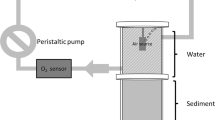
Abstract
Sediment resuspension can affect water quality in lakes and reservoirs. We investigated the effect of sediment resuspension on benthic fluxes of dissolved organic carbon (DOC), metals (Fe, Mn), and nutrients (N, P) in three drinking water reservoirs using sediment core incubations. Measurement of Fe and Mn fluxes, and of microbial potentials to degrade organic substrates (Biolog EcoPlates™) were employed to understand mechanisms regulating DOC exchange after sediment resuspension. Single sediment resuspension events resulted in DOC fluxes [−104 (into sediment) to 46 (release) mmol m−2 event−1] equal to 9–17 days of diffusive fluxes, making them a relevant process. Shallow reservoir sites were more likely to immobilize DOC after resuspension than deep sites. Sediment resuspension under anoxia always led to increases of DOC and metals in the overlying water. Resuspension did not necessarily mobilize nitrate or phosphorus even under anoxia, while ammonium was released after resuspension. Sediment resuspension increased hypolimnetic microbial potentials to utilize organic substrates in both spring and summer. However microbial cells counts and biomass either remained constant or decreased in summer. Adsorption to Fe minerals seemed to play a role in DOC immobilization as evidenced by a decrease in DOC:Fe molar ratios after resuspension in Fe limited sites and constant ratios in Fe rich sites. The results demonstrate a potential for DOC immobilization mainly by Fe minerals and to some extent by benthic microbes. Therefore, sediment resuspension can be beneficial for water quality in low nutrient, iron rich systems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson S, Valeur I, Nilsson I (1994) Influence of lime on soil respiration, leaching of DOC, and C/S relationships in the mor humus of a haplic podsol. Environ Int 20:81–88. doi:10.1016/0160-4120(94)90070-1
Andersson S, Nilsson SI, Saetre P (2000) Leaching of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in mor humus as affected by temperature and pH. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1–10. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00103-0
Björnsen Beratende Ingenieure GmbH (2012) Fortschreibung der Potentialstudie für das Bodesystem Bestandsaufnahme (Updating the potential study for Bode System inventory). In German. Talsperrenbetrieb Sachsen-Anhalt: Anstalt des öffentlichen Rechts, Blankenburg, Koblenz
Bloesch J (1995) Mechanisms, measurement and importance of sediment resuspension in lakes. Mar Freshwater Res 46:295–304. doi:10.1071/MF9950295
Carroll T, King S, Gray SR, Bolto BA, Booker NA (2000) The fouling of microfiltration membranes by NOM after coagulation treatment. Water Res 34:2861–2868. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00051-8
Chen C, Dynes JJ, Wang J, Sparks DL (2014) Properties of Fe-organic matter associations via coprecipitation versus adsorption. Environ Sci Technol 48:13751–13759. doi:10.1021/es503669u
Christian BW, Lind OT (2007) Multiple carbon substrate utilization by bacteria at the sediment-water interface: seasonal patterns in a stratified eutrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia 586:43–56. doi:10.1007/s10750-006-0476-6
Dadi T, Völkner C, Koschorreck M (2015) A sediment core incubation method to measure the flux of dissolved organic carbon between sediment and water. J Soil Sediment 15:2350–2358. doi:10.1007/s11368-015-1213-4
Dadi T, Friese K, Wendt-Potthoff K, Koschorreck M (2016) Benthic dissolved organic carbon fluxes in a drinking water reservoir. Limnol Oceanogr 61:445–459. doi:10.1002/lno.10224
de Vicente I, Cruz-Pizarro L, Rueda FJ (2010) Sediment resuspension in two adjacent shallow coastal lakes: controlling factors and consequences on phosphate dynamics. Aquat Sci 72:21–31. doi:10.1007/s00027-009-0107-1
