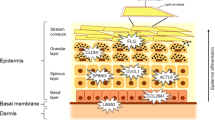
Abstract
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic pruritic skin disease affecting up to 15% of children in industrialized countries. AD belongs to the group of allergic disorders that include food allergy, allergic rhinitis, and asthma. A multifactorial background for AD has been suggested, with genetic as well as environmental factors influencing disease development. Genome-wide screens for AD have been completed in four different populations to date. Interestingly, the susceptibility regions identified for AD show little overlap with asthma susceptibility regions, suggesting that, at least in part, separate genes might be involved in the pathogenesis of the different atopic disorders. Instead, some of the identified regions overlap with susceptibility regions for psoriasis, another chronic skin disease. Thus, genes expressed in the skin might play an important role in AD pathogenesis, in addition to genes influencing atopic diatheses. Although no veritable “AD gene” has been identified by positional cloning to date, examples from other complex genetic disorders such as asthma show that this goal is likely to be reached in the near future. Candidate gene studies, on the other hand, have identified 19 genes that were shown to be associated with AD in at least one study. The results of genome-wide screens as well as candidate gene studies are evaluated here in detail.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Atopic dermatitis
- CE:
-
Cornified envelope
- EDC:
-
Epidermal differentiation complex
- IgE:
-
Immunoglobulin E
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- Th2:
-
T helper lymphocyte type 2
References
Williams H, Robertson C, Stewart A, Ait-Khaled N, Anabwani G, Anderson R, Asher I, Beasley R, Bjorksten B, Burr M et al (1999) Worldwide variations in the prevalence of symptoms of atopic eczema in the international study of asthma and allergies in childhood. J Allergy Clin Immunol 103:125–138
Leung DY, Bieber T (2003) Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 361:151–160
Kaiser HB (2004) Risk factors in allergy/asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc 25:7–10
Spergel JM, Paller AS (2003) Atopic dermatitis and the atopic march. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:S118–S127
Bohme M, Lannero E, Wickman M, Nordvall SL, Wahlgren CF (2002) Atopic dermatitis and concomitant disease patterns in children up to 2 years of age. Acta Derm Venereol 82:98–103
Cabon N, Ducombs G, Mortureux P, Perromat M, Taieb A (1996) Contact allergy to aeroallergens in children with atopic dermatitis: comparison with allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis 35:27–32
Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Simon D, Simon HU, Akdis CA, Wuthrich B (2001) Epidemiology, clinical features, and immunology of the “intrinsic” (non-IgE-mediated) type of atopic dermatitis (constitutional dermatitis). Allergy 56:841–849
Novak N, Bieber T (2003) Allergic and nonallergic forms of atopic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:252–262
Johansson SG, Bieber T, Dahl R, Friedmann PS, Lanier BQ, Lockey RF, Motala C, Ortega Martell JA, Platts-Mills TA, Ring J et al (2004) Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. J Allergy Clin Immunol 113:832–836
Dold S, Wjst M, von Mutius E, Reitmeir P, Stiepel E (1992) Genetic risk for asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis. Arch Dis Child 67:1018–1022
Schultz Larsen FV, Holm NV (1985) Atopic dermatitis in a population based twin series. Concordance rates and heritability estimation. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 114:159
