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Biol Psychiatry 65:304–312
Qin L, Wu X, Block ML, Liu Y, Breese GR, Hong JS, Knapp DJ, Crews FT (2007) Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 55:453–462
Bouchard J, Truong J, Bouchard K, Dunkelberger D, Desrayaud S, Moussaoui S, Tabrizi SJ, Stella N, Muchowski PJ (2012) Cannabinoid receptor 2 signaling in peripheral immune cells modulates disease onset and severity in mouse models of Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci 32:18259–18268
Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Broadwell RD (1995) Passage of cytokines across the blood–brain barrier. Neuroimmunomodulation 2:241–248
Perry VH, Cunningham C, Holmes C (2007) Systemic infections and inflammation affect chronic neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Immunol 7:161–167
Ek M, Engblom D, Saha S, Blomqvist A, Jakobsson PJ, Ericsson-Dahlstrand A (2001) Inflammatory response: pathway across the blood–brain barrier. Nature 410:430–431
Ransohoff RM, Kivisäkk P, Kidd G (2003) Three or more routes for leukocyte migration into the central nervous system. Nat Rev Immunol 3:569–581
Czirr E, Wyss-Coray T (2012) The immunology of neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest 122:1156–1163
Tracey KJ (2009) Reflex control of immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 9:418–428
Kortekaas R, Leenders KL, van Oostrom JC, Vaalburg W, Bart J, Willemsen AT, Hendrikse NH (2005) Blood–brain barrier dysfunction in parkinsonian midbrain in vivo. Ann Neurol 57:176–179
Zwilling D, Huang SY, Sathyasaikumar KV, Notarangelo FM, Guidetti P, Wu HQ, Lee J, Truong J, Andrews-Zwilling Y, Hsieh EW et al (2011) Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase inhibition in blood ameliorates neurodegeneration. Cell 145:863–874
Chen H, Jacobs E, Schwarzschild MA, McCullough ML, Calle EE, Thun MJ, Ascherio A (2005) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use and the risk for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 58:963–967
Manthripragada AD, Schernhammer ES, Qiu J, Friis S, Wermuth L, Olsen JH, Ritz B (2011) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroepidemiology 36:155–161
Imbimbo BP, Solfrizzi V, Panza F (2010) Are NSAIDs useful to treat Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment? Front Aging Neurosci 2
Senior K (2002) Dosing in phase II trial of Alzheimer’s vaccine suspended. Lancet Neurol 1:3
Frenkel D, Maron R, Burt DS, Weiner HL (2005) Nasal vaccination with a proteosome-based adjuvant and glatiramer acetate clears beta-amyloid in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest 115:2423–2433
Callaway E (2012) Alzheimer’s drugs take a new tack. Nature 489:13–14
Farlow M, Arnold SE, van Dyck CH, Aisen PS, Snider BJ, Porsteinsson AP, Friedrich S, Dean RA, Gonzales C, Sethuraman G et al (2012) Safety and biomarker effects of solanezumab in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 8:261–271
Strobel G, Zakaib G (2013) Solanezumab selected for Alzheimer’s A4 prevention trial. In: Alzheimer Research Forum–News. http://www.alzforum.org/new/detail.asp?id=3379. Accessed 05 March 2013.
Brodacki B, Staszewski J, Toczyłowska B, Kozłowska E, Drela N, Chalimoniuk M, Stepien A (2008) Serum interleukin (IL-2, IL-10, IL-6, IL-4), TNFalpha, and INFgamma concentrations are elevated in patients with atypical and idiopathic parkinsonism. Neurosci Lett 441:158–162
Licastro F, Pedrini S, Caputo L, Annoni G, Davis LJ, Ferri C, Casadei V, Grimaldi LM (2000) Increased plasma levels of interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and alpha-1-antichymotrypsin in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: peripheral inflammation or signals from the brain? J Neuroimmunol 103:97–102
Dobbs RJ, Charlett A, Purkiss AG, Dobbs SM, Weller C, Peterson DW (1999) Association of circulating TNF-alpha and IL-6 with ageing and parkinsonism. Acta Neurol Scand 100:34–41
Ono S, Hu J, Shimizu N, Imai T, Nakagawa H (2001) Increased interleukin-6 of skin and serum in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 187:27–34
Motta M, Imbesi R, Di Rosa M, Stivala F, Malaguarnera L (2007) Altered plasma cytokine levels in Alzheimer’s disease: correlation with the disease progression. Immunol Lett 114:46–51
Rentzos M, Nikolaou C, Andreadou E, Paraskevas GP, Rombos A, Zoga M, Tsoutsou A, Boufidou F, Kapaki E, Vassilopoulos D (2009) Circulating interleukin-10 and interleukin-12 in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 119:332–337
Rentzos M, Rombos A, Nikolaou C, Zoga M, Zouvelou V, Dimitrakopoulos A, Alexakis T, Tsoutsou A, Samakovli A, Michalopoulou M et al (2010) Interleukin-15 and interleukin-12 are elevated in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur Neurol 63:285–290
Fiala M, Chattopadhay M, La Cava A, Tse E, Liu G, Lourenco E, Eskin A, Liu PT, Magpantay L, Tse S et al (2010) IL-17A is increased in the serum and in spinal cord CD8 and mast cells of ALS patients. J Neuroinflammation 7:76
Alvarez XA, Franco A, Fernández-Novoa L, Cacabelos R (1996) Blood levels of histamine, IL-1 beta, and TNF-alpha in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease. Mol Chem Neuropathol 29:237–252
Singh VK, Guthikonda P (1997) Circulating cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease. J Psychiatr Res 31:657–660
Babu GN, Kumar A, Chandra R, Puri SK, Kalita J, Misra UK (2008) Elevated inflammatory markers in a group of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients from northern India. Neurochem Res 33:1145–1149
Speciale L, Calabrese E, Saresella M, Tinelli C, Mariani C, Sanvito L, Longhi R, Ferrante P (2007) Lymphocyte subset patterns and cytokine production in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neurobiol Aging 28:1163–1169
Houi K, Kobayashi T, Kato S, Mochio S, Inoue K (2002) Increased plasma TGF-beta1 in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 106:299–301
Bonotis K, Krikki E, Holeva V, Aggouridaki C, Costa V, Baloyannis S (2008) Systemic immune aberrations in Alzheimer’s disease patients. J Neuroimmunol 193:183–187
Scalzo P, de Miranda AS, Guerra Amaral DC, de Carvalho VM, Cardoso F, Teixeira AL (2011) Serum levels of chemokines in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimmunomodulation 18:240–244
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Ralph Andre for his help with editing the manuscript, Dr. Jonathan M Schott for his advice on AD antibody trials and Ray Young for his help with graphics. Our work is supported financially by UCL/UCLH Biomedical Research Centre (PhD studentship to UT), BBSRC, Medical Research Council, CHDI Foundation, EU FP7 grant (Paddington consortium) and the UK Dementia and Neurodegenerative Diseases Network (DeNDRoN).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Träger, U., Tabrizi, S.J. Peripheral inflammation in neurodegeneration. J Mol Med 91, 673–681 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1026-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1026-0