Abstract
Objective
Previous studies on the relationship between sleep duration and body mass index (BMI) have shown inconsistent results by using estimation strategies within the framework of ordinary least squares (OLS). This study examined the relationship between sleep duration and BMI by using quantile regression to account for the potential heterogeneous effect of sleep duration on BMI in different BMI categories.
Methods
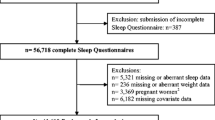
The data of 2,392 adults were from the 2005 Panel Study of Family Dynamics in Taiwan. The dependent variable was BMI of the respondents. Both OLS and quantile regression models were used for comparison.
Results
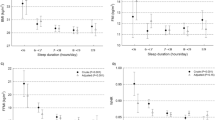
The OLS model does not show significant relationship, while the quantile regression model shows a U-shaped relationship between sleep duration and BMI beyond the 90th percentile in men (BMI = 28.69) and an inverse U-shaped relationship at the 30th percentile of BMI in women (BMI = 21.37).
Conclusions
Quantile regression can provide information that may be masked by OLS in analyzing the relationship between sleep duration and BMI. Sleep modification with the aim to obtain the optimal sleep duration may help to reduce BMI in obese men.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JW, Konz EC, Frederich RC, Wood CL (2001) Long-term weight-loss maintenance: a meta-analysis of US studies. Am J Clin Nutr 74:579–584
Berger KI, Goldring RM, Rapoport DM (2009) Obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 30:253–261
Bjorvatn B, Sagen IM, Oyane N, Waage S, Fetveit A, Pallesen S, Ursin R (2007) The association between sleep duration, body mass index and metabolic measures in the Hordaland Health Study. J Sleep Res 16:66–76
Cappuccio FP, Taggart FM, Kandala NB, Currie A, Peile E, Stranges S, Miller MA (2008) Meta-analysis of short sleep duration and obesity in children and adults. Sleep 31:619–626
Chaput JP, Despres JP, Bouchard C, Tremblay A (2007) Short sleep duration is associated with reduced leptin levels and increased adiposity: results from the Quebec family study. Obesity 15:253–261
Chaput JP, Despres JP, Bouchard C, Tremblay A (2008) The association between sleep duration and weight gain in adults: a 6-year prospective study from the Quebec Family Study. Sleep 31:517–523
Cournot M, Ruidavets JB, Marquie JC, Esquirol Y, Baracat B, Ferrieres J (2004) Environmental factors associated with body mass index in a population of Southern France. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 11:291–297
Department of Health (2010) Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan, Department of Health. http://nahsit.survey.sinica.edu.tw. Accessed 22 Apr 2010
Ezzati M, Martin H, Skjold S, Vander Hoorn S, Murray CJ (2006) Trends in national and state-level obesity in the USA after correction for self-report bias: analysis of health surveys. J R Soc Med 99:250–257
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kuczmarski RJ, Johnson CL (1998) Overweight and obesity in the United States: prevalence and trends, 1960–1994. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 22:39–47
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR (2010) Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA 303:235–241
Fogelholm M, Kronholm E, Kukkonen-Harjula K, Partonen T, Partinen M, Harma M (2007) Sleep-related disturbances and physical inactivity are independently associated with obesity in adults. Int J Obesity 31:1713–1721
Friedman JM (2009) Leptin at 14 y of age: an ongoing story. Am J Clin Nutr 89:973S–979S
Gangwisch JE, Malaspina D, Boden-Albala B, Heymsfield SB (2005) Inadequate sleep as a risk factor for obesity: analyses of the NHANES I. Sleep 28:1289–1296
Guh DP, Zhang W, Bansback N, Amarsi Z, Birmingham CL, Anis AH (2009) The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 9:88
Heslop P, Smith GD, Metcalfe C, Macleod J, Hart C (2002) Sleep duration and mortality: the effect of short or long sleep duration on cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in working men and women. Sleep Med 3:305–314
Knutson KL, Spiegel K, Penev P, Van Cauter E (2007) The metabolic consequences of sleep deprivation. Sleep Med Rev 11:163–178
Koenker R, Bassett G Jr (1978) Regression quantile. Econometrica 46:33–50
Koenker R, Hollack KF (2001) Quantile regression. J Econ Perspect 15:143–156
Kripke DF, Garfinkel L, Wingard DL, Klauber MR, Marler MR (2002) Mortality associated with sleep duration and insomnia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:131–136
