Abstract
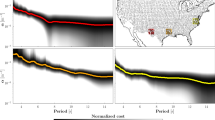
Seismic data are increasingly used to monitor subsurface velocity changes associated with tectonic and environmental processes that occur in different depth sections. To clarify the differences between effects associated with shallow and deep changes of properties, we conduct numerical experiments using simple layered models that include low velocities, low attenuation coefficients and stress-sensitivity of cracked rocks in the shallow crust. We find significant phase-velocity drops in the period range of 5–20 s when large structural changes occur in the top 1–3 km. The apparent velocity changes (δv/v) measured from the first part of the synthetic Rayleigh waves with a cross-correlation based technique show significant velocity drops in the period bands of 5–10 s and 10–20 s that are consistent with reported values of changes at seismogenic depth. The results highlight the importance of accounting for low velocities, attenuation coefficients and stress-sensitivity of parameters in the top 1–3 km in studies aiming to determine the source region of temporal changes. Analyses using different frequency ranges and calculations of apparent delay times over multiple period bands are essential for resolving the depth range of temporal changes of properties. For temporal changes occurring at seismogenic depths, the measured δv/v values at 5–10 s are significantly larger than those of 10–20 s, which are not observed for shallow changes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonilla, L. F., Guéguen, P., Ben-Zion, Y. (2018). Monitoring co-seismic temporal changes of shallow material during strong ground motion with interferometry and autocorrelation, Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, in press.
Brenguier, F., Campillo, M., Takeda, T., Aoki, Y., Shapiro, N. M., Briand, X., et al. (2014). Mapping pressurized volcanic fluids from induced crustal seismic velocity drops. Science, 345, 80–82.
Brenguier, F., Shapiro, N. M., Campillo, M., Ferrazzini, V., Duputel, Z., Coutant, O., et al. (2008). Towards forecasting volcanic eruptions using seismic noise. Nature Geoscience, 1, 126–130. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo104.
Cespedes, I., Huang, Y., Ophir, J., & Spratt, S. (1995). Methods for estimation of sub-sample time delays of digitized echo signals. Ultrasonic Imaging, 17, 142–171.
Chen, H., Ge, H., & Niu, F. (2014). Semiannual velocity variations around the 2008 M w 7.9 Wenchuan Earthquake fault zone revealed by ambient noise and ACROSS active source data. Earthquake Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-014-0089-5.
Cheng, X., Niu, F., & Wang, B. (2010). Coseismic velocity change in the rupture zone of the 2008 M w 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake observed from ambient seismic noise data. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 100, 2539–2550. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120090329.
Froment, B. M., Campillo, M., Chen, J. H., & Liu, Q. Y. (2013). Deformation at depth associated with the 12 May 2008 M w 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake from seismic ambient noise monitoring. Geophysical Research Letters, 40, 78–82. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012GL053995.
Hamiel, Y., Lyakhovsky, V., Stanchits, S., Dresen, G., & Ben-Zion, Y. (2009). Brittle deformation and damage-induced seismic wave anisotropy in rocks. Geophysical Journal International, 178, 901–909. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04200.x.
Hillers, G., Ben-Zion, Y., Campillo, M., & Zigone, D. (2015). Seasonal variations of seismic velocities in the San Jacinto Fault area observed with ambient seismic noise. Geophysical Journal International, 202, 920–932. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggv151.
Karabulut, H., & Bouchon, M. (2007). Spatial variability and non-linearity of strong ground motion near a fault. Geophysical Journal International, 45, 22–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246x.2007.03406.x.
Lecocq, T., Longuevergne, L., Pedersen, H. A., Brenguier, F., & Stammler, K. (2017). Monitoring ground water storage at mesoscale using seismic noise: 30 years of continuous observation and thermo-elastic and hydrological modeling. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14468-9.
Liu, H.-P., Anderson, D. L., & Kanamori, H. (1976). Velocity dispersion due to anelasticity; implications for seismology and mantle composition. Geophysical Journal International, 47(1), 41–58.
Liu, Z., Huang, J., Peng, Z., & Su, J. (2014). Seismic velocity changes in the epicentral region of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake measured from three-component ambient noise correlation techniques. Geophysical Research Letters, 41, 37–42. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL058682.
Lyakhovsky, V., Ben-Zion, Y., & Agnon, A. (1997). Distributed damage, faulting, and friction. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102, 27635–27649.
Meier, U., Shapiro, N. M., & Brenguier, F. (2010). Detecting seasonal variations in seismic velocities within Los Angeles basin from correlations of ambient seismic noise. Geophysical Journal International, 181, 985–996. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04550.x.
Nakata, N., & Snieder, R. (2011). Near-surface weakening in Japan after the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake. Geophysical Research Letters, 38, L17302.
Niu, F., Silver, P., Daley, T., Cheng, X., & Majer, E. (2008). Preseismic velocity changes observed from active source monitoring at the Parkfield SAFOD drill site. Nature, 454, 204–208.