Larsen FS, Holm NV, Henningsen K (1986) Atopic dermatitis. A genetic-epidemiologic study in a population-based twin sample. J Am Acad Dermatol 15:487–494
Farrall M (2004) Quantitative genetic variation: a post-modern view. Hum Mol Genet 13(Spec no. 1):R1–R7
Schultz Larsen F, Hanifin JM (1992) Secular change in the occurrence of atopic dermatitis. Acta DermVenereol Suppl (Stockh) 176:7–12
Burr ML, Butland BK, King S, Vaughan-Williams E (1989) Changes in asthma prevalence: two surveys 15 years apart. Arch Dis Child 64:1452–1456
Isolauri E, Huurre A, Salminen S, Impivaara O (2004) The allergy epidemic extends beyond the past few decades. Clin Exp Allergy 34:1007–1010
Martinez FD (2001) The coming-of-age of the hygiene hypothesis. Respir Res 2:129–132
Gehring U, Bolte G, Borte M, Bischof W, Fahlbusch B, Wichmann HE, Heinrich J (2001) Exposure to endotoxin decreases the risk of atopic eczema in infancy: a cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 108:847–854
Weiss ST (2002) Eat dirt—the hygiene hypothesis and allergic diseases. N Engl J Med 347:930–931
Flohr C, Pascoe D, Williams HC (2005) Atopic dermatitis and the ‘hygiene hypothesis’: too clean to be true? Br J Dermatol 152:202–216
Risch N, Merikangas K (1996) The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science 273:1516–1517
Hoffjan S, Nicolae D, Ober C (2003) Association studies for asthma and atopic diseases: a comprehensive review of the literature. Respir Res 4:14
Hirschhorn JN, Daly MJ (2005) Genome-wide association studies for common diseases and complex traits. Nat Rev Genet 6:95–108
Wang WY, Barratt BJ, Clayton DG, Todd JA (2005) Genome-wide association studies: theoretical and practical concerns. Nat Rev Genet 6:109–118
Lee YA, Wahn U, Kehrt R, Tarani L, Businco L, Gustafsson D, Andersson F, Oranje AP, Wolkertstorfer A, v Berg A et al (2000) A major susceptibility locus for atopic dermatitis maps to chromosome 3q21. Nat Genet 26:470–473
Bradley M, Soderhall C, Luthman H, Wahlgren CF, Kockum I, Nordenskjold M (2002) Susceptibility loci for atopic dermatitis on chromosomes 3, 13, 15, 17 and 18 in a Swedish population. Hum Mol Genet 11:1539–1548
Haagerup A, Bjerke T, Schiotz PO, Dahl R, Binderup HG, Tan Q, Kruse TA (2004) Atopic dermatitis—a total genome-scan for susceptibility genes. Acta Derm Venereol 84:346–352
Cookson WO, Ubhi B, Lawrence R, Abecasis GR, Walley AJ, Cox HE, Coleman R, Leaves NI, Trembath RC, Moffatt MF et al (2001) Genetic linkage of childhood atopic dermatitis to psoriasis susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 27:372–373
Hoffjan S, Ober C (2005) Genetic factors. In: Lenfant C (ed) Lung biology in health and disease. Marcel Dekker, NY (in press)
Louden BA, Pearce DJ, Lang W, Feldman SR (2004) A Simplified Psoriasis Area Severity Index (SPASI) for rating psoriasis severity in clinic patients. Dermatol Online J 10:7
Biedermann T, Rocken M, Carballido JM (2004) TH1 and TH2 lymphocyte development and regulation of TH cell-mediated immune responses of the skin. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 9:5–14
Sagoo GS, Cork MJ, Patel R, Tazi-Ahnini R (2004) Genome-wide studies of psoriasis susceptibility loci: a review. J Dermatol Sci 35:171–179
Sagoo GS, Tazi-Ahnini R, Barker JW, Elder JT, Nair RP, Samuelsson L, Traupe H, Trembath RC, Robinson DA, Iles MM (2004) Meta-analysis of genome-wide studies of psoriasis susceptibility reveals linkage to chromosomes 6p21 and 4q28–q31 in Caucasian and Chinese Hans population. J Invest Dermatol 122:1401–1405
