Abstract
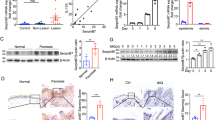
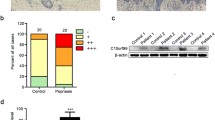
The HCR gene, officially called Coiled-Coil α-Helical Rod protein 1 (CCHCR1), located within the major psoriasis susceptibility locus PSORS1, is a plausible candidate gene for the risk effect. Recently, CCHCR1 was shown to promote steroidogenesis by interacting with the steroidogenic acute regulator protein (StAR). Here, we examined the role of CCHCR1 in psoriasis and cutaneous steroid metabolism. We found that CCHCR1 and StAR are expressed in basal keratinocytes in overlapping areas of the human skin, and CCHCR1 stimulated pregnenolone production in steroidogenesis assay. Overexpression of either the CCHCR1*WWCC risk allele or the non-risk allele enhanced steroid synthesis in vitro. Furthermore, the cytochrome P450scc enzyme was expressed in human keratinocytes and was induced by forskolin, a known activator of steroidogenesis, and forskolin also upregulated CCHCR1. CCHCR1 has an altered expression pattern in lesional psoriatic skin compared to normal healthy skin, suggesting its dysregulation in psoriasis. We found that the expression of CCHCR1 is downregulated twofold at the mRNA level in cultured non-lesional psoriatic keratinocytes when compared to non-psoriatic healthy cells. Our results also suggest a connection between CCHCR1 and vitamin D metabolism in keratinocytes. The expression of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene was lower in non-lesional psoriatic keratinocytes than in healthy cells. Furthermore, Vdr expression was downregulated in the keratinocytes of mice overexpressing the CCHCR1*WWCC risk allele when compared to keratinocytes from mice with the non-risk allele of CCHCR1. Finally, we demonstrate that other agents relevant for psoriasis and/or the regulation of steroidogenesis influence CCHCR1 expression in keratinocytes, including insulin, EGF, cholesterol, estrogen, and cyclosporin A. Taken the role of steroid hormones, including vitamin D and estrogen, in cell proliferation, epidermal barrier homeostasis, differentiation, and immune response, our results suggest a role for CCHCR1 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis via the regulation of skin steroid metabolism.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asumalahti K, Laitinen T, Itkonen-Vatjus R, Lokki ML, Suomela S, Snellman E, Saarialho-Kere U, Kere J (2000) A candidate gene for psoriasis near HLA-C, HCR (Pg8), is highly polymorphic with a disease-associated susceptibility allele. Hum Mol Genet 9:1533–1542
Asumalahti K, Veal C, Laitinen T, Suomela S, Allen M, Elomaa O, Moser M, de Cid R, Ripatti S, Vorechovsky I, Marcusson J, Nakagawa H, Lazaro X, Capon F, Novelli G, The Psoriasis Consortium, Saarialho-Kere U, Barker J, Thrembath R, Kere J (2002) Coding haplotype analysis supports HCR as the putative susceptibility gene for psoriasis at the MHC PSORS1 locus. Hum Mol Genet 11:589–597
Bowcock AM, Cookson WO (2004) The genetics of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and atopic dermatitis. Hum Mol Genet 13(Spec No 1):R43–R55
Suomela S, Elomaa O, Asumalahti K, Kariniemi AL, Karvonen SL, Peltonen J, Kere J, Saarialho-Kere U (2003) HCR, a candidate gene for psoriasis, is expressed differently in psoriasis and other hyperproliferative skin disorders and is downregulated by interferon-gamma in keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 121:1360–1364
Elomaa O, Majuri I, Suomela S, Asumalahti K, Jiao H, Mirzaei Z, Rozell B, Dahlman-Wright K, Pispa J, Kere J, Saarialho-Kere U (2004) Transgenic mouse models support HCR as an effector gene in the PSORS1 locus. Hum Mol Genet 13:1551–1561
Sugawara T, Shimizu H, Hoshi N, Nakajima A, Fujimoto S (2003) Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein-binding protein cloned by a yeast two-hybrid system. J Biol Chem 278:42487–42494
Stocco DM, Wang X, Jo Y, Manna PR (2005) Multiple signaling pathways regulating steroidogenesis and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression: more complicated than we thought. Mol Endocrinol 19:2647–2659
