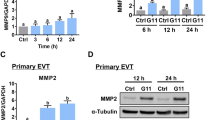
Abstract
Invasiveness is a common feature of trophoblast and tumors; however, while tumor invasion is uncontrolled, trophoblast invasion is strictly regulated. Both trophoblast and tumor cells express high levels of the immunomodulatory progesterone-induced blocking factor (PIBF), therefore, we aimed to test the possibility that PIBF might be involved in invasion. To this aim, we used PIBF-silenced or PIBF-treated trophoblast (HTR8/Svneo, and primary trophoblast) and tumor (HT-1080, A549, HCT116, PC3) cell lines. Silencing of PIBF increased invasiveness as well as MMP-2,-9 secretion of HTR8/SVneo, and decreased those of HT-1080 cells. PIBF induced immediate STAT6 activation in both cell lines. Silencing of IL-4Rα abrogated all the above effects of PIBF, suggesting that invasion-related signaling by PIBF is initiated through the IL-4Rα/PIBF-receptor complex. In HTR-8/SVneo, PIBF induced fast, but transient Akt and ERK phosphorylation, whereas in tumor cells, PIBF triggered sustained Akt, ERK, and late STAT3 activation. The late signaling events might be due to indirect action of PIBF. PIBF induced the expression of EGF and HB-EGF in HT-1080 cells. The STAT3-activating effect of PIBF was reduced in HB-EGF-deficient HT-1080 cells, suggesting that PIBF-induced HB-EGF contributes to late STAT3 activation. PIBF binds to the promoters of IL-6, EGF, and HB-EGF; however, the protein profile of the protein/DNA complex is different in the two cell lines. We conclude that in tumor cells, PIBF induces proteins, which activate invasion signaling, while—based on our previous data—PIBF might control trophoblast invasion by suppressing proinvasive genes.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BME:
-
Basement membrane extract
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFP:
-
Enhanced green fluorescent protein
- Erk:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase
- Fli1:
-
Friend leukemia integration 1
- GPI:
-
Glycophosphatidylinositol
- HB-EGF:
-
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor
- JAK:
-
Janus kinase
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IL-4Rα:
-
Interleukin-4 receptor alpha
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- NK:
-
Natural killer
- PI-3K:
-
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase
- PIBF:
-
Progesterone-induced blocking factor
- PIBFR:
-
PIBF-receptor
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PlGF:
-
Placental growth factor
- sHB-EGF:
-
soluble HB-EGF
- STAT:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription
- SV40:
-
Simian vacuolating virus 40
- Tg:
-
Transgene
- Th:
-
T helper
- TIMP:
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase
References
Seckl MJ, Sebire NJ, Berkowitz RS (2010) Gestational trophoblastic disease. Lancet 376:717–729
Cudihy D, Lee RV (2009) The pathophysiology of pre-eclampsia: current clinical concepts. J Obstet Gynaecol 29:576–582
Knöfler M (2010) Critical growth factors and signalling pathways controlling human trophoblast invasion. Int J Dev Biol 54:269–280
Szekeres-Bartho J, Kilar F, Falkay G, Csernus V, Torok A, Pacsa AS (1985) The mechanism of the inhibitory effect of progesterone on lymphocyte cytotoxicity: I. Progesterone-treated lymphocytes release a substance inhibiting cytotoxicity and prostaglandin synthesis. Am J Reprod Immunol Microbiol 9:15–18
Szekeres-Bartho J, Autran B, Debre P, Andreu G, Denver L, Chaouat G (1989) Immunoregulatory effects of a suppressor factor from healthy pregnant women’s lymphocytes after progesterone induction. Cell Immunol 122:281–294
Kozma N, Halasz M, Palkovics T, Szekeres-Bartho J (2006) The progesterone-induced blocking factor modulates the balance of PKC and intracellular Ca. Am J Reprod Immunol 55:122–129