Bowcock AM, Cookson WO (2004) The genetics of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and atopic dermatitis. Hum Mol Genet 13(Spec no. 1):R43–R55
Mischke D, Korge BP, Marenholz I, Volz A, Ziegler A (1996) Genes encoding structural proteins of epidermal cornification and S100 calcium-binding proteins form a gene complex (“epidermal differentiation complex”) on human chromosome 1q21. J Invest Dermatol 106:989–992
Bowcock AM, Shannon W, Du F, Duncan J, Cao K, Aftergut K, Catier J, Fernandez-Vina MA, Menter A (2001) Insights into psoriasis and other inflammatory diseases from large-scale gene expression studies. Hum Mol Genet 10:1793–1805
Nomura I, Gao B, Boguniewicz M, Darst MA, Travers JB, Leung DY (2003) Distinct patterns of gene expression in the skin lesions of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: a gene microarray analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:1195–1202
Sugiura H, Ebise H, Tazawa T, Tanaka K, Sugiura Y, Uehara M, Kikuchi K, Kimura T (2005) Large-scale DNA microarray analysis of atopic skin lesions shows overexpression of an epidermal differentiation gene cluster in the alternative pathway and lack of protective gene expression in the cornified envelope. Br J Dermatol 152:146–149
Kalinin AE, Kajava AV, Steinert PM (2002) Epithelial barrier function: assembly and structural features of the cornified cell envelope. BioEssays 24:789–800
Van Eerdewegh P, Little RD, Dupuis J, Del Mastro RG, Falls K, Simon J, Torrey D, Pandit S, McKenny J, Braunschweiger K et al (2002) Association of the ADAM33 gene with asthma and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Nature 418:426–430
Allen M, Heinzmann A, Noguchi E, Abecasis G, Broxholme J, Ponting CP, Bhattacharyya S, Tinsley J, Zhang Y, Holt R et al (2003) Positional cloning of a novel gene influencing asthma from chromosome 2q14. Nat Genet 35:258–263
Zhang Y, Leaves NI, Anderson GG, Ponting CP, Broxholme J, Holt R, Edser P, Bhattacharyya S, Dunham A, Adcock IM et al (2003) Positional cloning of a quantitative trait locus on chromosome 13q14 that influences immunoglobulin E levels and asthma. Nat Genet 34:181–186
Laitinen T, Polvi A, Rydman P, Vendelin J, Pulkkinen V, Salmikangas P, Makela S, Rehn M, Pirskanen A, Rautanen A et al (2004) Characterization of a common susceptibility locus for asthma-related traits. Science 304:300–304
McGovern DP, van Heel DA, Ahmad T, Jewell DP (2001) NOD2 (CARD15), the first susceptibility gene for Crohn’s disease. Gut 49:752–754
Peltekova VD, Wintle RF, Rubin LA, Amos CI, Huang Q, Gu X, Newman B, Van Oene M, Cescon D, Greenberg G et al (2004) Functional variants of OCTN cation transporter genes are associated with Crohn disease. Nat Genet 36:471–475
Stoll M, Corneliussen B, Costello CM, Waetzig GH, Mellgard B, Koch WA, Rosenstiel P, Albrecht M, Croucher PJ, Seegert D et al (2004) Genetic variation in DLG5 is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Genet 36:476–480
Wills-Karp M (2004) Interleukin-13 in asthma pathogenesis. Immunol Rev 202:175–190
Tazawa T, Sugiura H, Sugiura Y, Uehara M (2004) Relative importance of IL-4 and IL-13 in lesional skin of atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol Res 295:459–464
van der Pouw Kraan TC, van Veen A, Boeije LC, van Tuyl SA, de Groot ER, Stapel SO, Bakker A, Verweij CL, Aarden LA, van der Zee JS (1999) An IL-13 promoter polymorphism associated with increased risk of allergic asthma. Genes Immun 1:61–65
Arima K, Umeshita-Suyama R, Sakata Y, Akaiwa M, Mao XQ, Enomoto T, Dake Y, Shimazu S, Yamashita T, Sugawara N et al (2002) Upregulation of IL-13 concentration in vivo by the IL13 variant associated with bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 109:980–987
