Abstract
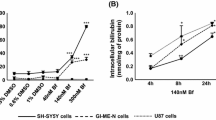
Unconjugated bilirubin (UCB) is the major degradation product of the heme catabolism. A growing body of evidences suggests that UCB plays major biological effects by inhibiting cell proliferation in cancer cell lines and eliciting cell toxicity particularly in neurons and glial cells. Early molecular events responsible for bilirubin-induced cytotoxicity remain poorly understood. Using HeLa cells and mouse embryonic fibroblasts, we found that UCB at a concentration of free pigment (Bf) of 80 nM induced oxidative stress, promoting a significant increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a decreased cell survival (by the MTT test). The ROS increase activated the antioxidant cell response through APE1/Ref-1, a master redox regulator in eukaryotic cells. Activation of APE1/Ref-1 was followed by a concomitant activation of Egr-1 transcription factor and by an upregulation of PTEN tumor suppressor, an Egr-1 target gene, leading to inhibition of cell growth. Blocking ROS generation with N-acetylcysteine pretreatment, restored cell survival, limited the upregulation of PTEN in response to UCB, and prevented the inhibition of cell proliferation. HeLa cells transfected with mutants of the PTEN promoter or silenced with APE1/Ref-1 small interference RNA confirmed that UCB modulates a signaling pathway involving APE1/Ref-1, Egr-1, and PTEN. These findings describe a new molecular pathway involved in the cytotoxic effects of UCB.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AP-1:
-
activator protein-1
- APE1/Ref-1:
-
apurinic apyrimidinic endonuclease/redox effector factor-1
- Egr-1:
-
early growth response protein-1
- H2DCFDA:
-
2,7-dichlorofluorescein diacetate
- HSA:
-
human serum albumin
- MEF:
-
mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- Mrp1:
-
multidrug resistance-associated protein 1
- MTT:
-
3(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl-2)-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium
- NAC:
-
N-acetyl-cysteine
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor-κB
- PTEN:
-
protein phosphatase and tensin homolog
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- siRNA:
-
small interference RNA
- UCB:
-
unconjugated bilirubin
- Bf:
-
free unconjugated bilirubin
References
Ostrow JE, Tiribelli C (2003) Bilirubin, a curse and a boon. Gut 52:1668–1670
Stocker R, Yamamoto Y, McDonagh AF, Glazer AN, Ames BN (1987) Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science 235:1043–1046
Rigato I, Ostrow JD, Tiribelli C (2005) Bilirubin and the risk of common non-hepatic diseases. Trends Mol Med 11:277–283
Gourley GR (1997) Bilirubin metabolism and kernicterus. Adv Pediatr 44:173–229
Wennberg RP, Ahlfors CE, Bhutani VK, Johnson LH, Shapiro SM (2006) Toward understanding kernicterus: a challenge to improve the management of jaundiced newborns. Pediatrics 117:474–485
Ahlfors CE (2001) Bilirubin-albumin binding and free bilirubin. J Perinatol 21(Suppl 1):S40–S42
Ostrow JD, Pascolo L, Brites D, Tiribelli C (2004) Molecular basis of bilirubin-induced neurotoxicity. Trends Mol Med 10:65–70
Ostrow JD, Pascolo L, Tiribelli C (2003) Reassessment of the unbound concentrations of unconjugated bilirubin in relation to neurotoxicity in vitro. Pediatr Res 54:926
Dorè S, Snyder SH (1999) Neuroprotective action of bilirubin against oxidative stress in primary hippocampal cultures. Ann N Y Acad Sci 890:167–172
Gennuso F, Fernetti C, Tirolo C, Testa N, LEpiscopo F, Caniglia S, Morale MC, Ostrow JD, Pascolo L, Tiribelli C, Marchetti B (2004) Bilirubin protects astrocytes from its own toxicity by inducing up-regulation and translocation of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (Mrp1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:2470–2475
Calligaris S, Cekic D, Roca-Burgos L, Gerin F, Mazzone G, Ostrow JD, Tiribelli C (2006) Multidrug resistance associated protein 1 protects against bilirubin-induced cytotoxicity. FEBS Lett 580:1355–1359
Keshavan P, Schwemberger SJ, Smith DL, Babcock GF, Zucker SD (2004) Unconjugated bilirubin induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells by triggering mitochondrial depolarization. Int J Cancer 112:433–445
Vitek L, Schwertner HA (2007) The heme catabolic pathway and its protective effects on oxidative stress-mediated diseases. Adv Clin Chem 3:1–57
