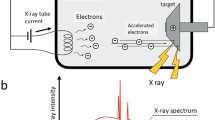
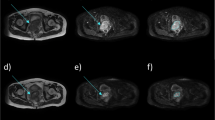
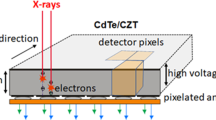
Abstract
Aims and Methods:
Delivery of high radiation doses while simultaneously sparing organs at risk requires advanced imaging for target volume definition, highly conformal dose distributions of intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), and narrow planning target volume (PTV) margins. Three-dimensional image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) with cone-beam computer tomography (CBCT), which results in more precise target localization, is quickly replacing two-dimensional (2D) IGRT. An overview on the clinical applications of kilovoltage gantry-mounted CBCT systems with emphasis on the most frequently targeted body sites (prostate, lung, head and neck) is provided based on a review of the relevant literature. Alternative imaging methods and their advantages/disadvantages are discussed.
Results:
IGRT with soft tissue detection improves set-up accuracy and is currently replacing 2D verification and frame-based stereotactic treatments; safety margins are significantly reduced by this IGRT technology. In addition, systematic changes of tumor volume and shape and of the normal tissue can be monitored allowing for adaptation of radiotherapy. IGRT in combination with conformal treatment planning allows for hypofractionated dose escalation, which results in improved rates of local tumor control with low rates of toxicity.
Conclusion:
CBCT allows for daily pretreatment position verification and online correction of set-up errors which improves the precision of patient repositioning with the possibility of shrinking safety margins, sparing organs at risk, and escalating radiation doses. A trend for better clinical outcome can be observed.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund und Methodik:
Die Verwendung von eskalierten Bestrahlungsdosen bei gleichzeitiger Schonung der Risikoorgane setzt multimodale Bildgebung zur Zielvolumendefinition, hochkonformale Bestrahlungsplanung mittels intensitätsmodulierter Radiotherapie und enge Sicherheitssäume voraus. Bildgeführte Strahlentherapie (IGRT) dient der präzisen Lokalisation des Zielvolumens, und konventionelle 2D Techniken wie Feldkontrollaufnahmen werden aktuell insbesondere durch dreidimensionale Cone-beam-(CBCT-)Technik ersetzt. Dieser Artikel gibt einen Literaturüberblick über den aktuellen Stand der IGRT mittels CBCT. Schwerpunkte sind die praktische Anwendung und klinischen Resultate bei Prostatakarzinom, Bronchialkarzinom und Kopf-Hals-Tumoren. Ergebnisse: Schlussfolgerungen: Schlüsselwörter:
Ergebnisse:
IGRT mittels CBCT ist hocheffektiv zur Verifikation der Patientenpositionierung und insbesondere zur Verifikation der Tumorposition. Rahmenbasierte Stereotaxie kann durch IGRT ersetzt werden, sowohl kraniell als auch extrakraniell. Bei Verwendung von IGRT-Techniken ohne ausreichenden Weichteilkontrast müssen größere Sicherheitssäume verwendet werden, um ein Verfehlen des Zielvolumens zu vermeiden. Zusätzlich sind mittels 3D IGRT systematische Veränderungen von Tumorvolumen, Tumorform und Lagebeziehung zu Risikoorganen darstellbar, was zur Adaption des Bestrahlungsplanes genutzt werden kann. Mittels konformaler IMRT-Bestrahlungstechniken und präziser IGRT konnten hypofraktionierte, eskalierte Bestrahlungsdosen sicher appliziert werden, was in verbesserter lokaler Tumorkontrolle ohne erhöhte Toxizität resultierte.
Schlussfolgerungen:
CBCT ermöglicht die Verifikation der Tumorposition zur Online-Korrektur von Positionsfehlern vor der Behandlung, was die Anwendung von kleinen Sicherheitssäumen, Normalgewebsschonung und Dosiseskalation ermöglicht. Die Verbesserung klinischer Ergebnisse wird durch diese Techniken erwartet und ist z.T. bereits in der Literatur dokumentiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaei P, Ding G, Guan H. Inclusion of the dose from kilovoltage cone beam CT in the radiation therapy treatment plans. Med Phys 2010;37:244–248.
Al-Mamgani A, van Putten WL, Heemsbergen WD et al. Update of Dutch multicenter dose-escalation trial of radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;72:980–988.
Bissonnette JP, Moseley DJ, Jaffray DA. A quality assurance program for image quality of cone-beam CT guidance in radiation therapy. Med Phys 2008;35:1807–1815.
Bhide SA, Davies M, Burke K et al. Weekly volume and dosimetric changes during chemoradiotherapy with intensity-modulated radiation therapy for head and neck cancer: a prospective observational study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2010;76:1360–1368.
