Abstract.
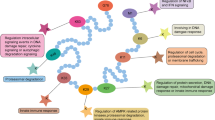
REGγ, a member of the 11S proteasome activators, has been shown to bind and activate the 20S proteasome to promote proteasome-dependent degradation of important regulatory proteins, such as SRC-3 and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21, p16, and p19, in a ubiquitin- and ATP-independent manner. Furthermore, REGγ has been shown to facilitate the turnover of tumor suppressor p53 by promoting MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination. The discovery that REGγ regulates cell-cycle regulators is consistent with previous studies where REGγ-deficient mice have shown retardation in body growth, decreased cell proliferation and increased apoptosis, indicating a potential role of REGγ in cancer development. Additionally, REGγ’s ability to promote viral protein degradation suggests its involvement in viral pathogenesis. This review presents an overview of the function of REGγ, a summary of the current literature, and insight into the possible biological function of REGγ relating to cancer, viral pathogenesis, and other diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Received 25 May 2008; received after revision 06 July 2008; accepted 21 July 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, I., Liu, J., Li, X. et al. REGγ, a proteasome activator and beyond?. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 3971 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8291-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8291-z