Summary.
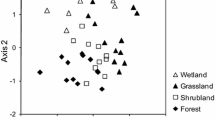
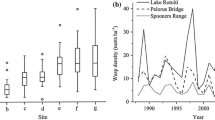
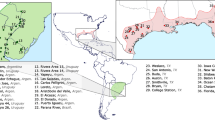
The Argentine ant, Linepithema humile, severely decreases the abundance and diversity of native ant fauna in areas where it invades, but coexists with a more diverse assemblage of ants in its native range. The greater ecological dominance of L. humile in the introduced range may be associated with differences in colony structure and population density in the introduced range relative to the native range. In this study, I compared aspects of L. humile’s colony structure, including density, the spatial pattern of nests and trails, and patterns of intraspecific aggression in parts of the introduced and native ranges. I also compared the number of ant species coexisting with L. humile. Introduced and native populations did not differ significantly in nest density, ant density, nest size, and nearest-neighbor distances. In three of the four study populations in the native range and all of the study populations in the introduced range, colonies were organized into supercolonies: they consisted of multiple, interconnected nests that were dense and spatially clumped, and aggression among conspecifics was rare. In one population in the native range, colonies were organized differently: they occupied single nest sites, nests were sparse and randomly dispersed, and ants from neighboring nests were aggressive toward each other. Species richness was significantly higher in the native range than in the introduced range, even in areas where L. humile formed dense supercolonies. The results suggest that differences in species coexistence between ranges may due to factors other than L. humile’s colony structure. One likely factor is the superior competitive ability of other ant species in the native range.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 23 January 2004; revised 30 March 2004; accepted 20 April 2004.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heller, N.E. Colony structure in introduced and native populations of the invasive Argentine ant, Linepithema humile. Insect. Soc. 51, 378–386 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-004-0770-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-004-0770-0