Abstract
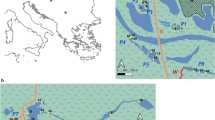
Using data from 31 ponds, we investigated the importance of environmental (e.g. habitat complexity, nutrient content, pH) and biotic factors (i.e. fish predation) on the spatial patterns of planktonic (phytoplankton and zooplankton) and benthic (macroinvertebrates) assemblages. We also evaluated the degree of concordance among assemblages and between the functional and taxonomic composition of assemblages, and test the hypothesis that surrogates of biodiversity (e.g. taxonomic or functional groups) can be used in pond conservation and biomonitoring studies. We found that the spatial patterns of benthic and pelagic assemblages were determined by macrophyte coverage, water quality and, to a lesser extent, fish. However, shifts in the taxonomic and functional composition were not congruent. Moreover, local environmental variation was slightly more important for the taxonomic than the functional composition of assemblages, except for phytoplankton. The degree of concordance among assemblages was also weak, which may be partly due to the fact that species respond individualistically to environmental variation. These findings also suggest that the coupling between benthic and pelagic habitats in flatland ponds is weak, and that the use of surrogate measures or indicator groups in pond conservation studies may not be appropriate.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1989) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 17th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Arndt H (1993) Rotifers as predators on components of the microbial web (Bacteria, Heterotrophic Flagellates, Ciliates)—a review. Hydrobiologia 255:231–246. doi:10.1007/Bf00025844
Barnett A, Beisner BE (2007) Zooplankton biodiversity and lake trophic state: explanations invoking resource abundance and distribution. Ecology 88(7):1675–1686. doi:10.1890/06-1056.1
Barnett AJ, Finlay K, Beisner BE (2007) Functional diversity of crustacean zooplankton communities: towards a trait-based classification. Freshw Biol 52(5):796–813. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2427.2007.01733.X
Bazzanti M, Mastrantuono L, Solimini AG (2012) Selecting macroinvertebrate taxa and metrics to assess eutrophication in different depth zones of Mediterranean lakes. Fundam Appl Limnol 180(2):133–143. doi:10.1127/1863-9135/2012/0200
Beisner BE, Peres PR, Lindstrom ES, Barnett A, Longhi ML (2006) The role of environmental and spatial processes in structuring lake communities from bacteria to fish. Ecology 87(12):2985–2991. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[2985:troeas]2.0.co;2
Burks RL, Jeppesen E, Lodge DM (2001) Littoral zone structures as Daphnia refugia against fish predators. Limnol Oceanogr 46(2):230–237
Burks RL, Lodge DM, Jeppesen E, Lauridsen TL (2002) Diel horizontal migration of zooplankton: costs and benefits of inhabiting the littoral. Freshw Biol 47(3):343–365. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.2002.00824.x
Chapin FS, Shaver GR (1985) Individualistic growth-response of tundra plant-species to environmental manipulations in the field. Ecology 66(2):564–576
Cheruvelil KS, Soranno PA, Madsen JD, Roberson MJ (2002) Plant architecture and epiphytic macroinvertebrate communities: the role of an exotic dissected macrophyte. J N Am Benthol Soc 21(2):261–277. doi:10.2307/1468414
Clarke KR, Ainsworth M (1993) A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 92:205–219
Collinson NH, Biggs J, Corfield A, Hodson MJ, Walker D, Whitfield M, Williams PJ (1995) Temporary and permanent ponds—an assessment of the effects of drying out on the conservation value of aquatic macroinvertebrate communities. Biol Conserv 74(2):125–133. doi:10.1016/0006-3207(95)00021-U
