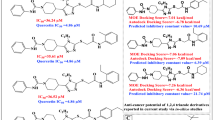
Abstract
Macrocyclic ring structures could have drug-like properties such as membrane permeability, metabolic stability, binding affinity, selectivity, and high-biological activities. Synthesized macrocyclic inhibitors have been studied and the effect of ring size has gained attention from drug design community. Marsault et al. showed a positive correlation between ring size and inhibitory activity against rennin. On the other hand, De Clercq et al. suggested that there would be some optimum ring size for histone deacetylase inhibitory activity. Therefore, macrocyclic effects appear elusive while intriguing. In this study, we have selected a large set of macrocyclic inhibitors (14–20-membered rings) to study macrocyclic effect on MerTK using molecular modeling techniques. We carefully positioned all the cyclic inhibitors into the binding pocket utilizing available information obtained from both experimental and theoretical means. Then, from the resultant binding poses, the ligand–receptor interactions were analyzed. Unlike previous reports, we could not observe any relevance between ring size and inhibitory activity. However, there is a correlation between the number of hydrogen bonds and inhibitory activity. Among these hydrogen-bonding interactions, active site residues Arg727, and Asn728 as well as two signature interactions at the hinge region were found to be crucial for MerTK inhibition. Furthermore, the importance of number of hydrogen bonding was further validated statistically by means of 3D-QSAR techniques such as CoMFA and CoMSIA. The involvement of Arg727 and Asn728 was checked graphically by CoMSIA hydrogen-bonding donor map. This outcome could be helpful for more potent MerTK inhibitor design. In addition, more detailed studies on ring size effect would be desirable to understand macrocyclic effects.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balupuri A, Balasubramanian PK, Cho SJ (2015) Molecular modeling study on Mer kinase inhibitors using 3D-QSAR and docking approaches. Med Chem Res 24:3730–3742
Balupuri A, Balasubramanian PK, Cho SJ (2016) Determination of structural requirements of Mer kinase inhibitors and binding interaction analysis using in silico approaches. Med Chem Res 25:3021–3029
Berthod H, Giessner-Prettre C, Pullman A (1967) Sur les rôles respectifs des électrons σ et π dans les propriétés des dérivés halogénés des molécules conjuguées. application à l'étude de l’uracile et du fluorouracile. Theor Chim Acta 8:212–222
Bridger GJ, Skerlj RT, Thornton D, Padmanabhan S, Martellucci SA, Henson GW, Abrams MJ, Yamamoto N, Vreese KD, Pauwels R, De Clercq E (1995) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of phenylenebis (methylene)-linked bis-tetraazamacrocycles that inhibit HIV replication. Effects of macrocyclic ring size and substituents on the aromatic linker. J Med Chem 38:366–378
Chirico N, Gramatica P (2012) Real external predictivity of QSAR models. Part 2. New intercomparable thresholds for different validation criteria and the need for scatter plot inspection. J Chem Inf Model 52:2044–2058
Clark M, Cramer RD, Van Opdenbosch N (1989) Validation of the general purpose Tripos 5.2 force field. J Comput Chem 10:982–1012
Cramer RD (1993) Partial least squares (PLS): its strengths and limitations. Perspect Drug Discov Des 1:269–278
Cramer RD, Bunce JD, Patterson DE, Frank IE (1988a) Crossvalidation, bootstrapping, and partial least squares compared with multiple regression in conventional QSAR studies. Mol Inform 7:18–25
Cramer RD, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988b) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967
Craven RJ, Xu L, Weiner TM, Fridell YW, Dent GA, Srivastava S, Varnum B, Liu ET, Cance WG (1995) Receptor tyrosine kinases expressed in metastatic colon cancer. Int J Cancer 60:791–797
Cummings CT, Deryckere D, Earp HS, Graham DK (2013) Molecular pathways: MERTK signaling in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19:5275–5280
