Abstract
Purpose
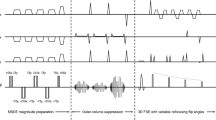
The close proximity of blood vessels to the brachial plexus nerves can confound nerve visualization in conventional fat-suppressed 3D T2-weighted sequences. Vessel suppression can be accomplished by means of motion-sensitizing preparation. The aim of this study was to qualitatively and semi-quantitatively evaluate short tau inversion recovery (STIR) 3D turbo spin echo (TSE) in conjunction with an adiabatic T2 preparation incorporating motion sensitization for magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) of the brachial plexus in a clinical routine setting.
Methods
The MRN of the brachial plexus was performed in 22 patients (age 45.5 ± 20.3 years) with different clinical implications using the proposed improved motion-sensitized driven equilibrium (iMSDE) STIR 3D TSE and the STIR 3D TSE. Images were evaluated regarding image quality, overall artifacts, artifacts caused by vessel signal, signal homogeneity, visibility of small nerves and signal contrast. Furthermore, signal-to-noise ratios (aSNR), nerve muscle contrast to noise ratios (aNMCNR) and nerve vessel contrast to noise ratios (aNVCNR) were calculated and compared.
Results
The incorporation of motion sensitization in the T2 preparation resulted in robust blood suppression across subjects, leading to significantly higher aNVCNRs (p < 0.001) and aNMCNRs (p < 0.05), increased conspicuousness of the nerves, better vessel suppression and image quality and less artifacts compared with STIR 3D TSE (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
The incorporation of the proposed adiabatic iMSDE-based motion sensitization was shown to provide robust blood suppression of vessels in close proximity to brachial plexus nerves. The use of STIR iMSDE 3D TSE can be considered for clinical MRN examinations of the brachial plexus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on management of multifocal motor neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society--first revision. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2010;15:295–301.
Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS.European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of paraproteinemic demyelinating neuropathies. Report of a Joint Task Force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society--first revision. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2010;15:185–95.
Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society--First Revision. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2010;15:1–9.
Gooch CL, Weimer LH. The electrodiagnosis of neuropathy: basic principles and common pitfalls. Neurol Clin. 2007;25:1–28.
Du R, Auguste KI, Chin CT, Engstrom JW, Weinstein PR. Magnetic resonance neurography for the evaluation of peripheral nerve, brachial plexus, and nerve root disorders. J Neurosurg. 2010;112:362–71.
Martinoli C, Gandolfo N, Perez MM, Klauser A, Palmieri F, Padua L, Tagliafico A. Brachial plexus and nerves about the shoulder. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2010;14:523–46.
Tagliafico A, Succio G, Emanuele Neumaier C, Serafini G, Ghidara M, Calabrese M, Martinoli C. MR imaging of the brachial plexus: comparison between 1.5-T and 3‑T MR imaging: preliminary experience. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40:717–24.
Chhabra A, Lee PP, Bizzell C, Soldatos T. 3 tesla MR neurography—technique, interpretation, and pitfalls. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40:1249–60.
Hiwatashi A, Togao O, Yamashita K, Kikuchi K, Ogata H, Yamasaki R, Yoneyama M, Kira JI, Honda H. Evaluation of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: 3D nerve-sheath signal increased with inked rest-tissue rapid acquisition of relaxation enhancement imaging (3D SHINKEI). Eur Radiol. 2017;27:447–53.
Schwarz D, Kele H, Kronlage M, Godel T, Hilgenfeld T, Bendszus M, Bäumer P. Diagnostic value of magnetic resonance neurography in cervical radiculopathy: plexus patterns and peripheral nerve lesions. Invest Radiol. 2018;53:158–66.
Gerevini S, Agosta F, Riva N, Spinelli EG, Pagani E, Caliendo G, Chaabane L, Copetti M, Quattrini A, Comi G, Falini A, Filippi M. MR imaging of brachial plexus and limb-girdle muscles in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Radiology. 2016;279:553–61.
Madhuranthakam AJ, Lenkinski RE. Technical advancements in MR neurography. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2015;19:86–93.
Viallon M, Vargas MI, Jlassi H, Lövblad KO, Delavelle J. High-resolution and functional magnetic resonance imaging of the brachial plexus using an isotropic 3D T2 STIR (Short Term Inversion Recovery) SPACE sequence and diffusion tensor imaging. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:1018–23.