Blessing M, Stsepankou D, Wertz H et al. Breath-hold target localization with simultaneous kilovoltage/megavoltage cone-beam computed tomography and fast reconstruction. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;2:201–204.
Blessing M, Stsepankou D, Wertz H et al. Breath-hold target localization with simultaneous kilovoltage/megavoltage cone-beam computed tomography and fast reconstruction. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2010;78:1219–1226.
Boda-Heggemann J, Walter C, Ma, S et al. Frameless stereotactic radiosurgery of a solitary liver metastasis using active breathing control and stereotactic ultrasound. Strahlenther Onkol 2006;182:216–221.
Boda-Heggemann J, Walter C, Rahn A et al. Repositioning accuracy of two different mask systems-3D revisited: comparison using true 3D/3D matching with cone-beam CT. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;66:1568–1575.
Bohrer M, Schroder P, Welzel G et al. Reduced rectal toxicity with ultrasound-based image guided radiotherapy using BAT (B-mode acquisition and targeting system) for prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 2008;184:674–678.
Breneman JC, Steinmetz R, Smith A et al. Frameless image-guided intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery: clinical outcomes for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;74:702–706.
Brock KK, McShan DL, Ten Haken RK et al. Inclusion of organ deformation in dose calculations. Med Phys 2003;30:290–295.
Castadot P, Geets X, Lee JA et al. Assessment by a deformable registration method of the volumetric and positional changes of target volumes and organs at risk in pharyngo-laryngeal tumors treated with concomitant chemo-radiation. Radiother Oncol 2010;95:209–217.
Chao KK, Goldstein NS, Yan D et al. Clinicopathologic analysis of extracapsular extension in prostate cancer: should the clinical target volume be expanded posterolaterally to account for microscopic extension? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;65:999–1007.
Chung HT, Xia P, Chan LW et al. Does image-guided radiotherapy improve toxicity profile in whole pelvic-treated high-risk prostate cancer? Comparison between IG-IMRT and IMRT. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;73:53–60.
de Boer HC, van Os MJ, Jansen PP et al. Application of the No Action Level (NAL) protocol to correct for prostate motion based on electronic portal imaging of implanted markers. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005;61:969–983.
de Crevoisier R, Tucker SL, Dong L et al. Increased risk of biochemical and local failure in patients with distended rectum on the planning CT for prostate cancer radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005;62:965–973.
Dearnaley DP, Hall E, Lawrence D et al. Phase III pilot study of dose escalation using conformal radiotherapy in prostate cancer: PSA control and side effects. Br J Cancer 2005;92:488–498.
Dearnaley DP, Sydes MR, Graham JD et al. Escalated-dose versus standard-dose conformal radiotherapy in prostate cancer: first results from the MRC RT01 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2007;8:475–487.
Den RB, Doemer A, Kubicek G et al. Daily image guidance with cone-beam computed tomography for head-and-neck cancer intensity-modulated radiotherapy: a prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2010;76:1353–1359.
Deurloo KE, Steenbakkers RJ, Zijp LJ et al. Quantification of shape variation of prostate and seminal vesicles during external beam radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005;61:228–238.
Deutschmann H, Steininger P, Nairz O et al. “Augmented reality” in conventional simulation by projection of 3-D structures into 2-D images: a comparison with virtual methods. Strahlenther Onkol 2008;184:93–99.
Dietrich L, Jetter S, Tucking T et al. Linac-integrated 4D cone beam CT: first experimental results. Phys Med Biol 2006;51:2939–2952.
Engels B, Soete G, Verellen D et al. Conformal arc radiotherapy for prostate cancer: increased biochemical failure in patients with distended rectum on the planning computed tomogram despite image guidance by implanted markers. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;74:388–391.
Eccles C, Brock KK, Bissonnette JP et al. Reproducibility of liver position using active breathing coordinator for liver cancer radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;64:751–759.
Fiorino C, Valdagni R, Rancati T et al. Dose-volume effects for normal tissues in external radiotherapy: pelvis. Radiother Oncol 2009;93:153–167.
Fuss M, Salter BJ, Cavanaugh SX, et al. Daily ultrasound-based image-guided targeting for radiotherapy of upper abdominal malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2004;59:1245–1256.
Galerani AP, Grills I, Hugo G et al. Dosimetric impact of online correction via cone-beam CT-based image guidance for stereotactic lung radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2010;78:1571–1578.
Graf R, Boehmer D, Budach V et al. Residual translational and rotational errors after kV X-ray image-guided correction of prostate location using implanted fiducials. Strahlenther Onkol 2010;186:544–550.
Graham SA, Moseley DJ, Siewerdsen JH et al. Compensators for dose and scatter management in cone-beam computed tomography. Med Phys 2007;34:2691–2703.
Grills IS, Hope AJ, Guckenberger M et al. A multinational pooled analysis of 434 cases of stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with volumetrically image-guided (VIGRT) stereotactic lung radiotherapy (SBRT): Results from the Elekta Collaborative Lung Research Group. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2010;28:7015.