Kozma N, Halasz M, Polgar B, Poehlmann TG, Markert UR, Palkovics T, Keszei M, Par G, Kiss K, Szeberenyi J, Grama L, Szekeres-Bartho J (2006) Progesterone-induced blocking factor activates STAT6 via binding to a novel IL-4 receptor. J Immunol 176:819–826
Shimonovitz S, Hurwitz A, Hochner-Celnikier D, Dushnik M, Anteby E, Yagel S (1998) Expression of gelatinase B by trophoblast cells: down-regulation by progesterone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 178:457–461
Chen JZ, Wong MH, Brennecke SP, Keogh RJ (2011) The effects of human chorionic gonadotropin, progesterone and oestradiol on trophoblast function. Mol Cell Endocrinol 342:73–80
Anderle C, Hammer A, Polgar B, Hartmann M, Wintersteiger R, Blaschitz A, Dohr G, Desoye G, Szekeres-Bartho J, Sedlmayr P (2008) Human trophoblast cells express the immunomodulator progesterone-induced blocking factor. J Reprod Immunol 79:26–36
Check JH, Nazari P, Check ML, Szekeres-Bartho J, Yuan W (2002) Evidence that the adverse effect of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation on successful pregnancy outcome following embryo transfer may be related to premature trophoblast invasion. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 29:83–86
Lachmann M, Gelbmann D, Kalman E, Polgar B, Buschle M, Von Gabain A, Szekeres-Bartho J, Nagy E (2004) PIBF (progesterone induced blocking factor) is overexpressed in highly proliferating cells and associated with the centrosome. Int J Cancer 112:51–60
Srivastava MD, Thomas A, Srivastava BI, Check JH (2007) Expression and modulation of progesterone induced blocking factor (PIBF) and innate immune factors in human leukemia cell lines by progesterone and mifepristone. Leuk Lymphoma 48:1610–1617
Check JH, Dix E, Sansoucie L (2009) Support for the hypothesis that successful immunotherapy of various cancers can be achieved by inhibiting a progesterone-associated immunomodulatory protein. Med Hypotheses 72:87–90
Rozenblum E, Vahteristo P, Sandberg T, Bergthorsson JT, Syrjakoski K, Weaver D, Haraldsson K, Johannsdottir HK, Vehmanen P, Nigam S, Golberger N, Robbins C, Pak E, Dutra A, Gillander E, Stephan DA, Bailey-Wilson J, Juo SH, Kainu T, Arason A et al (2002) A genomic map of a 6-Mb region at 13q21-q22 implicated in cancer development: identification and characterization of candidate genes. Hum Genet 110:111–121
Kim K, Rhee K (2011) The pericentriolar satellite protein CEP90 is crucial for integrity of the mitotic spindle pole. J Cell Sci 124:338–347
Szekeres-Bartho J, Polgar B (2010) PIBF: the double edged sword. Pregnancy and tumor. Am J Reprod Immunol 64:77–86
Hannan NJ, Paiva P, Dimitriadis E, Salamonsen LA (2009) Models for study of human embryo implantation: choice of cell lines? Biol Reprod 82:235–245
Takao T, Asanoma K, Kato K, Fukushima K, Tsunematsu R, Hirakawa T, Matsumura S, Seki H, Takeda S, Wake N (2011) Isolation and characterization of human trophoblast side-population (SP) cells in primary villous cytotrophoblasts and HTR-8/SVneo cell line. PLoS One 6:e21990
Bilban M, Tauber S, Haslinger P, Pollheimer J, Saleh L, Pehamberger H, Wagner O, Knöfler M (2010) Trophoblast invasion: assessment of cellular models using gene expression signatures. Placenta 31:989–996
Petroff MG, Phillips TA, Ka H, Pace JL, Hunt JS (2006) Isolation and culture of term human trophoblast cells. In: Soares MJ, Hunt JS (eds) Placenta and trophoblast, methods in molecular medicine, vol 1. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 203–217
Polgar B, Kispal G, Lachmann M, Paar C, Nagy E, Csere P, Miko E, Szereday L, Varga P, Szekeres-Bartho J (2003) Molecular cloning and immunologic characterization of a novel cDNA coding for progesterone-induced blocking factor. J Immunol 171:5956–5963