Cottenie K (2005) Integrating environmental and spatial processes in ecological community dynamics. Ecol Lett 8(11):1175–1182. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00820.x
Diehl S (1992) Fish predation and benthic community structure: the role of omnivory and habitat complexity. Ecology 73(5):1646–1661. doi:10.2307/1940017
Dodson SI, Lillie RA, Will-Wolf S (2005) Land use, water chemistry, aquatic vegetation, and zooplankton community structure of shallow lakes. Ecol Appl 15(4):1191–1198. doi:10.1890/04-1494
Dolson R, McCann K, Rooney N, Ridgway M (2009) Lake morphometry predicts the degree of habitat coupling by a mobile predator. Oikos 118(8):1230–1238. doi:10.1111/J.1600-0706.2009.17351.X
Fonseca BM, Bicudo CED (2010) How important can the presence/absence of macrophytes be in determining phytoplankton strategies in two tropical shallow reservoirs with different trophic status? J Plankton Res 32(1):31–46. doi:10.1093/Plankt/Fbp107
Gilinsky E (1984) The role of fish predation and spatial heterogeneity in determining benthic community structure. Ecology 65(2):455–468. doi:10.2307/1941408
Hansson LA, Nicolle A, Brodersen J, Romare P, Nilsson PA, Bronmark C, Skov C (2007) Consequences of fish predation, migration, and juvenile ontogeny on zooplankton spring dynamics. Limnol Oceanogr 52(2):696–706
Havens KE (2008) Cyanobacteria blooms: effects on aquatic ecosystems. Cyanobact Harmful Algal Blooms: State Sci Res Needs 619:733–747
Heino J (2008) Patterns of functional biodiversity and function-environment relationships in lake littoral macroinvertebrates. Limnol Oceanogr 53(4):1446–1455. doi:10.4319/lo.2008.53.4.1446
Heino J (2011) A macroecological perspective of diversity patterns in the freshwater realm. Freshw Biol 56(9):1703–1722. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2011.02610.x
Heino J, Muotka T, Paavola R, Hämäläinen H, Koskenniemi E (2002) Correspondence between Regional Delineations and Spatial Patterns in Macroinvertebrate Assemblages of Boreal Headwater Streams. J N Am Benthol Soc 21(3):397–413. doi:10.2307/1468478
Heino J, Mykra H, Kotanen J, Muotka T (2007) Ecological filters and variability in stream macroinvertebrate communities: do taxonomic and functional structure follow the same path? Ecography 30(2):217–230. doi:10.1111/j.2007.0906-7590.04894.x
Heino J, Tolonen KT, Kotanen J, Paasivirta L (2009) Indicator groups and congruence of assemblage similarity, species richness and environmental relationships in littoral macroinvertebrates. Biodivers Conserv 18(12):3085–3098. doi:10.1007/s10531-009-9626-2
Hoeinghaus DJ, Winemiller KO, Birnbaum JS (2007) Local and regional determinants of stream fish assemblage structure: inferences based on taxonomic vs. functional groups. J Biogeogr 34(2):324–338. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2699.2006.01587.X
Hoffmann MD, Dodson SI (2005) Land use, primary productivity, and lake area as descriptors of zooplankton diversity. Ecology 86(1):255–261. doi:10.1890/03-0833
Jeppesen E, Jensen JP, Jensen C, Faafeng B, Hessen DO, Sondergaard M, Lauridsen T, Brettum P, Christoffersen K (2003) The impact of nutrient state and lake depth on top-down control in the pelagic zone of lakes: a study of 466 lakes from the temperate zone to the arctic. Ecosystems 6(4):313–325. doi:10.1007/S10021-002-0145-1
Johnson RK, Hering D (2010) Spatial congruency of benthic diatom, invertebrate, macrophyte, and fish assemblages in European streams. Ecol Appl 20(4):978–992. doi:10.1890/08-1153.1
Johnson RK, Goedkoop W, Sandin L (2004) Spatial scale and ecological relationships between the macroinvertebrate communities of stony habitats of streams and lakes. Freshw Biol 49(9):1179–1194. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2427.2004.01262.X
