Summary.
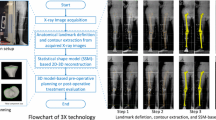
14 human femurs were scanned by CAT and 3D reconstructed. In every specimen digital documentation of CCD and antetorsion (AT) angle was performed. With a special software package (Orthodoc) virtual preoperative planning for implantation of a cementless total hip alloplasty was undertaken. The specimens were randomised into two groups, one of which had manual and the other one robot implantation of the femoral component. After implantation all specimens were evaluated again by CAT and CCT and AT angle were documented again. The preoperative CCD angle was 126.7 ° (SD = 4.0) in the manual group and 127.8 ° (SD = 4.3) in the robodoc group. Postoperatively the angle averaged 131.9 ° (SD = 0.8) in the manual group and 133.2 ° (SD = 1.9) in the robodoc group. Significant differences were found for the AT angle in both groups. The preoperative AT angle in the manual group was 31.3 ° (SD = 8.8), decreasing to 20.5 ° (SD = 9.5) after implantation. In the robodoc group this angle was 30.9 ° (SD = 8.0) before and 31.3 ° (SD = 8.7) after implantation. The difference between pre- and postoperative AT angle averaged 10.8 ° (SD = 6.4) in the manual group and only 0.4 ° (SD = 0.9) in the robodoc-group. Conclusion: With the technique used, preoperative planning in hip alloarthroplasty is much more accurate than with the conventional technique with plain X-ray. The virtual preoperative planning can be transferred to the intraoperative setting with high precision. These factors may lead to an increase in outcome quality.
Zusammenfassung.
Von 14 humanen Femura wurden anhand von CT-Daten dreidimensionale Rekonstruktionen durchgeführt. An jedem Präparat erfolgte die digitale Dokumentation des Centrum-Collum-Diaphysen(CCD)- und Antetorsionswinkels (AT). Mit Hilfe eines speziellen Operationsplanungsprogramms wurde für jeden Femur eine virtuelle Operationsplanung für die Implantation einer zementfreien Hüftendoprothese durchgeführt. Die so ermittelten Endoprothesen wurden – nach randomisierter Zuweisung von je 7 Femura zu den Gruppen standardisiert manuelle bzw. robotergestützte Implantation – eingebracht. Anschließend wurden alle Präparate wiederum computertomographisch erfaßt und unter Verwendung eines artefaktunterdrückenden Algorithmus dreidimensional rekonstruiert. Die präoperativ dokumentierten Parameter wurden anschließend erneut ermittelt. Der Mittelwert der CCD-Winkel betrug präoperativ in der manuellen Gruppe 126,7 ° (SD = 4,0) und in der Robotergruppe 127,8 ° (SD = 4,3). Postoperativ änderte er sich in der 1. Gruppe im Mittel auf 131,9 ° (SD = 0,8) und in der 2. Gruppe auf 133,2 ° (SD = 1,9). Signifikante Unterschiede ergaben sich beim AT-Winkel. Dieser betrug in der manuellen Gruppe präoperativ 31,3 ° (SD = 8,8) und lag postoperativ lediglich noch bei 20,5 ° (SD = 9,5). In der Robotergruppe lag dieser Winkel vor der Implantation bei 30,9 ° (SD = 8,0) und nach der Implantation bei 31,3 ° (SD = 8,7). Die Betragsdifferenz zwischen prä- und postoperativem AT-Winkel betrug in der manuellen Gruppe 10,8 ° (SD = 6,4) und in der Robotergruppe 0,4 ° (SD = 0,9; p = 0,01). Fazit: Mit der verwendeten Technologie ist eine weitaus exaktere Berechnung möglich als mit den bisherigen, allein auf Röntgenbildern basierenden Operationsplanungen. Die virtuelle Operationsplanung läßt sich mit Hilfe von Robotersystemen mit hoher Präzision umsetzen. Die verwendete Technik scheint in der Lage zu sein, eine Verbesserung in der Prozeß- und Ergebnisqualität mit sich zu bringen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jerosch, J., v. Hasselbach, C., Filler, T. et al. Qualitätssteigerung in der präoperativen Planung und intraoperativen Umsetzung durch die Verwendung von computerassistierten Systemen und Operationsrobotern – eine experimentelle Untersuchung. Chirurg 69, 973–976 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001040050524
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001040050524