Guckenberger M, Baier K, Guenther I, et al. Reliability of the bony anatomy in image-guided stereotactic radiotherapy of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;69:294–301.
Guckenberger M, Krieger T, Richter A, et al. Potential of image-guidance, gating and real-time tracking to improve accuracy in pulmonary stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 2009;91:288–295.
Guckenberger M, Meyer J, Wilbert J et al. Precision of image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) in six degrees of freedom and limitations in clinical practice. Strahlenther Onkol 2007;183:307–313.
Guckenberger M, Meyer J, Wilbert J et al. Cone-beam CT based image-guidance for extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy of intrapulmonary tumors. Acta Oncol 2006;45:897–906.
Guckenberger M, Ok S, Polat B et al. Toxicity after intensity-modulated, image-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 2010;186: 535–543. (Erratum: Strahlenther Onkol: 2010;186:705)
Guckenberger M, Richter A, Wilbert J et al. Cone-beam CT based image-guidance for hypofractionated radiotherapy of intrapulmonary lesions—evaluation of benefits and limitations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;66:154.
Guckenberger M, Wilbert J, Richter A et al. Potential of adaptive radiotherapy to escalate the radiation dose in combined radiochemotherapy for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2011;79:901–908.
Guckenberger M, Wulf J, Mueller G et al. Dose-response relationship for image-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy of pulmonary tumors: relevance of 4D dose calculation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;74:47–54.
Heinzerling JH, Anderson JF, Papiez L et al. Four-dimensional computed tomography scan analysis of tumor and organ motion at varying levels of abdominal compression during stereotactic treatment of lung and liver. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;70:1571–1578.
Islam MK, Purdie TG, Norrlinger BD et al. Patient dose from kilovoltage cone beam computed tomography imaging in radiation therapy. Med Phys 2006;33:1573–1582.
Jaffray DA, Siewerdsen JH, Wong JW et al. Flat-panel cone-beam computed tomography for image-guided radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002;53:1337–1349.
Kashani R, Balter JM, Hayman JA et al. Short-term and long-term reproducibility of lung tumor position using active breathing control (ABC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;65:1553–1559.
Kohler FM, Boda-Heggemann J, Kupper B et al. Phantom measurements to quantify the accuracy of a commercially available cone-beam CT gray-value matching algorithm using multiple Fiducials. Strahlenther Onkol 2009;185:49–55.
Kuban DA, Tucker SL, Dong L et al. Long-term results of the M. D. Anderson randomized dose-escalation trial for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;70:67–74.
Kupelian PA, Willoughby TR, Reddy CA et al. Impact of image guidance on outcomes after external beam radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;70:1146–1150.
Kupelian P, Willoughby T, Mahadevan A et al. Multi-institutional clinical experience with the Calypso System in localization and continuous, real-time monitoring of the prostate gland during external radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;67:1088–1098.
Lagerwaard FJ, Van Sornsen de Koste JR, Nijssen-Visser MR et al. Multiple “slow” CT scans for incorporating lung tumor mobility in radiotherapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2001;51:932–937.
Lamba M, Breneman JC, Warnick RE. Evaluation of image-guided positioning for frameless intracranial radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;74:913–919.
Letourneau D, Martinez AA, Lockman D et al. Assessment of residual error for online cone-beam CT-guided treatment of prostate cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005;62:1239–1246.
Li H, Zhu XR, Zhang L et al. Comparison of 2D radiographic images and 3D cone beam computed tomography for positioning head-and-neck radiotherapy patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;71:916–925.
Liao ZX, Komaki RR, Thames HD Jr. et al. Influence of technologic advances on outcomes in patients with unresectable, locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer receiving concomitant chemoradiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2010;76:775–781.
McNair HA, Brock J, Symonds-Tayler JR et al. Feasibility of the use of the Active Breathing Co ordinator (ABC) in patients receiving radical radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Radiother Oncol 2009;93:424–429.
McNair HA, Hansen VN, Parker CC et al. A comparison of the use of bony anatomy and internal markers for offline verification and an evaluation of the potential benefit of online and offline verification protocols for prostate radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;71:41–50.
Meyer J, Wilbert J, Baier K et al. Positioning accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography in combination with a HexaPOD robot treatment table. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;67:1220–1228.
Moseley DJ, White EA, Wiltshire KL et al. Comparison of localization performance with implanted fiducial markers and cone-beam computed tomography for on-line image-guided radiotherapy of the prostate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;67:942–953.
Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: can SBRT be comparable to surgery? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2010 (in print)
Partridge M, Tree A, Brock J et al. Improvement in tumour control probability with active breathing control and dose escalation: a modelling study. Radiother Oncol 2009;91:325–329.
