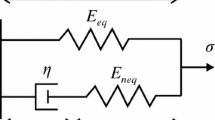
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to develop a new unified class of 3D nonlinear anisotropic finite deformation inelasticity model that (1) exhibits rate-independent or dependent hysteretic response (i.e., response wherein reversal of the external stimuli does not cause reversal of the path in state space) with or without yield surfaces. The hysteresis persists with quasistatic loading. (2) Encompasses a wide range of different types of inelasticity models (such as Mullins effect in rubber, rock and soil mechanics, traditional metal plasticity, hysteretic behavior of shape memory materials) into a simple unified framework that is relatively easy to implement in computational schemes and (3) does not require any a priori particular notion of plastic strain or yield function. The core idea behind the approach is the development of an system of implicit rate equations that allow for the continuity of the response but with different rates along different directions. The theory, which is in purely mechanical setting, subsumes and generalizes many commonly used approaches for hypoelasticity and rate-independent plasticity. We illustrate its capability by modeling the Mullins effect which is the inelastic behavior of certain rubbery materials. We are able to simulate the entire cyclic response without the use of additional internal variables, i.e., the entire response is modeled by using an implicit function of stress and strain measures and their rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saito, T., Furuta, T., Hwang, J.H., Kuramoto, S., Nishino, K., Suzuki, N., Chen, R., Yamada, A., Ito, K., Seno, Y., et al.: Multi functional titanium alloy “gum metal”. In: Materials Science Forum, vol. 426. Trans Tech Publ, pp. 681–688 (2003)
Li T., Morris J. Jr., Nagasako N., Kuramoto S., Chrzan D.: Ideal engineering alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(10), 105503 (2007)
Tromas C., Villechaise P., Gauthier-Brunet V., Dubois S.: Slip line analysis around nanoindentation imprints in Ti3SnC2: a new insight into plasticity of max-phase materials. Philos. Mag. 91(7-9), 1265–1275 (2011)
Yeh J.-W., Chen S.-K., Lin S.-J., Gan J.-Y., Chin T.-S., Shun T.-T., Tsau C.-H., Chang S.-Y.: Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6(5), 299–303 (2004)
Withey E., Jin M., Minor A., Kuramoto S., Chrzan D., Morris J.: The deformation of gum metal in nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 493(1), 26–32 (2008)
Diani J., Fayolle B., Gilormini P.: A review on the Mullins effect. Eur. Polym. J. 45(3), 601–612 (2009)
Puglisi, G., Saccomandi, G.: Multi-scale modelling of rubber-like materials and soft tissues: an appraisal. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 472(2187), 20160060 (2016)
Rajagopal K., Srinivasa A.: Inelastic response of solids described by implicit constitutive relations with nonlinear small strain elastic response. Int. J. Plast. 71, 1–9 (2015)
Srinivasa A.: On the use of the upper triangular (or QR) decomposition for developing constitutive equations for green-elastic materials. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 60, 1–12 (2012)
Rajagopal K.R.: On implicit constitutive theories. Appl. Math. 48(4), 279–319 (2003)
Rajagopal K., Srinivasa A.: On the response of non-dissipative solids. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 463(2078), 357–367 (2007)
Szabó L., Balla M.: Comparison of some stress rates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 25(3), 279–297 (1989)
Bernstein B.: Hypo-elasticity and elasticity. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 6(1), 89–104 (1960)
Green A.E., Naghdi P.M.: Rate-type constitutive equations and elastic-plastic materials. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 11(7), 725–734 (1973)
Rajagopal K., Srinivasa A.: On the thermomechanics of materials that have multiple natural configurations part i: viscoelasticity and classical plasticity. Z. für Angew. Math. Phys. ZAMP 55(5), 861–893 (2004)
Zienkiewicz O.C., Chan A., Pastor M., Schrefler B., Shiomi T.: Computational Geomechanics. Wiley, Chichester (1999)
Pastor M., Zienkiewicz O., Chan A.: Generalized plasticity and the modelling of soil behaviour. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 14(3), 151–190 (1990)
Thamburaja P., Ekambaram R.: Coupled thermo-mechanical modelling of bulk-metallic glasses: theory, finite-element simulations and experimental verification. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55(6), 1236–1273 (2007)
Ogden, R., Roxburgh, D.: A pseudo–elastic model for the Mullins effect in filled rubber. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, vol. 455. The Royal Society, pp. 2861–2877 (1999)
Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: A constitutive model for the Mullins effect with permanent set in particle-reinforced rubber. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41(7), 1855–1878 (2004)
Rajagopal K.: Remarks on the notion of pressure. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 71, 165–172 (2015)
De Tommasi D., Puglisi G., Saccomandi G.: A micromechanics-based model for the Mullins effect. J. Rheol. (1978-present) 50(4), 495–512 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajagopal, K.R., Srinivasa, A.R. An implicit three-dimensional model for describing the inelastic response of solids undergoing finite deformation. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 67, 86 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-016-0671-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-016-0671-x