Ducey TF, Vanotti MB, Shriner AD, Szogi AA, Ellison AQ (2010) Characterization of a microbial community capable of nitrification at cold temperature. Bioresour Technol 101:491–500. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.07.091
Edzwald JK, Tobiason JE (1999) Enhanced coagulation: US requirements and a broader view. Water Sci Technol 40:63–70. doi:10.1016/s0273-1223(99)00641-1
Eikebrokk B, Vogt RD, Liltved H (2004) NOM increase in Northern European source waters: discussion of possible causes and impacts on coagulation/contact filtration processes. Water Sci Technol 4:47–54
Evans CD, Monteith DT, Cooper DM (2005) Long-term increases in surface water dissolved organic carbon: Observations, possible causes and environmental impacts. Environ Pollut 137:55–71. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.12.031
Evans CD et al (2012) Acidity controls on dissolved organic carbon mobility in organic soils. Global Change Biol 18:3317–3331. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2012.02794.x
Fischer J, Krogman R, Quist M (2013) Influences of native and non-native benthivorous fishes on aquatic ecosystem degradation. Hydrobiologia 711:187–199. doi:10.1007/s10750-013-1483-z
Friese K, Schultze M, Boehrer B, Buettner O, Herzsprung P, Koschorreck M, Kuehn B, Roenicke H, Tittel J, Wendt-Potthoff K et al (2014) Ecological response of two hydro-morphological similar pre-dams to contrasting land-use in the Rappbode reservoir system (Germany). Int Rev Hydrobiol 99(5):335–349. doi:10.1002/iroh.201301672
Garstecki T, Wickham SA, Arndt H (2002) Effects of experimental sediment resuspension on a coastal planktonic microbial food web. Estuar Coast Shelf S 55:751–762. doi:10.1006/ecss.2001.0937
Gibson B, Ptacek C, Blowes D, Daugherty S (2015) Sediment resuspension under variable geochemical conditions and implications for contaminant release. J Soil Sediment 15:1644–1656. doi:10.1007/s11368-015-1106-6
Goetz D, Kröger R, Miranda LE (2014) Effects of Smallmouth Buffalo, Ictiobus bubalus biomass on water transparency, nutrients, and productivity in shallow experimental ponds. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92:503–508. doi:10.1007/s00128-014-1231-8
Gough R, Holliman PJ, Heard TR, Freeman C (2014) Dissolved organic carbon and trihalomethane formation potential removal during coagulation of a typical UK upland water with alum, PAX-18 and PIX-322. J Water Supply Res T 63:650–660. doi:10.2166/aqua.2014.007
Gu B, Schmitt J, Chen Z, Liang L, McCarthy JF (1994) Adsorption and desorption of natural organic matter on iron oxide: mechanisms and models. Environ Sci Technol 28:38–46. doi:10.1021/es00050a007
Guggenberger G, Kaiser K, Zech W (1998) Mobilization and immobilization of dissolved organic matter in forest soils. Z Pflanz Bodenkunde 161:401–408. doi:10.1002/jpln.1998.3581610408
Guizien K, Dupuy C, Ory P, Montanie H, Hartmann H, Chatelain M, Karpytchev M (2014) Microorganism dynamics during a rising tide: disentangling effects of resuspension and mixing with offshore waters above an intertidal mudflat. J Marine Syst 129:178–188. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.05.010
Holmroos H, Hietanen S, Niemisto J, Horppila J (2012) Sediment resuspension and denitrification affect the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio of shallow lake waters. Fund Appl Limnol 180:193–205. doi:10.1127/1863-9135/2012/0223
Jiang D, Huang Q, Cai P, Rong X, Chen W (2007) Adsorption of Pseudomonas putida on clay minerals and iron oxide. Colloid Surface B 54:217–221. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.10.030
Jones TG, Evans CD, Jones DL, Hill PW, Freeman C (2015) Transformations in DOC along a source to sea continuum; impacts of photo-degradation, biological processes and mixing. Aquat Sci. doi:10.1007/s00027-015-0461-0