Del Re G (1958) 812. A simple MO–LCAO method for the calculation of charge distributions in saturated organic molecules. J Chem Soc (Resumed) 4031–4040. https://doi.org/10.1039/JR9580004031
Driggers EM, Hale SP, Lee J, Terrett NK (2008) The exploration of macrocycles for drug discovery—an underexploited structural class. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:608
Eisenberg D, Schwarz E, Komaromy M, Wall R (1984) Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol 179:125–142
Evans AL, Blackburn JW, Taruc K, Kipp A, Dirk BS, Hunt NR, Barr SD, Dikeakos JD, Heit B (2017) Antagonistic coevolution of MER tyrosine kinase expression and function. Mol Biol Evol 34:1613–1628
Gadhe CG, Kothandan G, Cho SJ (2012) Large variation in electrostatic contours upon addition of steric parameters and the effect of charge calculation schemes in CoMFA on mutagenicity of MX analogues. Mol Simul 38:861–871
Gasteiger J, Marsili M (1980) Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 36:3219–3228
Giordanetto F, Kihlberg J (2013) Macrocyclic drugs and clinical candidates: what can medicinal chemists learn from their properties? J Med Chem 57:278–295
Gradillas A, and Perez‐Castells J (2010) Synthesis of Natural Products Containing Macrocycles by Alkene Ring‐Closing Metathesis. Metathesis in Natural Product Synthesis: Strategies, Substrates and Catalysts 149–182. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527629626.ch5
Graham DK, Dawson TL, Mullaney DL, Snodgrass HR, Earp HS (1994) Cloning and mRNA expression analysis of a novel human protooncogene, c-mer. Cell growth & differentiation: the molecular biology journal of the American Association for. Cancer Res 5:647–657
Halgren TA (1999) MMFF VI. MMFF94s option for energy minimization studies. J Comput Chem 20:720–729
Hamzah N, and Tjahjono DA (2016) Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Study, Compound Development, Pharmacophore Feature, and Molecular Docking of Pyrazolo-[3, 4-d]-Pyrimidine Derivatives as Mer Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. Int J Chemtech Res 9:323–337
Hawkins PC (2017) Conformation generation: the state of the art. J Chem Inf Model 57:1747–1756
Hojjat-Farsangi M (2014) Small-molecule inhibitors of the receptor tyrosine kinases: promising tools for targeted cancer therapies. Int J Mol Sci 15:13768–13801
Holland SJ, Pan A, Franci C, Hu Y, Chang B, Li W, Duan M, Torneros A, Yu J, Heckrodt TJ (2010) R428, a selective small molecule inhibitor of Axl kinase, blocks tumor spread and prolongs survival in models of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 70:1544–1554
Holland SJ, Powell MJ, Franci C, Chan EW, Friera AM, Atchison RE, Mclaughlin J, Swift SE, Pali ES, Yam G (2005) Multiple roles for the receptor tyrosine kinase axl in tumor formation. Cancer Res 65:9294–9303
Huey R, Morris GM, Olson AJ, Goodsell DS (2007) A semiempirical free energy force field with charge‐based desolvation. J Comput Chem 28:1145–1152
Jakalian A, Jack DB, Bayly CI (2002) Fast, efficient generation of high‐quality atomic charges. AM1‐BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. J Comput Chem 23:1623–1641
Kamath S, Buolamwini JK (2003) Receptor-guided alignment-based comparative 3D-QSAR studies of benzylidene malonitrile tyrphostins as EGFR and HER-2 kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem 46:4657–4668
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J Med Chem 37:4130–4146
Knubel KH, Pernu BM, Sufit A, Nelson S, Pierce AM, Keating AK (2014) MerTK inhibition is a novel therapeutic approach for glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget 5:1338
Lemke G, Rothlin CV (2008) Immunobiology of the TAM receptors. Nat Rev Immunol 8:327
Li Y-P, Weng X, Ning F-X, Ou J-B, Hou J-Q, Luo H-B, Li D, Huang Z-S, Huang S-L, Gu L-Q (2013) 3D-QSAR studies of azaoxoisoaporphine, oxoaporphine, and oxoisoaporphine derivatives as anti-AChE and anti-AD agents by the CoMFA method. J Mol Graph Model 41:61–67