Lauderdale DS, Knutson KL, Yan LL, Liu K, Rathouz PJ (2008) Self-reported and measured sleep duration: how similar are they? Epidemiology 19:838–845
Lauderdale DS, Knutson KL, Rathouz PJ, Yan LL, Hulley SB, Liu K (2009) Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between objectively measured sleep duration and body mass index: the CARDIA Sleep Study. Am J Epidemiol 170:805–813
Leicester A, Windmeijer F (2004) The ‘fat tax’: economic incentives to reduce obesity. The Institute for Fiscal Studies Briefing Notes BN49. http://www.ifs.org.uk/bns/bn49.pdf. Accessed 10 June 2010
Lin YC, Yen LL, Chen SY, Kao MD, Tzeng MS, Huang PC, Pan WH (2003) Prevalence of overweight and obesity and its associated factors: findings from National Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan, 1993–1996. Prev Med 37:233–241
Lockley SW, Skene DJ, Arendt J (1999) Comparison between subjective and actigraphic measurement of sleep and sleep rhythms. J Sleep Res 8:175–183
Lopez-Garcia E, Faubel R, Leon-Munoz L, Zuluaga MC, Banegas JR, Rodriguez-Artalejo F (2008) Sleep duration, general and abdominal obesity, and weight change among the older adult population of Spain. Am J Clin Nutr 87:310–316
Low S, Chin MC, Deurenberg-Yap M (2009) Review on epidemic of obesity. Ann Acad Med Singapore 38:57–59
McLaren L, Auld MC, Godley J, Still D, Gauvin L (2010) Examining the association between socioeconomic position and body mass index in 1978 and 2005 among Canadian working-age women and men. Int J Public Health 55:193–200
Misra A, Khurana L (2008) Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in developing countries. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:S9–S30
Pan WH, Flegal KM, Chang HY, Yeh WT, Yeh CJ, Lee WC (2004) Body mass index and obesity-related metabolic disorders in Taiwanese and US whites and blacks: implications for definitions of overweight and obesity for Asians. Am J Clin Nutr 79:31–39
Patel SR, Malhotra A, Gottlieb DJ, White DP, Hu FB (2006a) Correlates of long sleep duration. Sleep 29:881–889
Patel SR, Malhotra A, White DP, Gottlieb DJ, Hu FB (2006b) Association between reduced sleep and weight gain in women. Am J Epidemiol 164:947–954
Popkin BM, Gordon-Larsen P (2004) The nutrition transition: worldwide obesity dynamics and their determinants. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28(Suppl 3):S2–S9
Prentice AM (2006) The emerging epidemic of obesity in developing countries. Int J Epidemiol 35:93–99
Raymond SU, Leeder S, Greenberg HM (2006) Obesity and cardiovascular disease in developing countries: a growing problem and an economic threat. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 9:111–116
Shankar B (2010) Obesity in China: the differential impacts of covariates along the BMI distribution. Obesity 18:1660–1666
Stifel DC, Averett SL (2009) Childhood overweight in the United States: a quantile regression approach. Econ Hum Biol 7:387–397
St-Onge MP, Perumean-Chaney S, Desmond R, Lewis CE, Yan LL, Person SD, Allison DB (2010) Gender differences in the association between sleep duration and body composition: the Cardia Study. Int J Endocrinol. doi:10.1155/2010/726071
Stranges S, Cappuccio FP, Kandala NB, Miller MA, Taggart FM, Kumari M, Ferrie JE, Shipley MJ, Brunner EJ, Marmot MG (2008) Cross-sectional versus prospective associations of sleep duration with changes in relative weight and body fat distribution: the Whitehall II Study. Am J Epidemiol 167:321–329
Vgontzas AN (2008) Does obesity play a major role in the pathogenesis of sleep apnoea and its associated manifestations via inflammation, visceral adiposity, and insulin resistance? Arch Physiol Biochem 114:211–223
Vgontzas AN, Bixler EO, Chrousos GP, Pejovic S (2008) Obesity and sleep disturbances: meaningful sub-typing of obesity. Arch Physiol Biochem 114:224–236
Wen CP, David Cheng TY, Tsai SP, Chan HT, Hsu HL, Hsu CC, Eriksen MP (2009) Are Asians at greater mortality risks for being overweight than Caucasians? Redefining obesity for Asians. Public Health Nutr 12:497–506
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CM., Chang, CK. & Yeh, CY. A quantile regression approach to re-investigate the relationship between sleep duration and body mass index in Taiwan. Int J Public Health 57, 485–493 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-011-0239-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-011-0239-7