Zucker SD, Horn PS, Sherman KE (2004) Serum bilirubin levels in the U.S. population: gender effect and inverse correlation with colorectal cancer. Hepatology 40:827–835
Rodrigues CM, Sola S, Brites D (2002) Bilirubin induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in developing rat brain neurons. Hepatology 35:1186–1195
Oakes GH, Bend JR (2005) Early steps in bilirubin-mediated apoptosis in murine hepatoma (Hepa 1c1c7) cells are characterized by aryl hydrocarbon receptor-independent oxidative stress and activation of the mitochondrial pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 19:244–255
Tell G, Damante G, Caldwell D, Kelley MR (2005) The intracellular localization of APE1/Ref-1: more than a passive phenomenon? Antioxid Redox Signal 7:367–384
Xanthoudakis S, Curran T (1992) Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J 11:653–665
Xanthoudakis S, Miao G, Wang F, Pan YC, Curran T (1992) Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J 11:3323–3335
Huang RP, Wu JX, Fan Y, Adamson ED (1996) UV activates growth factor receptors via reactive oxygen intermediates. J Cell Biol 133:211–220
Liu C, Rangnekar VM, Adamson E, Mercola D (1998) Suppression of growth and transformation and induction of apoptosis by EGR-1. Cancer Gene Ther 5:3–28
Huang RP, Fan Y, de Belle I, Niemeyer C, Gottardis MM, Mercola D, Adamson ED (1997) Decreased Egr-1 expression in human, mouse and rat mammary cells and tissues correlates with tumor formation. Int J Cancer 72:102–109
Krones-Herzig A, Mittal S, Yule K, Liang H, English C, Urcis R, Soni T, Adamson ED, Mercola D (2005) Early growth response 1 acts as a tumor suppressor in vivo and in vitro via regulation of p53. Cancer Res 65:5133–5143
Virolle T, Adamson ED, Baron V, Birle D, Mercola D, Mustelin T, de Belle I (2001) The Egr-1 transcription factor directly activates PTEN during irradiation-induced signaling. Nat Cell Biol 3:1124–1128
Sansal I, Sellers WR (2004) The biology and clinical relevance of the PTEN tumor suppressor pathway. J Clin Oncol 22:2954–2963
Pines A, Bivi N, Romanello M, Damante G, Kelley MR, Adamson ED, DAndrea P, Quadrifoglio F, Moro L, Tell G (2005) Cross-regulation between Egr-1 and APE/Ref-1 during early response to oxidative stress in the human osteoblastic HOBIT cell line: evidence for an autoregulatory loop. Free Radic Res 39:269–281
McDonagh AF, Assisi F (1972) The ready isomerization of bilirubin-IXα in aqueous solution. Biochem J 129:797–800
Ostrow JD, Mukerjee P (2007) Solvent partition of 14C-unconjugated bilirubin to remove labeled polar impurities. Transl Res 149:37–45
Bayón JE, Pascolo L, Gonzalo-Orden JM, Altonaga JR, Gonzalez-Gallego J, Webster CC, Haigh WG, Stelzner M, Pekow C, Tiribelli C, Ostrow JD (2001) Pitfalls in preparation of (3)H-unconjugated bilirubin by biosynthetic labeling from precursor (3)H-5-aminolevulinic acid in the dog. J Lab Clin Med 138:313–321
Hertzog PJ (2001) Isolation of embryonic fibroblasts and their use in the in vitro characterization of gene function. Methods Mol Biol 158:205–215
Freshney RI (1994) Culture of animal cells. A manual of basic technique, 3rd edn. Wiley-Liss Inc., New York
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Roca-Burgos L, Calligaris S, Wennberg RP, Ahlfors CE, Malik SG, Ostrow JD, Tiribelli C (2006) Factors affecting the binding of bilirubin to serum albumins: validation and application of the peroxidase method. Pediatr Res 60:724–728
Denizot F, Lang R (1986) Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods 89:271–277
Frenkel K, Gleichauf C (1991) Hydrogen peroxide formation by cells treated with a tumor promoter. Free Radic Res Commun 2:783–794
Pines A, Perrone L, Bivi N, Romanello M, Damante G, Gulisano M, Kelley MR, Quadrifoglio F, Tell G (2005) Activation of APE1/Ref-1 is dependent on reactive oxygen species generated after purinergic receptor stimulation by ATP. Nucleic Acids Res 33:4379–4394
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bours V, Burd PR, Brown K, Villalobos J, Park S, Ryseck RP, Bravo R, Kelly K, Siebenlist U (1992) A novel mitogen-inducible gene product related to p50/p105-NF-kappa B participates in transactivation through a kappa B site. Mol Cell Biol 12:685–695