Zouboulis CC, Degitz K (2004) Androgen action on human skin—from basic research to clinical significance. Exp Dermatol 13(Suppl 4):5–10
Thiboutot D, Jabara S, McAllister JM, Sivarajah A, Gilliland K, Cong Z, Clawson G (2003) Human skin is a steroidogenic tissue: steroidogenic enzymes and cofactors are expressed in epidermis, normal sebocytes, and an immortalized sebocyte cell line (SEB-1). J Invest Dermatol 120:905–914
Slominski A, Zjawiony J, Wortsman J, Semak I, Stewart J, Pisarchik A, Sweatman T, Marcos J, Dunbar C, Tuckey R (2004) A novel pathway for sequential transformation of 7-dehydrocholesterol and expression of the P450scc system in mammalian skin. Eur J Biochem 271:4178–4188
Bikle DD, Oda Y, Xie Z (2005) Vitamin D and skin cancer: a problem in gene regulation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 97:83–91
Segre JA (2006) Epidermal barrier formation and recovery in skin disorders. J Clin Invest 116:1150–1158
Shapiro LJ, Yen P, Pomerantz D, Martin E, Rolewic L, Mohandas T (1989) Molecular studies of deletions at the human steroid sulfatase locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 86:8477–8481
Kanda N, Watanabe S (2003) 17beta-estradiol inhibits oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in keratinocytes by promoting bcl-2 expression. J Invest Dermatol 121:1500–1509
Murase JE, Chan KK, Garite TJ, Cooper DM, Weinstein GD (2005) Hormonal effect on psoriasis in pregnancy and post partum. Arch Dermatol 141:601–606
Namazi MR (2005) Steroid sulfatase inhibitors as novel additions to the antipsoriatic armamentarium. Med Sci Monit 11:HY7–HY9
Halsall JA, Osborne JE, Pringle JH, Hutchinson PE (2005) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms, particularly the novel A-1012G promoter polymorphism, are associated with vitamin D3 responsiveness and non-familial susceptibility in psoriasis. Pharmacogenet Genomics 15:349–355
Alpy F, Stoeckel ME, Dierich A, Escola JM, Wendling C, Chenard MP, Vanier MT, Gruenberg J, Tomasetto C, Rio MC (2001) The steroidogenic acute regulatory protein homolog MLN64, a late endosomal cholesterol-binding protein. J Biol Chem 276:4261–4269
Holttä-Vuori M, Alpy F, Tanhuanpää K, Jokitalo E, Mutka AL, Ikonen E (2005) MLN64 is involved in actin-mediated dynamics of late endocytic organelles. Mol Biol Cell 16:3873–3886
Apter D, Jänne O, Karvonen P, Vihko R (1976) Simultaneous determination of five sex hormones in human serum by radioimmunoassay after chromatography on lipidex-5000. Clin Chem 22:32–38
Jans R, Atanasova G, Jadot M, Poumay Y (2004) Cholesterol depletion upregulates involucrin expression in epidermal keratinocytes through activation of p38. J Invest Dermatol 123:564–573
Karvonen SL, Korkiamäki T, Ylä-Outinen H, Nissinen M, Teerikangas H, Pummi K, Karvonen J, Peltonen J (2000) Psoriasis and altered calcium metabolism: downregulated capacitative calcium influx and defective calcium-mediated cell signaling in cultured psoriatic keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 114:693–700
Pollack SE, Furth EE, Kallen CB, Arakane F, Kiriakidou M, Kozarsky KF, Strauss JF 3rd (1997) Localization of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in human tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:4243–4251
Harikrishna JA, Black SM, Szklarz GD, Miller WL (1993) Construction and function of fusion enzymes of the human cytochrome P450scc system. DNA Cell Biol 12:371–379
Chen W, Tsai SJ, Liao CY, Tsai RY, Chen YJ, Pan BJ, Hung CL, Zouboulis CC (2006) Higher levels of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein and type I 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the scalp of men with androgenetic alopecia. J Invest Dermatol 126:2332–2335
Mamluk R, Greber Y, Meidan R (1999) Hormonal regulation of messenger ribonucleic acid expression for steroidogenic factor-1, steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, and cytochrome P450 side-chain cleavage in bovine luteal cells. Biol Reprod 60:628–634
Stocco DM (2001) StAR protein and the regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol 63:193–213
Venencie PY, Meduri G, Pissard S, Jolivet A, Loosfelt H, Milgrom E, Misrahi M (1999) Luteinizing hormone/human chorionic gonadotrophin receptors in various epidermal structures. Br J Dermatol 141:438–446