He JQ, Chan-Yeung M, Becker AB, Dimich-Ward H, Ferguson AC, Manfreda J, Watson WT, Sandford AJ (2003) Genetic variants of the IL13 and IL4 genes and atopic diseases in at-risk children. Genes Immun 4:385–389
Tsunemi Y, Saeki H, Nakamura K, Sekiya T, Hirai K, Kakinuma T, Fujita H, Asano N, Tanida Y, Wakugawa M et al (2002) Interleukin-13 gene polymorphism G4257A is associated with atopic dermatitis in Japanese patients. J Dermatol Sci 30:100–107
Liu X, Nickel R, Beyer K, Wahn U, Ehrlich E, Freidhoff LR, Bjorksten B, Beaty TH, Huang SK (2000) An IL13 coding region variant is associated with a high total serum IgE level and atopic dermatitis in the German multicenter atopy study (MAS-90). J Allergy Clin Immunol 106:167–170
Hummelshoj T, Bodtger U, Datta P, Malling HJ, Oturai A, Poulsen LK, Ryder LP, Sorensen PS, Svejgaard E, Svejgaard A (2003) Association between an interleukin-13 promoter polymorphism and atopy. Eur J Immunogenet 30:355–359
Heinzmann A, Mao XQ, Akaiwa M, Kreomer RT, Gao PS, Ohshima K, Umeshita R, Abe Y, Braun S, Yamashita T et al (2000) Genetic variants of IL-13 signalling and human asthma and atopy. Hum Mol Genet 9:549–559
Howard TD, Whittaker PA, Zaiman AL, Koppelman GH, Xu J, Hanley MT, Meyers DA, Postma DS, Bleecker ER (2001) Identification and association of polymorphisms in the interleukin-13 gene with asthma and atopy in a Dutch population. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 25:377–384
Graves PE, Kabesch M, Halonen M, Holberg CJ, Baldini M, Fritzsch C, Weiland SK, Erickson RP, von Mutius E, Martinez FD (2000) A cluster of seven tightly linked polymorphisms in the IL-13 gene is associated with total serum IgE levels in three populations of white children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 105:506–513
Leung TF, Tang NL, Chan IH, Li AM, Ha G, Lam CW (2001) A polymorphism in the coding region of interleukin-13 gene is associated with atopy but not asthma in Chinese children. Clin Exp Allergy 31:1515–1521
Hershey GK, Friedrich MF, Esswein LA, Thomas ML, Chatila TA (1997) The association of atopy with a gain-of-function mutation in the alpha subunit of the interleukin-4 receptor. N Engl J Med 337:1720–1725
Oiso N, Fukai K, Ishii M (2000) Interleukin 4 receptor alpha chain polymorphism Gln551Arg is associated with adult atopic dermatitis in Japan. Br J Dermatol 142:1003–1006
Callard RE, Hamvas R, Chatterton C, Blanco C, Pembrey M, Jones R, Sherriff A, Henderson J (2002) An interaction between the IL-4R alpha gene and infection is associated with atopic eczema in young children. Clin Exp Allergy 32:990–993
Tanaka K, Sugiura H, Uehara M, Hashimoto Y, Donnelly C, Montgomery DS (2001) Lack of association between atopic eczema and the genetic variants of interleukin-4 and the interleukin-4 receptor alpha chain gene: heterogeneity of genetic backgrounds on immunoglobulin E production in atopic eczema patients. Clin Exp Allergy 31:1522–1527
Hackstein H, Hecker M, Kruse S, Bohnert A, Ober C, Deichmann KA, Bein G (2001) A novel polymorphism in the 5′ promoter region of the human interleukin-4 receptor alpha-chain gene is associated with decreased soluble interleukin-4 receptor protein levels. Immunogenetics 53:264–269
Novak N, Kruse S, Kraft S, Geiger E, Kluken H, Fimmers R, Deichmann KA, Bieber T (2002) Dichotomic nature of atopic dermatitis reflected by combined analysis of monocyte immunophenotyping and single nucleotide polymorphisms of the interleukin-4/interleukin-13 receptor gene: the dichotomy of extrinsic and intrinsic atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 119:870–875