Nur, A., & Simmons, G. (1969). The effect of saturation on velocity in low porosity rocks. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 7, 183–193.
Obermann, A., Froment, B., Campillo, M., Larose, E., Planes, T., Valette, B., et al. (2014). Noise correlations to image structural and mechanical changes associated with the M w 7.9 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Journal of Geophysical Research, 119, 3155–3168.
Obermann, A., Planes, T., Hadziioannou, C., & Campillo, M. (2016). Lapse-time-dependent coda-wave depth sensitivity to local velocity perturbations in 3-d heterogeneous elastic media. Geophysical Journal International, 207, 59–66.
Obermann, A., Planes, T., Hadziioannou, C., & Campillo, M. (2018). 4-D imaging of subsurface changes with coda waves: numerical studies of sensitivity kernels and applications to the M w 7.9, 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, Pure and Applied Geophysics, in press.
Obermann, A., Planes, T., Larose, E., & Sens-Schönfelder, C. (2013). Depth sensitivity of seismic coda waves to velocity perturbations in an elastic heterogeneous medium. Geophysical Journal International, 194, 372–382.
Peng, Z., & Ben-Zion, Y. (2006). Temporal changes of shallow seismic velocity around the Karadere-Duzce branch of the north Anatolian fault and strong ground motion. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 163, 567–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-005-0034-6.
Rivet, D., Campillo, M., Shapiro, N. M., Cruz-Atienza, V., Radiguet, M., Cotte, N., et al. (2011). Seismic evidence of nonlinear crustal deformation during a large slow slip event in Mexico. Geophysical Research Letters, 38, L08308. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL047151.
Roux, P., & Ben-Zion, Y. (2014). Monitoring fault zone environments with correlations of earthquake waveforms. Geophysical Journal International, 196, 1073–1081. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggt441.
Rubinstein, J. L., & Beroza, G. C. (2005). Depth constraints on nonlinear strong ground motion from the 2004 Parkfield earthquake. Geophysical Research Letters, 32, L14313. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL023189.
Sawazaki, K., Sato, H., Nakahara, H., & Nishimura, T. (2009). Time-lapse changes of seismic velocity in the shallow ground caused by strong ground motion shock of the 2000 Western-Tottori Earthquake, Japan, as revealed from coda deconvolution analysis. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99, 352–366.
Schaff, D. P., & Beroza, G. C. (2004). Coseismic and postseismic velocity changes measured by repeating earthquakes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109, B10302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JB003011.
Sens-Schönfelder, C., & Larose, E. (2010). Lunar noise correlation, imaging and monitoring. Earthquake Science, 23, 519–530.
Sens-Schönfelder, C., & Wegler, U. (2006). Passive image interferometry and seasonal variations of seismic velocities at Merapi volcano, Indonesia. Geophysical Research Letters, 33, L21302.
Silver, P. G., Daley, T. M., Niu, F., & Majer, E. L. (2007). Active source monitoring of cross-well seismic travel time for stress-induced changes. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 97, 281–293.
Wegler, U., & Sens-Schönfelder, C. (2007). Fault zone monitoring with passive image interferometry. Geophysical Journal International, 168, 1029–1033.
Wessel, P., Smith, W. H. F., Scharroo, R., Luis, J. F., & Wobbe, F. (2013). Generic mapping tools: improved version released. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 94(45), 409–410. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013EO450001.
Wu, C., Delorey, A., Brenguier, F., Hadziioannou, C., Daub, E. G., & Johnson, P. (2016). Constraining depth range of S wave velocity decrease after large earthquakes near Parkfield, California. Geophysical Research Letters, 43, 6129–6136. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL069145.
Wu, C., Peng, Z., & Ben-Zion, Y. (2009). Non-linearity and temporal changes of fault zone site response associated with strong ground motion. Geophysical Journal International, 176, 265–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.04005.x.
Yamamura, K., Sano, O., Utada, H., Takei, Y., Nakao, S., & Fukao, Y. (2003). Long-term observation of in situ seismic velocity and attenuation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002jb002005.
Zhao, P., & Peng, Z. (2009). Depth extent of damage zones around the central Calaveras fault from waveform analysis of repeating earthquakes. Geophysical Journal International, 179, 1817–1830. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04385.x.
Acknowledgements
All figures are made using the Generic Mapping Tools (www.gmt.soest.hawaii.edu; Wessel et al. 2013). We thank Dr. Anne Obermann and another anonymous reviewer for their constructive comments and suggestions, which significantly improved the quality of this paper. C.Y. and F.N. were supported by NSF (Grant EAR-1251667) and G.L. was funded by NSFc (Grant 41630209). Y.B.Z. acknowledges support by the Wiess visiting professorship program of Rice University and the Department of Energy (award DESC0016520).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Li, G., Niu, F. et al. Significant Effects of Shallow Seismic and Stress Properties on Phase Velocities of Rayleigh Waves Up to 20 s. Pure Appl. Geophys. 176, 1255–1267 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-2075-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-2075-7