Mittal V (2004) Improving the efficiency of RNA interference in mammals. Nat Rev Genet 5:355–365
van de Wetering M, Oving I, Muncan V, Pon Fong MT, Brantjes H, van Leenen D, Holstege FC, Brummelkamp TR, Agami R, Clevers H (2003) Specific inhibition of gene expression using a stably integrated, inducible small-interfering-RNA vector. EMBO Rep 4:609–615
Tell G, Pines A, Arturi F, Cesaratto L, Adamson E, Puppin C, Presta I, Russo D, Filetti S, Damante G (2004) Control of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) gene expression in normal and neoplastic thyroid cells. Endocrinology 145:4660–4666
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C (1995) A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods 184:39–51
Homburg CH, de Haas M, von dem Borne AE, Verhoeven AJ, Reutelingsperger CP, Roos D (1995) Human neutrophils lose their surface Fc gamma RIII and acquire Annexin V binding sites during apoptosis in vitro. Blood 85:532–540
Huang RP, Adamson ED (1993) Characterization of the DNA-binding properties of the early growth response-1 (Egr-1) transcription factor: evidence for modulation by a redox mechanism. DNA Cell Biol 12:265–273
Nakano H, Nakajima A, Sakon-Komazawa S, Piao JH, Xue X, Okumura K (2006) Reactive oxygen species mediate crosstalk between NF-kappaB and JNK. Cell Death Differ 13:730–737
Gaiddon C, Moorthy NC, Prives C (1999) Ref-1 regulates the transactivation and pro-apoptotic functions of p53 in vivo. EMBO J 18:5609–5621
Stambolic V, MacPherson D, Sas D, Lin Y, Snow B, Jang Y, Benchimol S, Mak TW (2001) Regulation of PTEN transcription by p53. Mol Cell 8:317–325
Patel L, Pass I, Coxon P, Downes CP, Smith SA, Macphee CH (2001) Tumor suppressor and anti-inflammatory actions of PPARgamma agonists are mediated via upregulation of PTEN. Curr Biol 11:764–768
Kim S, Domon-Dell C, Kang J, Chung DH, Freund JN, Evers BM (2004) Down-regulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by the tumor necrosis factor-alpha/nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB)-inducing kinase/NF-kappaB pathway is linked to a default IkappaB-alpha autoregulatory loop. J Biol Chem 279:4285–4291
Whelan JT, Forbes SL, Bertrand FE (2007) CBF-1 (RBP-Jkappa) binds to the PTEN promoter and regulates PTEN gene expression. Cell Cycle 6:80–84
Robertson KA, Hill DP, Xu Y, Liu L, Van Epps S, Hockenbery DM, Park JR, Wilson TM, Kelley MR (1997) Down-regulation of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease expression is associated with the induction of apoptosis in differentiating myeloid leukemia cells. Cell Growth Differ 8:443–449
Fung H, Demple B (2005) A vital role for Ape1/Ref1 protein in repairing spontaneous DNA damage in human cells. Mol Cell 17:463–470
Bhakat KK, Izumi T, Yang SH, Hazra TK, Mitra S (2003) Role of acetylated human AP-endonuclease (APE1/Ref-1) in regulation of the parathyroid hormone gene. EMBO J 22:6299–6309
Finkel T (2003) Oxidant signals and oxidative stress. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:247–254
Izumi T, Brown DB, Naidu CV, Bhakat KK, Macinnes MA, Saito H, Chen DJ, Mitra S (2005) Two essential but distinct functions of the mammalian abasic endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:5739–5743
Ramana CV, Boldogh I, Izumi T, Mitra S (1998) Activation of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease in human cells by reactive oxygen species and its correlation with their adaptive response to genotoxicity of free radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:5061–5066
Acknowledgement
The financial support of Telethon–Italy (grant GGP 05062) of MiUR (PRIN 2005 to GT, CT and FQ) and of Fondo Studi Fegato (Grant to CT) is gratefully acknowledged. SC was supported by a PhD fellowship by Ministero Affari Esteri, Rome, Italy. The authors wish to thank E. Adamson for the PTEN promoter plasmids.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L. Cesaratto and S. D. Calligaris contributed equally to the present work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cesaratto, L., Calligaris, S.D., Vascotto, C. et al. Bilirubin-induced cell toxicity involves PTEN activation through an APE1/Ref-1-dependent pathway. J Mol Med 85, 1099–1112 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0204-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0204-3