Marques IJ, Weiss FU, Vlecken DH, Nitsche C, Bakkers J, Lagendijk AK, Partecke LI, Heidecke CD, Lerch MM, Bagowski CP (2009) Metastatic behaviour of primary human tumours in a zebrafish xenotransplantation model. BMC Cancer 9:128
La Rocca G, Pucci-Minafra I, Marrazzo A, Taormina P, Minafra S (2004) Zymographic detection and clinical correlations of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in breast cancer sera. Br J Cancer 90:1414–1421
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Carey MF, Peterson CL, Smale ST (2009) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). In: Transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes: concepts, strategies, and techniques AUTHOR: Please double-check this reference-->CSHL Press, Cold Spring Harbour, New York
Mione MC, Trede SN (2010) The zebrafish as a model for cancer. Dis Model Mech 3:517–523
Mason SD, Joyce JA (2011) Proteolytic networks in cancer. Trends Cell Biol 21:228–237
Staun-Ram E, Goldman S, Gabarin D, Shalev E (2004) Expression and importance of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 (MMP-2 and -9) in human trophoblast invasion. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2:59
Carey GB, Semenova E, Qi X, Keegan AD (2007) IL-4 protects the B-cell lymphoma cell line CH31 from anti-IgM-induced growth arrest and apoptosis: contribution of the PI-3 kinase/AKT pathway. Cell Res 17:942–955
So EY, Oh J, Jang JY, Kim JH, Lee CE (2007) Ras/Erk pathway positively regulates Jak1/STAT6 activity and IL-4 gene expression in Jurkat T cells. Mol Immunol 44:3416–3426
Aggarwal BB, Sethi G, Ahn KS, Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Kunnumakkara AB, Sung B, Ichikawa H (2006) Targeting signal-transducer-and-activator-of-transcription-3 for prevention and therapy of cancer: modern target but ancient solution. Ann NY Acad Sci 1091:151–169
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S, Sung B (2009) Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: how intimate is the relationship? Ann NY Acad Sci 1171:59–76
Devarajan E, Huang S (2009) STAT3 as a central regulator of tumor metastases. Curr Mol Med 9:626–633
Xie TX, Wei D, Liu M, Gao AC, Ali-Osman F, Sawaya R, Huang S (2004) Stat3 activation regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tumor invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 23:3550–3560
Waldner MJ, Foersch S, Neurath MF (2012) Interleukin-6: a key regulator of colorectal cancer development. Int J Biol Sci 8:1248–1253
Wu CT, Hsieh CC, Lin CC, Chen WC, Hong JH, Chen MF (2012) Significance of IL-6 in the transition of hormone-resistant prostate cancer and the induction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Mol Med 90:1343–1355
Tu B, Du L, Fan QM, Tang Z, Tang TT (2012) STAT3 activation by IL-6 from mesenchymal stem cells promotes the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett 325:80–88
Ferretti C, Bruni L, Dangles-Marie V, Pecking AP, Bellet D (2007) Molecular circuits shared by placental and cancer cells, and their implications in the proliferative, invasive and migratory capacities of trophoblasts. Hum Reprod Update 13:121–141
Miko E, Halasz M, Jericevic-Mulac B, Wicherek L, Arck P, Arato G, Skret Magierlo J, Rukavina D, Szekeres-Bartho J (2011) Progesterone-induced blocking factor (PIBF) and trophoblast invasiveness. J Reprod Immunol 90:50–57
Halasz M, Polgar B, Kozma N, Berta G, Toth G, Szekeres-Bartho J (2008) Identifying the receptor-binding part of PIBF. Am J Reprod Immunol 60:88
Kim D, Kim S, Koh H, Yoon S, Chung A, Cho KS, Chung J (2001) Akt/PKB promotes cancer cell invasion via increased motility and metalloproteinase production. FASEB J 15:1953–1962
Reddy KB, Nabha SM, Atanaskova N (2003) Role of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:395–403