Lehmann B (2005) The vitamin D3 pathway in human skin and its role for regulation of biological processes. Photochem Photobiol 81:1246–1251
Chen ML, Perez A, Sanan DK, Heinrich G, Chen TC, Holick MF (1996) Induction of vitamin D receptor mRNA expression in psoriatic plaques correlates with clinical response to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Invest Dermatol 106:637–641
Kanda N, Watanabe S (2005) Regulatory roles of sex hormones in cutaneous biology and immunology. J Dermatol Sci 38:1–7
Raychaudhuri SP, Navare T, Gross J, Raychaudhuri SK (2003) Clinical course of psoriasis during pregnancy. Int J Dermatol 42:518–520
Boyd AS, Morris LF, Phillips CM, Menter MA (1996) Psoriasis and pregnancy: Hormone and immune system interaction. Int J Dermatol 35:169–172
Kanda N, Watanabe S (2003) 17beta-estradiol inhibits the production of RANTES in human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 120:420–427
Kanda N, Watanabe S (2003) 17beta-estradiol inhibits the production of interferon-induced protein of 10 kDa by human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 120:411–419
Kanda N, Watanabe S (2003) 17Beta-estradiol inhibits MCP-1 production in human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 120:1058–1066
Liu HY, Buenafe AC, Matejuk A, Ito A, Zamora A, Dwyer J, Vandenbark AA, Offner H (2002) Estrogen inhibition of EAE involves effects on dendritic cell function. J Neurosci Res 70:238–248
Correale J, Arias M, Gilmore W (1998) Steroid hormone regulation of cytokine secretion by proteolipid protein-specific CD4+ T cell clones isolated from multiple sclerosis patients and normal control subjects. J Immunol 161:3365–3374
Kanda N, Watanabe S (2004) 17beta-estradiol stimulates the growth of human keratinocytes by inducing cyclin D2 expression. J Invest Dermatol 123:319–328
Adorini L (2002) Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D receptor ligands in autoimmune diseases. Int Immunopharmacol 2:1017–1028
Gingras S, Turgeon C, Brochu N, Soucy P, Labrie F, Simard J (2003) Characterization and modulation of sex steroid metabolizing activity in normal human keratinocytes in primary culture and HaCaT cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 87:167–179
Wertheimer E, Spravchikov N, Trebicz M, Gartsbein M, Accili D, Avinoah I, Nofeh-Moses S, Sizyakov G, Tennenbaum T (2001) The regulation of skin proliferation and differentiation in the IR null mouse: implications for skin complications of diabetes. Endocrinology 142:1234–1241
Takahashi H, Honma M, Miyauchi Y, Nakamura S, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Iizuka H (2004) Cyclic AMP differentially regulates cell proliferation of normal human keratinocytes through ERK activation depending on the expression pattern of B-raf. Arch Dermatol Res 296:74–82
Hedin L, Rosberg S (1983) Forskolin effects on the cAMP system and steroidogenesis in the immature rat ovary. Mol Cell Endocrinol 33:69–80
Won YH, Sauder DN, McKenzie RC (1994) Cyclosporin A inhibits keratinocyte cytokine gene expression. Br J Dermatol 130:312–319
Guryev O, Carvalho RA, Usanov S, Gilep A, Estabrook RW (2003) A pathway for the metabolism of vitamin D3: unique hydroxylated metabolites formed during catalysis with cytochrome P450scc (CYP11A1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14754–14759
Acknowledgements and funding
We thank Ranja Eklund and Alli Tallqvist for their excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by the Academy of Finland, the Sigrid Juselius Foundation, Finska Läkaresällskapet, the Finnish Konkordia Fund, the Maud Kuistila Memorial Foundation, the Biomedicum Helsinki Foundation, Swedish Research Council, and the Helsinki University Hospital research fund (TYH4226).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiala, I., Suomela, S., Huuhtanen, J. et al. The CCHCR1 (HCR) gene is relevant for skin steroidogenesis and downregulated in cultured psoriatic keratinocytes. J Mol Med 85, 589–601 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0155-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0155-0