Jones JI, Waldron S (2003) Combined stable isotope and gut contents analysis of food webs in plant-dominated, shallow lakes. Freshw Biol 48(8):1396–1407. doi:10.1046/J.1365-2427.2003.01095.X
Kovalenko KE, Thomaz SM, Warfe DM (2012) Habitat complexity: approaches and future directions. Hydrobiologia 685(1):1–17. doi:10.1007/S10750-011-0974-Z
Kruk C, Mazzeo N, Lacerot G, Reynolds CS (2002) Classification schemes for phytoplankton: a local validation of a functional approach to the analysis of species temporal replacement. J Plankton Res 24(9):901–912. doi:10.1093/plankt/24.9.901
Lopes PM, Caliman A, Carneiro LS, Bini LM, Esteves FA, Farjalla V, Bozelli RL (2011) Concordance among assemblages of upland Amazonian lakes and the structuring role of spatial and environmental factors. Ecol Indic 11(5):1171–1176. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2010.12.017
MacArthur R, Wilson EO (1967) The theory of island biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Marklund O, Sandsten H, Hansson LA, Blindow I (2002) Effects of waterfowl and fish on submerged vegetation and macroinvertebrates. Freshw Biol 47(11):2049–2059. doi:10.1046/J.1365-2427.2002.00949.X
McCann KS, Rasmussen JB, Umbanhowar J (2005) The dynamics of spatially coupled food webs. Ecol Lett 8(5):513–523. doi:10.1111/J.1461-0248.2005.00742.X
Meerhoff M, Fosalba C, Bruzzone C, Mazzeo N, Noordoven W, Jeppesen E (2006) An experimental study of habitat choice by Daphnia: plants signal danger more than refuge in subtropical lakes. Freshw Biol 51(7):1320–1330. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2427.2006.01574.X
Meerhoff M, Clemente JM, De Mello FT, Iglesias C, Pedersen AR, Jeppesen E (2007) Can warm climate-related structure of littoral predator assemblies weaken the clear water state in shallow lakes? Glob Change Biol 13(9):1888–1897. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2486.2007.01408.X
Merrit RW, Cummins KW (1984) An introduction to the insects of North America, 2nd edn. Kendall/Hunt, New York
Moss B, Stephen D, Alvarez C, Becares E, Van de Bund W, Collings SE, Van Donk E, De Eyto E, Feldmann T, Fernandez-Alaez C, Fernandez-Alaez M, Franken RJM, Garcia-Criado F, Gross EM, Gyllstrom M, Hansson LA, Irvine K, Jarvalt A, Jensen JP, Jeppesen E, Kairesalo T, Kornijow R, Krause T, Kunnap H, Laas A, Lille E, Lorens B, Luup H, Miracle MR, Noges P, Noges T, Nykanen M, Ott I, Peczula W, Peeters ETHM, Phillips G, Romo S, Russell V, Salujoe J, Scheffer M, Siewertsen K, Smal H, Tesch C, Timm H, Tuvikene L, Tonno I, Virro T, Vicente E, Wilson D (2003) The determination of ecological status in shallow lakes—a tested system (ECOFRAME) for implementation of the European Water Framework Directive. Aquat Conserv-Mar Freshw Ecosyst 13(6):507–549. doi:10.1002/Aqc.592
Mulderij G, Van Nes EH, Van Donk E (2007) Macrophyte-phytoplankton interactions: the relative importance of allelopathy versus other factors. Ecol Model 204(1–2):85–92. doi:10.1016/J.Ecolmodel.2006.12.020
Muylaert K, Perez-Martinez C, Sanchez-Castillo P, Lauridsen TL, Vanderstukken M, Declerck SAJ, Van der Gucht K, Conde-Porcuna JM, Jeppesen E, De Meester L, Vyverman W (2010) Influence of nutrients, submerged macrophytes and zooplankton grazing on phytoplankton biomass and diversity along a latitudinal gradient in Europe. Hydrobiologia 653(1):79–90. doi:10.1007/S10750-010-0345-1
Mykra H, Heino J, Muotka T (2008) Concordance of stream macroinvertebrate assemblage classifications: how general are patterns from single-year surveys? Biol Conserv 141(5):1218–1223. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2008.02.017