Liang F, Wan S, Li Z, Xiong X, Yang L, Zhou X, Wu C (2006) Medical applications of macrocyclic polyamines. Curr Med Chem 13:711–727
Linger RM, Keating AK, Earp HS, Graham DK (2008) TAM receptor tyrosine kinases: biologic functions, signaling, and potential therapeutic targeting in human cancer. Adv cancer Res 100:35–83
Madhavan T, Gadhe CG, Kothandan G, Lee K, Cho SJ (2012) Various atomic charge calculation schemes of CoMFA on HIF‐1 inhibitors of moracin analogs. Int J Quantum Chem 112:995–1005
Madsen CM, Clausen MH (2011) Biologically active macrocyclic compounds–from natural products to diversity‐oriented synthesis. Eur J Org Chem 2011:3107–3115
Mallinson J, Collins I (2012) Macrocycles in new drug discovery. Future Med Chem 4:1409–1438
Marsault E, Peterson ML (2011) Macrocycles are great cycles: applications, opportunities, and challenges of synthetic macrocycles in drug discovery. J Med Chem 54:1961–2004
Marsault E, Peterson ML (2017) Practical Medicinal Chemistry with Macrocycles: Design, Synthesis, and Case Studies, John Wiley & Sons. Place. ISBN: 978-1-119-09256-8
Mciver AL, Zhang W, Liu Q, Jiang X, Stashko MA, Nichols J, Miley MJ, Norris‐Drouin J, Machius M, Deryckere D (2017) Discovery of macrocyclic pyrimidines as MerTK‐specific inhibitors. ChemMedChem 12:207–213
Neubauer A, Fiebeler A, Graham DK, O’bryan JP, Schmidt CA, Barckow P, Serke S, Siegert W, Snodgrass HR, Huhn D (1994) Expression of axl, a transforming receptor tyrosine kinase, in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood 84:1931–1941
Nguyen K-QN, Tsou W-I, Calarese DA, Kimani SG, Singh S, Hsieh S, Liu Y, Lu B, Wu Y, Garforth SJ (2014) Overexpression of MERTK receptor tyrosine kinase in epithelial cancer cells drives efferocytosis in a gain-of-function capacity. J Biol Chem 289:25737–25749
Pratim Roy P, Paul S, Mitra I, Roy K (2009) On two novel parameters for validation of predictive QSAR models. Molecules 14:1660–1701
Schlegel J, Sambade MJ, Sather S, Moschos SJ, Tan A-C, Winges A, Deryckere D, Carson CC, Trembath DG, Tentler JJ (2013) MERTK receptor tyrosine kinase is a therapeutic target in melanoma. J Clin Investig 123:2257–2267
Wang X, Liu J, Zhang W, Stashko MA, Nichols J, Miley MJ, Norris-Drouin J, Chen Z, Machius M, Deryckere D (2016) Design and synthesis of novel macrocyclic Mer tyrosine kinase inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett 7:1044–1049
Watts KS, Dalal P, Tebben AJ, Cheney DL, Shelley JC (2014) Macrocycle conformational sampling with MacroModel. J Chem Inf Model 54:2680–2696
Wessjohann LA, Ruijter E, Garcia-Rivera D, Brandt W (2005) What can a chemist learn from nature’s macrocycles?–A brief, conceptual view. Mol Divers 9:171–186
Wold S, Ruhe A, Wold H, Dunn I Wj (1984) The collinearity problem in linear regression. The partial least squares (PLS) approach to generalized inverses. SIAM J Sci Stat Comput 5:735–743
Yu J, Rupasinghe C, Wilson JL, Taylor L, Rahimi N, Mierke D, Polgar P (2015a) Targeting receptor tyrosine kinases and their downstream signaling with cell‐penetrating peptides in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Chem Biol Drug Des 85:586–597
Yu Z, Li X, Ge C, Si H, Cui L, Gao H, Duan Y, Zhai H (2015b) 3D-QSAR modeling and molecular docking study on Mer kinase inhibitors of pyridine-substituted pyrimidines. Mol Divers 19:135–147
Zhou S, Zhou L, Cui R, Tian Y, Li X, You R, Zhong L (2016) Pharmacophore-based 3D-QSAR modeling, virtual screening and molecular docking analysis for the detection of MERTK inhibitors with novel scaffold. Comb Chem high throughput Screen 19:73–96
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant (MRC, 2015-009070) and Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2016RID1AIB01007060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhujbal, S.P., Keretsu, S., Balasubramanian, P.K. et al. Macrocyclic effect on inhibitory activity: a modeling study on MerTK inhibitors. Med Chem Res 28, 1923–1938 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-019-02424-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-019-02424-3