Soundararajan R, Jagannadha R (2004) Trophoblast “pseudo-tumorigenesis”: significance and contributory factors. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2:15
Yang SY, Miah A, Pabari A, Winslet M (2011) Growth factors and their receptors in cancer metastases. Front Biosci 16:531–538
Qiu Q, Yang M, Tsang BK, Gruslin A (2004) EGF-induced trophoblast secretion of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 involves activation of both PI3K and MAPK signalling pathways. Reproduction 128:355–363
Busch S, Renaud SJ, Schleussner E, Graham CH, Markert UR (2009) mTOR mediates human trophoblast invasion through regulation of matrix-remodeling enzymes and is associated with serine phosphorylation of STAt3. Exp Cell Res 135:1724–1733
Haslinger P, Haider S, Sonderegger S, Otten JV, Pollheimer J, Whitley G, Knofler M (2013) AKT isoforms 1 and 3 regulate basal and epidermal growth factor-stimulated SGHPL-5 trophoblast cell migration in humans. Biol Reprod 88(54):1–11
Ren HB, Jiang ZY, Sun LZ, Fan MS, Zou YF (2011) Effect of epidermal growth factor on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and the signalling pathways involved in the trophoblast cell line JEG-3. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 46:521–526
Fiorelli A, Ricciardi C, Pannone G, Santoro A, Bufo P, Santini M, Serpico R, Rullo R, Pierantoni GM, Domenico M (2011) Interplay between steroid receptors and neoplastic progression in sarcoma tumors. J Cell Physiol 226:2997–3003
Higashiyama S, Iwabuki H, Morimoto C, Hieda M, Inoue H, Matsushita N (2008) Membrane-anchored growth factors, the epidermal growth factor family: beyond receptor ligands. Cancer Sci 99:214–220
Jessmon P, Leach RE, Armant DR (2009) Diverse functions of HBEGF during pregnancy. Mol Reprod Dev 76:1116–1127
Leach RE, Kilburn B, Wang J, Liu Z, Romero R, Armant DR (2004) Heparin binding EGF-like growth factor regulates human extravillous cytotrophoblast development during conversion to the invasive phenotype. Dev Biol 15:223–237
Miyazono K (2012) Ectodomain shedding of HB-EGF: a potential target for cancer therapy. J Biochem 151:1–3
Jessmon P, Kilburn BA, Romero R, Leach RE, Armant DR (2010) Function-specific intracellular signalling pathways downstream of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor utilized by human trophoblasts. Biol Reprod 82:921–929
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–137
Champion H, Innes BA, Robson SC, Lash GE, Bulmer JN (2012) Effects of interleukin-6 on extravillous trophoblast invasion in early human pregnancy. Mol Hum Reprod 18:391–400
Fitzgerald JS, Poehlmann TG, Schleussner E, Markert UR (2008) Trophoblast invasion: the role of intracellular cytokine signalling via signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). Hum Reprod Update 14:335–344
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Charles Graham (Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada L7L 3N6) for the gift of HTR8/SVneo cell line. We also thank Dr. Istvan Magyary (Faculty of Animal Science, Kaposvar University, Kaposvar, Hungary) for the zebrafish strain. This work was supported by the Hungarian National Research Fund (OTKA 77717), the University of Pécs (34039/KA-PostDoc12-03), the Hungarian Ministry of Health (ETT 286/2009), and the Research Team on Innovation (SROP-4.2.2/08/1/2008-0011), TÁMOP-4.2.1/B-10/1-2010-0002, and by TÁMOP-4.2.2.A-11/1/KONV-2012-0053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halasz, M., Polgar, B., Berta, G. et al. Progesterone-induced blocking factor differentially regulates trophoblast and tumor invasion by altering matrix metalloproteinase activity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 4617–4630 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1404-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1404-3