Nixdorf B, Deneke R (1997) Why ‘very shallow’ lakes are more successful opposing reduced nutrient loads. Hydrobiologia 342:269–284. doi:10.1023/A:1017012012099
Norlin JI, Bayley SE, Ross LCM (2005) Submerged macrophytes, zooplankton and the predominance of low- over high-chlorophyll states in western boreal, shallow-water wetlands. Freshw Biol 50(5):868–881. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2005.01366.x
Oertli B, Auderset Joye D, Castella E, Juge R, Cambin D, Lachavanne JB (2002) Does size matter? The relationship between pond area and biodiversity. Biol Conserv 104(1):59–70. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(01)00154-9
Oksanen J, Blanchet F, Kindt R, Legendre P, O’Hara R, Simpson G, Stevens M, Wagner H (2011) Vegan: community ecology package. Version 1.17-11
Olden JD (2003) A species-specific approach to modeling biological communities and its potential for conservation. Conserv Biol 17(3):854–863. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.2003.01280.x
Olden JD, Joy MK, Death RG (2006) Rediscovering the species in community-wide predictive modeling. Ecol Appl 16(4):1449–1460. doi:10.1890/1051-0761(2006)016[1449:rtsicp]2.0.co;2
Paavola R, Muotka T, Virtanen R, Heino J, Jackson D, Maki-Petays A (2006) Spatial scale affects community concordance among fishes, benthic macroinvertebrates, and bryophytes in streams. Ecol Appl 16(1):368–379. doi:10.1890/03-5410
Pennak RW (1973) Some evidence for aquatic macrophytes as repellents for a limnetic species of daphnia. Internationale Revue der gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie 58(4):569–576
Pinder LCV (1986) Biology of freshwater Chironomidae. Annu Rev Entomol 31:1–23. doi:10.1146/annurev.en.31.010186.000245
Pinel-Alloul B, Niyonsenga T, Legendre P (1995) Spatial and environmental components of freshwater zooplankton structure. Ecoscience 2(1):1–19
Post DM, Pace ML, Hairston NG (2000) Ecosystem size determines food-chain length in lakes. Nature 405(6790):1047–1049. doi:10.1038/35016565
R Development Core Team (2012) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Reynolds CS, Huszar V, Kruk C, Naselli-Flores L, Melo S (1997) Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J Plankton Res 24:417–428
Rosenzweig ML (1995) Species diversity in space and time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sanders RW, Porter KG, Bennett SJ, Debiase AE (1989) Seasonal patterns of bacterivory by Flagellates, Ciliates, Rotifers, and Cladocerans in a fresh-water planktonic community. Limnol Oceanogr 34(4):673–687
Schriver P, Bogestrand J, Jeppesen E, Sondergaard M (1995) Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish-zooplankton-phytoplankton interactions—large-scale enclosure experiments in a shallow eutrophic lake. Freshw Biol 33(2):255–270. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2427.1995.Tb01166.X
Sinistro R, Izaguirre I, Asikian V (2006) Experimental study on the microbial plankton community in a South American wetland (Lower Parand River Basin) and the effect of the light deficiency due to the floating macrophytes. J Plankton Res 28(8):753–768. doi:10.1093/Plankt/Fbl008
Sondergaard M, Moss B (1998) Impact of submerged macrophytes on phytoplankton in shallow freshwater lakes. Ecol Stu An 131:115–132
Stephen D, Balayla DM, Becares E, Collings SE, Fernandez-Alaez C, Fernandez-Alaez M, Ferriol C, Garcia P, Goma J, Gyllstrom M, Hansson LA, Hietala J, Kairesalo T, Miracle MR, Romo S, Rueda J, Stahl-Delbanco A, Svensson M, Vakkilainen K, Valentin M, Van de Bund WJ, Van Donk E, Vicente E, Villena MJ, Moss B (2004) Continental-scale patterns of nutrient and fish effects on shallow lakes: introduction to a pan-European mesocosm experiment. Freshw Biol 49(12):1517–1524. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2004.01302.x