Vargas MI, Viallon M, Nguyen D, Beaulieu JY, Delavelle J, Becker M. New approaches in imaging of the brachial plexus. Eur J Radiol. 2010;74:403–10.
Chhabra A, Thawait GK, Soldatos T, Thakkar RS, Del Grande F, Chalian M, Carrino JA. High-resolution 3T MR neurography of the brachial plexus and its branches, with emphasis on 3D imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:486–97.
Oudeman J, Coolen BF, Mazzoli V, Maas M, Verhamme C, Brink WM, Webb AG, Strijkers GJ, Nederveen AJ. Diffusion-prepared neurography of the brachial plexus with a large field-of-view at 3T. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;43:644–654.
Chhabra A, Zhao L, Carrino JA, Trueblood E, Koceski S, Shteriev F, Lenkinski L, Sinclair CD, Andreisek G. MR neurography: advances. Radiol Res Pract. 2013;2013:809568.
Cervantes B, Kirschke JS, Klupp E, Kooijman H, Börnert P, Haase A, Rummeny EJ, Karampinos DC. Orthogonally combined motion- and diffusion-sensitized driven equilibrium (OC-MDSDE) preparation for vessel signal suppression in 3D turbo spin echo imaging of peripheral nerves in the extremities. Magn Reson Med. 2018;79:407–415.
Kasper JM, Wadhwa V, Scott KM, Rozen S, Xi Y, Chhabra A. SHINKEI—a novel 3D isotropic MR neurography technique: technical advantages over 3DIRTSE-based imaging. Eur Radiol. 2015;25:1672–7.
Yoneyama M, Nakumara M, Okukari T, Tabuchi T, Takemura A, Obara M, Ogura J. High-resolution 3D volumetric nerve-sheath weighted RARE imaging (3D SHINKEI). In: Proceedings of the 19th annual meeting of ISMRM. 2011. p. 2721.
Yoneyama M, Takahara T, Kwee TC, Nakamura M, Tabuchi T. Rapid high resolution MR neurography with a diffusion-weighted pre-pulse. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2013;12:111–9.
Jenista ER, Rehwald WG, Chen EL, Kim HW, Klem I, Parker MA, Kim RJ. Motion and flow insensitive adiabatic T2-preparation module for cardiac MR imaging at 3 Tesla. Magn Reson Med. 2013;70:1360–8.
Nezafat R, Ouwerkerk R, Derbyshire AJ, Stuber M, McVeigh ER. Spectrally selective B1-insensitive T2 magnetization preparation sequence. Magn Reson Med. 2009;61:1326–35.
Weidlich D, Schlaeger S, Kooijman H, Börnert P, Kirschke JS, Rummeny EJ, Haase A, Karampinos DC. T2 mapping with magnetization-prepared 3D TSE based on a modified BIR-4 T2 preparation. NMR Biomed. Epub 2017 Aug 4.
Cervantes B. High-resolution DWI of the lumbar plexus using B1-insensitive velocity-compensated diffusion-prepared 3D TSE. In: Proceedings of the 24th annual meeting of ISMRM. 2016.
Wang X, Harrison C, Mariappan YK, Gopalakrishnan K, Chhabra A, Lenkinski RE, Madhuranthakam AJ. MR neurography of brachial plexus at 3.0 T with robust fat and blood suppression. Radiology. 2017;283:538–46.
Mürtz P, Kaschner M, Lakghomi A, Gieseke J, Willinek WA, Schild HH, Thomas D. Diffusion-weighted MR neurography of the brachial and lumbosacral plexus: 3.0 T versus 1.5 T imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2015;84:696–702.
Funding
The present work was partially supported by Philips Healthcare and the European Union (ERC-StG 2014 iBack).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
E. Klupp, B. Cervantes, N. Sollmann, F. Treibel, D. Weidlich, T. Baum, E.J. Rummeny, C. Zimmer, J.S. Kirschke and D.C. Karampinos declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klupp, E., Cervantes, B., Sollmann, N. et al. Improved Brachial Plexus Visualization Using an Adiabatic iMSDE-Prepared STIR 3D TSE. Clin Neuroradiol 29, 631–638 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-018-0706-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-018-0706-0