Kalbitz K, Solinger S, Park JH, Michalzik B, Matzner E (2000) Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: a review. Soil Sci 165:277–304. doi:10.1097/00010694-200004000-00001
Kerr JG, Eimers MC (2012) Decreasing soil water Ca2+ reduces DOC adsorption in mineral soils: Implications for long-term DOC trends in an upland forested catchment in southern Ontario, Canada. Sci Total Environ 427–428:298–307. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.016
Koschinsky A, Gaye-Haake B, Arndt C, Maue G, Spitzy A, Winkler A, Halbach P (2001) Experiments on the influence of sediment disturbances on the biogeochemistry of the deep-sea environment. Deep Sea Res Part II 48:3629–3651. doi:10.1016/S0967-0645(01)00060-1
Laskov C, Herzog C, Lewandowski J, Hupfer M (2007) Miniaturized photometrical methods for the rapid analysis of phosphate, ammonium, ferrous iron, and sulfate in porewater of freshwater sediments. Limnol Oceanogr Meth 5:63–71. doi:10.4319/lom.2007.5.63
Liang Y, Liu X, Xiao H, Gao X, Li W, Xiong J (2016) Impact of high water level fluctuations on stable isotopic signature of POM and source identification in a floodplain lake-Bang Lake (Poyang Lake). Environ Earth Sci 75:1–12. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4847-z
Liikanen A, Martikainen PJ (2003) Effect of ammonium and oxygen on methane and nitrous oxide fluxes across sediment–water interface in a eutrophic lake. Chemosphere 52:1287–1293. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00224-8
Lovstedt CB, Bengtsson L (2008) The role of non-prevailing wind direction on resuspension and redistribution of sediments in a shallow lake. Aquat Sci 70:304–313. doi:10.1007/s00027-008-8047-8
May KR (1965) A new graticule for particle counting and sizing. J Sci Instrum 42:500–501. doi:10.1088/0950-7671/42/7/416
Mayer LM (1994) Surface area control of organic carbon accumulation in continental shelf sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:1271–1284. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(94)90381-6
Mc Dowell WM (1985) Kinetics and mechanisms of dissolved organic carbon retention in a headwater stream. Biogeochemistry 1:329–352. doi:10.1007/BF02187376
Meijer ML et al (1994) Long-term responses to fish-stock reduction in small shallow lakes: interpretation of five-year results of four biomanipulation cases in The Netherlands and Denmark. Hydrobiologia 275–276:457–466. doi:10.1007/BF00026734
Morgan B, Rate AW, Burton ED (2012) Water chemistry and nutrient release during the resuspension of FeS-rich sediments in a eutrophic estuarine system. Sci Total Environ 432:47–56. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.065
Müller S, Mitrovic S, Baldwin D (2015) Oxygen and dissolved organic carbon control release of N, P and Fe from the sediments of a shallow, polymictic lake. J Soil Sediment. doi:10.1007/s11368-015-1298-9
Münster U, Einiö P, Nurminen J, Overbeck J (1992) Extracellular enzymes in a polyhumic lake: important regulators in detritus processing. Hydrobiologia 229:225–238. doi:10.1007/BF00007002
Niemistö J, Holmroos H, Pekcan-Hekim Z, Horppila J (2008) Interactions between sediment resuspension and sediment quality decrease the TN:TP ratio in a shallow lake. Limnol Oceanogr 53:2407–2415. doi:10.4319/lo.2008.53.6.2407
Nowlin WH, Evarts JL, Vanni MJ (2005) Release rates and potential fates of nitrogen and phosphorus from sediments in a eutrophic reservoir. Freshw Biol 50:301–322
Paul L (2003) Nutrient elimination in pre-dams: results of long term studies. Hydrobiologia 504:289–295. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008528.34920.b2
Peter S, Isidorova A, Sobek S (2016) Enhanced carbon loss from anoxic lake sediment through diffusion of dissolved organic carbon. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 121:1959–1977. doi:10.1002/2016JG003425.