Polat B, Wilbert J, Baier K et al. Nonrigid patient setup errors in the head-and-neck region. Strahlenther Onkol 2007;183:506–511.
Purdie TG, Bissonnette JP, Franks K et al. Cone-beam computed tomography for on-line image guidance of lung stereotactic radiotherapy: localization, verification, and intrafraction tumor position. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;68:243–252.
Ramakrishna N, Rosca F, Friesen S et al. A clinical comparison of patient setup and intra-fraction motion using frame-based radiosurgery versus a frameless image-guided radiosurgery system for intracranial lesions. Radiother Oncol 2010;95:109–115.
Richter A, Wilbert J, Baier K et al. Feasibility study for markerless tracking of lung tumors in stereotactic body radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2010;78:618–627.
Rowell NP, Williams CJ. Radical radiotherapy for stage I/II non-small cell lung cancer in patients not sufficiently fit for or declining surgery (medically inoperable). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001:CD002935.
Siewerdsen JH, Jaffray DA. Cone-beam computed tomography with a flat-panel imager: magnitude and effects of x-ray scatter. Med Phys 2001;28:220–231.
Sonke JJ, Belderbos J. Adaptive radiotherapy for lung cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol 2010;20:94–106.
Sonke JJ, Lebesque J, van Herk M. Variability of four-dimensional computed tomography patient models. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;70:590–598.
Sonke JJ, Rossi M, Wolthaus J et al. Frameless stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer using four-dimensional cone beam CT guidance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;74:567–574.
Sonke JJ, Zijp L, Remeijer P et al. Respiratory correlated cone beam CT. Medical physics 2005;32:1176–1186.
Smitsmans MH, de Bois J, Sonke JJ et al. Automatic prostate localization on cone-beam CT scans for high precision image-guided radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005;63:975–984.
Smitsmans MH, Pos FJ, de Bois J et al. The influence of a dietary protocol on cone beam CT-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;71:1279–1286.
Sterzing F, Welzel T, Sroka-Perez G et al. Reirradiation of multiple brain metastases with helical tomotherapy. A multifocal simultaneous integrated boost for eight or more lesions. Strahlenther Onkol 2009;185:89–93.
Thilmann C, Nill S, Tucking T et al. Correction of patient positioning errors based on in-line cone beam CTs: clinical implementation and first experiences. Radiat Oncol 2006;1:16.
Thongphiew D, Wu QJ, Lee WR et al. Comparison of online IGRT techniques for prostate IMRT treatment: adaptive vs repositioning correction. Med Phys 2009;36:1651–1662.
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA; 303:1070–1076.
Tsai CL, Wu JK, Wang CW et al. Using cone-beam computed tomography to evaluate the impact of bladder filling status on target position in prostate radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 2009;185:588–595.
Valicenti RK, Michalski JM, Bosch WR et al. Is weekly port filming adequate for verifying patient position in modern radiation therapy? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1994;30:431–438.
van Herk M, Bruce A, Kroes AP et al. Quantification of organ motion during conformal radiotherapy of the prostate by three dimensional image registration. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1995;33:1311–1320.
van Kranen S, van Beek S, Rasch C et al. Setup uncertainties of anatomical sub-regions in head-and-neck cancer patients after offline CBCT guidance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;73:1566–1573.
Walter C, Boda-Heggemann J, Wertz H et al. Phantom and in-vivo measurements of dose exposure by image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT): MV portal images vs. kV portal images vs. cone-beam CT. Radiother Oncol 2007;85:418–423.
Wertz H, Lohr F, Dobler B et al. Dosimetric consequences of a translational isocenter correction based on image guidance for intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) of the prostate. Phys Med Biol 2007;52:5655–5665.
Wertz H, Stsepankou D, Blessing M et al. Fast kilovoltage/megavoltage (kVMV) breathhold cone-beam CT for image-guided radiotherapy of lung cancer. Phys Med Biol 2010;55:4203–4217.
Willner J, Baier K, Caragiani E et al. Dose, volume, and tumor control prediction in primary radiotherapy of non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002;52:382–389.
Wulf J, Hadinger U, Oppitz U et al. Impact of target reproducibility on tumor dose in stereotactic radiotherapy of targets in the lung and liver. Radiother Oncol 2003;66:141–150.
Yan TD, Black D, Bannon PG et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and nonrandomized trials on safety and efficacy of video-assisted thoracic surgery lobectomy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:2553–2562.
Zietman AL, DeSilvio ML, Slater JD et al. Comparison of conventional-dose vs high-dose conformal radiation therapy in clinically localized adenocarcinoma of the prostate: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2005;294:1233–1239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boda-Heggemann, J., Lohr, F., Wenz, F. et al. kV Cone-Beam CT-Based IGRT. Strahlenther Onkol 187, 284–291 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-011-2236-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-011-2236-4