Abstract
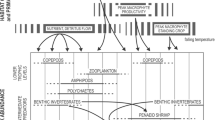
Large differences in δ 2H of primary producers between aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems are used to identify subsidies, discriminate organic matter sources, and reduce uncertainty in food web studies. Previous investigations of hydrogen isotope ratios suggest there may be predictable differences between the δ 2H of water and organic matter for different types of primary producers. We define the difference in the net isotopic discrimination between water and bulk organic matter (om) as: ΔH = (δ 2Hom − δ 2Hwater) ÷ (1 + δ 2Hwater ÷ 1,000). We summarized ΔH values from published literature and we measured the δ 2H of water and primary producers in order to compare ΔH among aquatic and terrestrial primary producers. Measurements were made from three water body types (lake, river, coastal lagoon) and their associated watersheds. Although we predicted a large and equivalent net isotopic discrimination for aquatic primary producers, we found considerable variability among groups of aquatic producers. Macroalgae, benthic microalgae, and phytoplankton had more negative ΔH values (i.e. greater isotopic discrimination) than both aquatic macrophytes and terrestrial vegetation. The more positive δ 2Hom and hence lower ΔH of terrestrial vegetation was expected due to relative increases in the heavier isotope, deuterium, during transpiration. However, the more positive values of δ 2Hom and relatively low ΔH in aquatic macrophytes, even submerged species, was unexpected. Marine macroalgae had high variability in δ 2Hom as a group, but low variability within distinct species. Variability among types of primary producers in δ 2Hom and in ΔH should be assessed when hydrogen is used in isotopic studies of food webs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babler AL, Pilanti A, Vanni MJ (2011) Terrestrial support of detritivorous fish populations decreases with watershed size. Ecosphere 2: Article 76
Barbour MM, Roden JS, Farquhar GD, Ehleringer JR (2004) Expressing leaf water and cellulose oxygen isotope ratios as enrichment above source water reveals evidence of a peclet effect. Oecologia 138(3):426–435
Batt RD, Carpenter SR, Cole JJ, Pace ML, Cline TJ, Johnson RA, Seekell DA (2012) Resources supporting the food web of a naturally productive lake. Limnol Oceanogr 57(5):1443–1452
Bowen GJ, Wassenaar LI, Hobson KA (2005) Global application of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes to wildlife forensics. Oecologia 143(3):337–348
Bunn SE, Leigh C, Jardine TD (2013) Diet-tissue fractionation of δ 15N by consumers from streams and rivers. Limnol Oceanogr 58(3):765–773
Caraco N, Bauer JE, Cole JJ, Petsch S, Raymond P (2010) Millennial-aged organic carbon subsidies to a modern river food web. Ecology 91(8):2385–2393
Chesson LA, Podlesak DW, Cerling TE, Ehleringer JR (2009) Evaluating uncertainty in the calculations of non-exchangeable hydrogen fractions within organic materials. Rapid Commun Mass SP 23(9):1275–1280
Cole JJ, Solomon CT (2012) Terrestrial support of zebra mussels and the Hudson River food web: a multi-isotope, bayesian analysis. Limnol Oceanogr 57(6):1802–1815
Cole JJ, Carpenter SR, Kitchell J, Pace ML, Solomon CT, Weidel B (2011) Strong evidence for terrestrial support of zooplankton in small lakes based on stable isotopes of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(5):1975–1980
Cuntz M, Ogee J, Farquhar GD, Peylin P, Cernusak LA (2007) Modelling advection and diffusion of water isotopologues in leaves. Plant Cell Environ 30(8):892–909
Deines P, Wooller MJ, Grey J (2009) Unravelling complexities in benthic food webs using a dual stable isotope (hydrogen and carbon) approach. Freshw Biol 54(11):2243–2251
DeNiro MJ, Epstein S (1981) Isotopic composition of cellulose from aquatic organisms. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45(10):1885–1894
Doucett RR, Marks JC, Blinn DW, Caron M, Hungate BA (2007) Measuring terrestrial subsidies to aquatic food webs using stable isotopes of hydrogen. Ecology 88(6):1587–1592