Tachet H, Richoux P, Bournaud M, Usseglio-Polaterra P (2002) Invertebres d’Eau Douce: Systematique, Biologie, Ecologie. CNRS Editions, Paris
Teixeira-de Mello F, Meerhoff M, Pekcan-Hekim Z, Jeppesen E (2009) Substantial differences in littoral fish community structure and dynamics in subtropical and temperate shallow lakes. Freshw Biol 54(6):1202–1215. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2427.2009.02167.X
Tolonen KT, Hamalainen H, Holopainen IJ, Karjalainen J (2001) Influences of habitat type and environmental variables on littoral macroinvertebrate communities in a large lake system. Arch Hydrobiol 152(1):39–67
Tolonen KT, Holopainen IJ, Hamalainen H, Rahkola-Sorsa M, Ylostalo P, Mikkonen K, Karjalainen J (2005) Littoral species diversity and biomass: concordance among organismal groups and the effects of environmental variables. Biodivers Conserv 14(4):961–980. doi:10.1007/s10531-004-8414-2
Trigal C, Garcia-Criado F, Fernandez-Alaez C (2009) Towards a multimetric index for ecological assessment of Mediterranean flatland ponds: the use of macroinvertebrates as bioindicators. Hydrobiologia 618:109–123. doi:10.1007/s10750-008-9569-8
Utermölh (1958) Zur vervollkommnung der quantative phytoplankton-methodik. Mitteilungen aus Institut Verhein Limnologie 9
Vadeboncoeur Y, Vander Zanden MJ, Lodge DM (2002) Putting the lake back together: reintegrating benthic pathways into lake food web models. Bioscience 52(1):44–54. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2002)052[0044:Ptlbtr]2.0.Co;2
Vakkilainen K, Kairesalo T, Hietala J, Balayla DM, Becares E, Van de Bund WJ, Van Donk E, Fernandez-Alaez M, Gyllstrom M, Hansson LA, Miracle MR, Moss B, Romo S, Rueda J, Stephen D (2004) Response of zooplankton to nutrient enrichment and fish in shallow lakes: a pan-European mesocosm experiment. Freshw Biol 49(12):1619–1632. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2004.01300.x
Vanderstukken M, Mazzeo N, Van Colen W, Declerck SAJ, Muylaert K (2011) Biological control of phytoplankton by the subtropical submerged macrophytes Egeria densa and Potamogeton illinoensis: a mesocosm study. Freshw Biol 56(9):1837–1849. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2427.2011.02624.X
Villéger S, Miranda JR, Hernandez DF, Mouillot D (2012) Low functional β-diversity despite high taxonomic β-diversity among tropical estuarine fish communities. PLoS One 7(7):e40679. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040679
Warfe DM, Barmuta LA (2006) Habitat structural complexity mediates food web dynamics in a freshwater macrophyte community. Oecologia 150(1):141–154. doi:10.1007/S00442-006-0505-1
Yates A, Bailey R (2010) Covarying patterns of macroinvertebrate and fish assemblages along natural and human activity gradients: implications for bioassessment. Hydrobiologia 637(1):87–100. doi:10.1007/s10750-009-9987-2
Zankai NP (1991) Feeding of Nauplius Stages of Eudiaptomus-Gracilis on Mixed Plastic Beads. J Plankton Res 13(2):437–453. doi:10.1093/Plankt/13.2.437
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the people involved in the collection and analysis of the samples, especially, Ana Conty, Saúl Blanco, Carlos. R. Villafane, Silvia Trigal and Roxana Calvo. The Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology (REN 2003-03718/HID) and the Regional Government of Castilla y León (LE33/03) gave financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trigal, C., Fernandez-Alaez, C. & Fernandez-Alaez, M. Congruence between functional and taxonomic patterns of benthic and planktonic assemblages in flatland ponds. Aquat Sci 76, 61–72 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-013-0312-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-013-0312-9