Hosomi N, Fukai K, Oiso N, Kato A, Ishii M, Kunimoto H, Nakajima K (2004) Polymorphisms in the promoter of the interleukin-4 receptor alpha chain gene are associated with atopic dermatitis in Japan. J Invest Dermatol 122:843–845
Mitsuyasu H, Izuhara K, Mao XQ, Gao PS, Arinobu Y, Enomoto T, Kawai M, Sasaki S, Dake Y, Hamasaki N et al (1998) Ile50Val variant of IL4R alpha upregulates IgE synthesis and associates with atopic asthma. Nat Genet 19:119–120
Izuhara K, Yanagihara Y, Hamasaki N, Shirakawa T, Hopkin JM (2000) Atopy and the human IL-4 receptor alpha chain. J Allergy Clin Immunol 106:S65–S71
Sandford AJ, Chagani T, Zhu S, Weir TD, Bai TR, Spinelli JJ, Fitzgerald JM, Behbehani NA, Tan WC, Pare PD (2000) Polymorphisms in the IL4, IL4RA, and FCERIB genes and asthma severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 106:135–140
Bottini N, Borgiani P, Otsu A, Saccucci P, Stefanini L, Greco E, Fontana L, Hopkin JM, Mao XQ, Shirakawa T (2002) IL-4 receptor alpha chain genetic polymorphism and total IgE levels in the English population: two-locus haplotypes are more informative than individual SNPs. Clin Genet 61:288–292
Ober C, Leavitt SA, Tsalenko A, Howard TD, Hoki DM, Daniel R, Newman DL, Wu X, Parry R, Lester LA et al (2000) Variation in the interleukin 4-receptor alpha gene confers susceptibility to asthma and atopy in ethnically diverse populations. Am J Hum Genet 66:517–526
Risma KA, Wang N, Andrews RP, Cunningham CM, Ericksen MB, Bernstein JA, Chakraborty R, Hershey GK (2002) V75R576 IL-4 receptor alpha is associated with allergic asthma and enhanced IL-4 receptor function. J Immunol 169:1604–1610
Smith DL, Smith JG, Wong SW, deShazo RD (1995) Netherton’s syndrome: a syndrome of elevated IgE and characteristic skin and hair findings. J Allergy Clin Immunol 95:116–123
Chavanas S, Bodemer C, Rochat A, Hamel-Teillac D, Ali M, Irvine AD, Bonafe JL, Wilkinson J, Taieb A, Barrandon Y et al (2000) Mutations in SPINK5, encoding a serine protease inhibitor, cause Netherton syndrome. Nat Genet 25:141–142
Walley AJ, Chavanas S, Moffatt MF, Esnouf RM, Ubhi B, Lawrence R, Wong K, Abecasis GR, Jones EY, Harper JI et al (2001) Gene polymorphism in Netherton and common atopic disease. Nat Genet 29:175–178
Kato A, Fukai K, Oiso N, Hosomi N, Murakami T, Ishii M (2003) Association of SPINK5 gene polymorphisms with atopic dermatitis in the Japanese population. Br J Dermatol 148:665–669
Nishio Y, Noguchi E, Shibasaki M, Kamioka M, Ichikawa E, Ichikawa K, Umebayashi Y, Otsuka F, Arinami T (2003) Association between polymorphisms in the SPINK5 gene and atopic dermatitis in the Japanese. Genes Immun 4:515–517
Kabesch M, Carr D, Weiland SK, von Mutius E (2004) Association between polymorphisms in serine protease inhibitor, kazal type 5 and asthma phenotypes in a large German population sample. Clin Exp Allergy 34:340–345
Kusunoki T, Okafuji I, Yoshioka T, Saito M, Nishikomori R, Heike T, Sugai M, Shimizu A, Nakahata T (2005) SPINK5 polymorphism is associated with disease severity and food allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 115:636–638
Tanaka K, Roberts MH, Yamamoto N, Sugiura H, Uehara M, Mao XQ, Shirakawa T, Hopkin JM (2002) Genetic variants of the receptors for thromboxane A2 and IL-4 in atopic dermatitis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 292:776–780
Gern JE, Reardon CL, Hoffjan S, Nicolae D, Li Z, Roberg KA, Neaville WA, Carlson-Dakes K, Adler K, Hamilton R et al (2004) Effects of dog ownership and genotype on immune development and atopy in infancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 113:307–314