Emerson SR, Hedges JI (2008) Chemical oceanography and the marine carbon cycle. Cambridge University Press, New York
Epstein S, Yapp CJ, Hall JH (1976) Determination of D–H ratio of non-exchangeable hydrogen in cellulose extracted from aquatic and land plants. Earth Planet Sci Lett 30(2):241–251
Estep MF, Dabrowski H (1980) Tracing food webs with stable hydrogen isotopes. Science 209(4464):1537–1538
Fenton GE, Ritz DA (1989) Spatial variability of 13C:12C and D:H in Ecklonia radiata (C.Ag) J. Agardh (Laminariales). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 28(1):95–101
Finlay JC, Doucett RR, McNeely C (2010) Tracing energy flow in stream food webs using stable isotopes of hydrogen. Freshw Biol 55(5):941–951
Flanagan LB, Comstock JP, Ehleringer JR (1991) Comparison of modeled and observed environmental-influences on the stable oxygen and hydrogen isotope composition of leaf water in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol 96(2):588–596
Fry B (2006) Stable isotope ecology. Springer, New York
Hou J, D’Andrea WJ, Huang Y (2008) Can sedimentary leaf waxes record D/H ratios of continental precipitation? Field, model, and experimental assessments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72(14):3503–3517
Jardine TD, Kidd KA, Cunjak RA (2009) An evaluation of deuterium as a food source tracer in temperate streams of eastern Canada. J N Am Benthol Soc 28(4):885–893
Karlsson J, Berggren M, Ask J, Byström P, Jonsson A, Laudon H, Jansson M (2012) Terrestrial organic matter support of lake food webs: evidence from lake metabolism and stable hydrogen isotopes of consumers. Limnol Oceanogr 57(4):1042–1048
Keeley JE (1998) CAM photosynthesis in submerged aquatic plants. Bot Rev 64(2):121–175
Kendall C, Coplen T (2001) Distribution of oxygen-18 and deuterium in river waters across the US. Hydrol Processes 15(7):1363–1393
Krabbenhoft DP, Webster KE (1995) Transient hydrogeological controls on the chemistry of a seepage lake. Water Resour Res 31(9):2295–2305
Luo YH, Sternberg L (1991) Deuterium heterogeneity in starch and cellulose nitrate of CAM and C3 plants. Phytochemistry 30(4):1095–1098
Luo YH, Sternberg L (1992) Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic fractionation during heterotrophic cellulose synthesis. J Exp Bot 43(246):47–50
Luo YH, Sternberg L, Suda S, Kumazawa S, Mitsui A (1991) Extremely low D/H ratios of photo-produced hydrogen by cyanobacteria. Plant Cell Physiol 32(6):897–900
Macko SA, Estep M, Lee W (1983) Stable hydrogen isotope analysis of food-webs on laboratory and field populations of marine amphipods. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 72(3):243–249
McCutchan J, Lewis W, Kendall C, McGrath C (2003) Variation in trophic shift for stable isotope ratios of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. Oikos 102(2):378–390
Pagano AM, Titus JE (2007) Submersed macrophyte growth at low pH: carbon source influences response to dissolved inorganic carbon enrichment. Freshw Biol 52(12):2412–2420
Peterson BJ, Fry B (1987) Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 18:293–320
Phillips DL, Gregg JW (2001) Uncertainty in source partitioning using stable isotopes. Oecologia 127(2):171–179
Post DM (2002) Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 83(3):703–718
Rascio N (2002) The underwater life of secondarily aquatic plants: some problems and solutions. Crit Rev Plant Sci 21(4):401–427
Riera P, Richard P (1996) Isotopic determination of food sources of Crassostrea gigas along a trophic gradient in the estuarine bay of Marennes-Oleron. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 42(3):347–360
Roden JS, Ehleringer JR (1999) Observations of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in leaf water confirm the Craig–Gordon model under wide-ranging environmental conditions. Plant Physiol 120(4):1165–1173
Roden JS, Lin GG, Ehleringer JR (2000) A mechanistic model for interpretation of hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in tree-ring cellulose. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64(1):21–35