Pütz K, Benndorf J (1998) The importance of pre-reservoirs for the control of eutrophication of reservoirs. Water Sci Technol 37:317–324. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00039-0
Reddy KR, Fisher MM, Ivanoff D (1996) Resuspension and diffusive flux of nitrogen and phosphorus in a hypereutrophic lake. J Environ Qual 25:363–371. doi:10.2134/jeq1996.00472425002500020022x
Ritzrau W, Graf G (1992) Increase of microbial biomass in the benthic turbidity zone of Kiel Bight after resuspension by a storm event. Limnol Oceanogr 37:1081–1086. doi:10.4319/lo.1992.37.5.1081
Roberts J, Chick A, Oswald L, Thompson P (1995) Effect of carp, Cyprinus carpio L, an exotic benthivorous fish, on aquatic plants and water quality in experimental ponds. Mar Freshw Res 46:1171–1180. doi:10.1071/mf9951171
Rožić M, Cerjan-Stefanović Š, Kurajica S, Vančina V, Hodžić E (2000) Ammoniacal nitrogen removal from water by treatment with clays and zeolites. Water Res 34:3675–3681. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00113-5
Saad OALO, Conrad R (1993) Temperature dependence of nitrification, denitrification, and turnover of nitric oxide in different soils. Biol Fert Soils 15:21–27. doi:10.1007/bf00336283
Scheffer M, Portielje R, Zambrano L (2003) Fish facilitate wave resuspension of sediment. Limnol Oceanogr 48:1920–1926. doi:10.4319/lo.2003.48.5.1920
Simon M, Azam F (1989) Protein content and protein synthesis rates of planktonic marine bacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 51:201–213. doi:10.3354/meps051201
Skoog AC, Arias-Esquivel VA (2009) The effect of induced anoxia and reoxygenation on benthic fluxes of organic carbon, phosphate, iron, and manganese. Sci Total Environ 407:6085–6092. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.08.030
Søndergaard M, Jeppesen E, Mortensen E, Dall E, Kristensen P, Sortkjær O (1990) Phytoplankton biomass reduction after planktivorous fish reduction in a shallow, eutrophic lake: a combined effect of reduced internal P-loading and increased zooplankton grazing. Hydrobiologia 200–201:229–240. doi:10.1007/BF02530342
Søndergaard M, Kristensen P, Jeppesen E (1992) Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind-exposed Lake Arresø, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 228:91–99. doi:10.1007/BF00006480
Søndergaard M, Liboriussen L, Pedersen A, Jeppesen E (2008) Lake restoration by fish removal: short- and long-term effects in 36 Danish lakes. Ecosystems 11:1291–1305. doi:10.1007/s10021-008-9193-5
Stumm W, Morgen JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Tammeorg O, Niemisto J, Mols T, Laugaste R, Panksep K, Kangur K (2013) Wind-induced sediment resuspension as a potential factor sustaining eutrophication in large and shallow Lake Peipsi. Aquat Sci 75:559–570. doi:10.1007/s00027-013-0300-0
Tengberg A, Almroth E, Hall P (2003) Resuspension and its effects on organic carbon recycling and nutrient exchange in coastal sediments: in situ measurements using new experimental technology. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 285–286:119–142. doi:10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00523-3
Tipping E (1981) The adsorption of aquatic humic substances by iron oxides. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:191–199. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(81)90162-9
Wainright SC (1990) Sediment-to-water fluxes of particulate material and microbes by resuspension and their contribution to the planktonic food web. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 62:271–281. doi:10.3354/meps062271
Wendt-Potthoff K, Kloß C, Schultze M, Koschorreck M (2014) Anaerobic metabolism of two hydro-morphological similar pre-dams under contrasting nutrient loading (Rappbode Reservoir System, Germany). Int Rev Hydrobiol 99:350–362. doi:10.1002/iroh.201301673
Wobus A, Bleul C, Maassen S, Scheerer C, Schuppler M, Jacobs E, Röske I (2003) Microbial diversity and functional characterization of sediments from reservoirs of different trophic state. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 46:331–347. doi:10.1016/S0168-6496(03)00249-6
Ziervogel K et al (2016) Enhanced particle fluxes and heterotrophic bacterial activities in Gulf of Mexico bottom waters following storm-induced sediment resuspension. Deep Sea Res Pt II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 129:77–88. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.06.017
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the TALKO project (BMBF 02WT1290A). We thank Corinna Völkner for assisting with field sampling and cell counts, Juliane Schmidt for assistance in the laboratory, and the UFZ GEWANA for sample analysis. We acknowledge the stimulating reviews of Jürg Bloesch and an anonymous reviewer which significantly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dadi, T., Wendt-Potthoff, K. & Koschorreck, M. Sediment resuspension effects on dissolved organic carbon fluxes and microbial metabolic potentials in reservoirs. Aquat Sci 79, 749–764 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-017-0533-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-017-0533-4