Cook DN, Pisetsky DS, Schwartz DA (2004) Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of human disease. Nat Immunol 5:975–979
Ahmad-Nejad P, Mrabet-Dahbi S, Breuer K, Klotz M, Werfel T, Herz U, Heeg K, Neumaier M, Renz H (2004) The toll-like receptor 2 R753Q polymorphism defines a subgroup of patients with atopic dermatitis having severe phenotype. J Allergy Clin Immunol 113:565–567
Baldini M, Vercelli D, Martinez FD (2002) CD14: an example of gene by environment interaction in allergic disease. Allergy 57:188–192
Colilla S, Nicolae D, Pluzhnikov A, Blumenthal MN, Beaty TH, Bleecker ER, Lange EM, Rich SS, Meyers DA, Ober C et al (2003) Evidence for gene–environment interactions in a linkage study of asthma and smoking exposure. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111:840–846
Howard TD, Koppelman GH, Xu J, Zheng SL, Postma DS, Meyers DA, Bleecker ER (2002) Gene–gene interaction in asthma: IL4RA and IL13 in a Dutch population with asthma. Am J Hum Genet 70:230–236
Israel E, Chinchilli VM, Ford JG, Boushey HA, Cherniack R, Craig TJ, Deykin A, Fagan JK, Fahy JV, Fish J et al (2004) Use of regularly scheduled albuterol treatment in asthma: genotype-stratified, randomised, placebo-controlled cross-over trial. Lancet 364:1505–1512
Nishio Y, Noguchi E, Ito S, Ichikawa E, Umebayashi Y, Otsuka F, Arinami T (2001) Mutation and association analysis of the interferon regulatory factor 2 gene (IRF2) with atopic dermatitis. J Hum Genet 46:664–667
Rafatpanah H, Bennett E, Pravica V, McCoy MJ, David TJ, Hutchinson IV, Arkwright PD (2003) Association between novel GM-CSF gene polymorphisms and the frequency and severity of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:593–598
He JQ, Ruan J, Chan-Yeung M, Becker AB, Dimich-Ward H, Pare PD, Sandford AJ (2003) Polymorphisms of the GM-CSF genes and the development of atopic diseases in at-risk children. Chest 123:438S
Kawashima T, Noguchi E, Arinami T, Yamakawa-Kobayashi K, Nakagawa H, Otsuka F, Hamaguchi H (1998) Linkage and association of an interleukin 4 gene polymorphism with atopic dermatitis in Japanese families. J Med Genet 35:502–504
Elliott K, Fitzpatrick E, Hill D, Brown J, Adams S, Chee P, Stewart G, Fulcher D, Tang M, Kemp A et al (2001) The −590C/T and −34C/T interleukin-4 promoter polymorphisms are not associated with atopic eczema in childhood. J Allergy Clin Immunol 108:285–287
Yamamoto N, Sugiura H, Tanaka K, Uehara M (2003) Heterogeneity of interleukin 5 genetic background in atopic dermatitis patients: significant difference between those with blood eosinophilia and normal eosinophil levels. J Dermatol Sci 33:121–126
Sengler C, Haider A, Sommerfeld C, Lau S, Baldini M, Martinez F, Wahn U, Nickel R (2003) Evaluation of the CD14 C-159 T polymorphism in the German multicenter allergy study cohort. Clin Exp Allergy 33:166–169
Tsunemi Y, Saeki H, Nakamura K, Sekiya T, Hirai K, Fujita H, Asano N, Kishimoto M, Tanida Y, Kakinuma T et al (2002) Interleukin-12 p40 gene (IL12B) 3′-untranslated region polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci 30:161–166
Cox HE, Moffatt MF, Faux JA, Walley AJ, Coleman R, Trembath RC, Cookson WO, Harper JI (1998) Association of atopic dermatitis to the beta subunit of the high affinity immunoglobulin E receptor. Br J Dermatol 138:182–187
Safronova OG, Vavilin VA, Lyapunova AA, Makarova SI, Lyakhovich VV, Kaznacheeva LF, Manankin NA, Batychko OA, Gavalov SM (2003) Relationship between glutathione S-transferase P1 polymorphism and bronchial asthma and atopic dermatitis. Bull Exp Biol Med 136:73–75