Sachse D, Billaut I, Bowen GJ, Chikaraishi Y, Dawson TE, Feakins SJ, Freeman KH, Magill CR, McInerney FA, van der Meer MTJ, Polissar P, Robins RJ, Sachs JP, Schmidt H-L, Sessions AL, White JWC, West JB, Kahmen A (2012) Molecular paleo-hydrology: interpreting the hydrogen-isotopic composition of lipid biomarkers from photosynthesizing organisms. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 40:221–249
Sand-Jensen K, Pedersen MF, Nielsen SL (1992) Photosynthetic use of inorganic carbon among primary and secondary water plants in streams. Freshw Biol 27(2):283–293
Schiegl WE, Vogel JC (1970) Deuterium content of organic matter. Earth Planet Sci Lett 7(4):307–313
Sculthorpe CD (1967) The biology of aquatic vascular plants. Edward Arnold, London
Sessions AL (2006) Seasonal changes in D/H fractionation accompanying lipid biosynthesis in Spartina alterniflora. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70(9):2153–2162
Sessions AL, Burgoyne TW, Schimmelmann A, Hayes JM (1999) Fractionation of hydrogen isotopes in lipid biosynthesis. Org Geochem 30(9):1193–1200
Shu Y, Feng X, Posmentier ES, Sonder LJ, Faiia AM, Yakir D (2008) Isotopic studies of leaf water. Part 1: a physically based two-dimensional model for pine needles. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72(21):5175–5188
Smith BN, Epstein S (1970) Biogeochemistry of stable isotopes of hydrogen and carbon in salt marsh biota. Plant Physiol 48(5):738–742
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (2012) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research, 4th edn. W. H. Freeman and Co, New York
Solomon CT, Carpenter SR, Clayton MK, Cole JJ, Coloso JJ, Pace ML, Weidel BC (2011) Terrestrial, benthic, and pelagic resource use in lakes: results from a three-isotope bayesian mixing model. Ecology 92(5):1115–1125
Sternberg L, DeNiro MJ, Johnson HB (1986) Oxygen and hydrogen isotope ratios of water from photosynthetic tissues of CAM and C(3) plants. Plant Physiol 82(2):428–431
Vander Zanden M, Rasmussen J (2001) Variation in delta N-15 and delta C-13 trophic fractionation: implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnol Oceanogr 46(8):2061–2066
Vanderklift MA, Ponsard S (2003) Sources of variation in consumer-diet delta(15)N enrichment: a meta-analysis. Oecologia 136(2):169–182
Wahbeh MI (1997) Amino acid and fatty acid profiles of four species of macroalgae from Aqaba and their suitability for use in fish diets. Aquaculture 159(1–2):101–109
Wassenaar LI, Hobson KA (2003) Comparative equilibration and online technique for determination of non-exchangeable hydrogen of keratins for use in animal migration studies. Isotopes Environ Health Stud 39(3):211–217
Wilkinson GM, Carpenter SR, Cole JJ, Pace ML, Yang C (2013) Terrestrial support of pelagic consumers: patterns and variability revealed by a multi-lake study. Freshw Biol 58(10):2037–2049
Yakir D (1992) Variations in the natural abundance of O-18 and deuterium in plant carbohydrates. Plant Cell Environ 15(9):1005–1020
Yakir D, DeNiro MJ (1990) Oxygen and hydrogen isotope fractionation during cellulose metabolism in Lemna gibba L. Plant Physiol 93(1):325–332
Yakir D, DeNiro MJ, Rundel PW (1989) Isotopic inhomogeneity of leaf water—evidence and implications for the use of isotopic signals transduced by plants. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53(10):2769–2773
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation via grants DEB #0621014, DEB #0917696, DEB#1119739, DEB#1237733. We thank the University of Notre Dame Environmental Research Center for facilitating our work. We graciously acknowledge Grace Wilkinson, Chris Solomon, Heather Malcom, and David Fisher for help with collecting samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hondula, K.L., Pace, M.L., Cole, J.J. et al. Hydrogen isotope discrimination in aquatic primary producers: implications for aquatic food web studies. Aquat Sci 76, 217–229 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-013-0331-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-013-0331-6