Abstract.
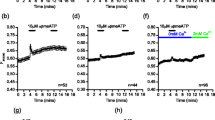
Mast cells play pivotal roles in allergic and inflammatory processes via distinct activation pathways. Mucosal and serosal mast cells are activated by the IgE/FcɛRI pathway, while only serosal mast cells are activated by basic secretagogues. We show that CD47 receptors are expressed on rat peritoneal mast cells. 4N1K, a peptide agonist of CD47, rapidly caused exocytosis. Such exocytosis required increased intracellular calcium and was inhibited by pertussis toxin and an antibody against the βγ dimer of a Gi protein. Cooperation with integrins and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins was necessary, since anti-integrin antibodies and pretreatment with phosphatidylinositol-phospholipase C reduced exocytosis. Depletion of membrane cholesterol inhibited exocytosis and decreased CD47 in lipid rafts, consistent with a CD47/integrin/Gi protein complex being located in rafts. An anti-CD47 antibody inhibited exocytosis induced by 4N1K and by mastoparan and spermine, suggesting that basic secretagogues might target CD47. We propose that 4N1K-stimulated mast cell exocytosis involves a CD47/integrin/Gi protein complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 8 December 2008; received after revision 12 January 2009; accepted 29 January 2009
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sick, E., Niederhoffer, N., Takeda, K. et al. Activation of CD47 receptors causes histamine secretion from mast cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 1271–1282 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-8778-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-8778-2