Vavilin VA, Safronova OG, Lyapunova AA, Lyakhovich VV, Kaznacheeva LF, Manankin NA, Molokova AV (2003) Interaction of GSTM1, GSTT1, and GSTP1 genotypes in determination of predisposition to atopic dermatitis. Bull Exp Biol Med 136:388–391
Jang N, Stewart G, Jones G (2005) Polymorphisms within the PHF11 gene at chromosome 13q14 are associated with childhood atopic dermatitis. Genes Immun
Mao XQ, Shirakawa T, Yoshikawa T, Yoshikawa K, Kawai M, Sasaki S, Enomoto T, Hashimoto T, Furuyama J, Hopkin JM et al (1996) Association between genetic variants of mast-cell chymase and eczema. Lancet 348:581–583
Mao XQ, Shirakawa T, Enomoto T, Shimazu S, Dake Y, Kitano H, Hagihara A, Hopkin JM (1998) Association between variants of mast cell chymase gene and serum IgE levels in eczema. Hum Hered 48:38–41
Kawashima T, Noguchi E, Arinami T, Kobayashi K, Otsuka F, Hamaguchi H (1998) No evidence for an association between a variant of the mast cell chymase gene and atopic dermatitis based on case-control and haplotype-relative-risk analyses. Hum Hered 48:271–274
Pascale E, Tarani L, Meglio P, Businco L, Battiloro E, Cimino-Reale G, Verna R, D’Ambrosio E (2001) Absence of association between a variant of the mast cell chymase gene and atopic dermatitis in an Italian population. Hum Hered 51:177–179
Iwanaga T, McEuen A, Walls AF, Clough JB, Keith TP, Rorke S, Barton SJ, Holgate ST, Holloway JW (2004) Polymorphism of the mast cell chymase gene (CMA1) promoter region: lack of association with asthma but association with serum total immunoglobulin E levels in adult atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy 34:1037–1042
Kabesch M, Peters W, Carr D, Leupold W, Weiland SK, Von Mutius E (2003) Association between polymorphisms in caspase recruitment domain containing protein 15 and allergy in two German populations. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111:813–817
Nickel RG, Casolaro V, Wahn U, Beyer K, Barnes KC, Plunkett BS, Freidhoff LR, Sengler C, Plitt JR, Schleimer RP et al (2000) Atopic dermatitis is associated with a functional mutation in the promoter of the C–C chemokine RANTES. J Immunol 164:1612–1616
Kozma GT, Falus A, Bojszko A, Krikovszky D, Szabo T, Nagy A, Szalai C (2002) Lack of association between atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome and polymorphisms in the promoter region of RANTES and regulatory region of MCP-1. Allergy 57:160–163
Tsunemi Y, Saeki H, Nakamura K, Sekiya T, Hirai K, Fujita H, Asano N, Tanida Y, Kakinuma T, Wakugawa M et al (2002) Eotaxin gene single nucleotide polymorphisms in the promoter and exon regions are not associated with susceptibility to atopic dermatitis, but two of them in the promoter region are associated with serum IgE levels in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci 29:222–228
Arkwright PD, Chase JM, Babbage S, Pravica V, David TJ, Hutchinson IV (2001) Atopic dermatitis is associated with a low-producer transforming growth factor beta(1) cytokine genotype. J Allergy Clin Immunol 108:281–284
Vasilopoulos Y, Cork MJ, Murphy R, Williams HC, Robinson DA, Duff GW, Ward SJ, Tazi-Ahnini R (2004) Genetic association between an AACC insertion in the 3′ UTR of the stratum corneum chymotryptic enzyme gene and atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 123:62–66
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the “Forschungsförderung der Ruhr-Universität Bochum (FoRUM)”, grant F377-03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffjan, S., Epplen, J.T. The genetics of atopic dermatitis: recent findings and future options. J Mol Med 83, 682–692 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-005-0672-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-005-0672-2