Abstract
Background
Recent researches in the field of genetics have extended our knowledge through the discovery of genetic factors associated with autoimmune diseases (AID). Genetics by itself, however, cannot elucidate all the uncertainties encountered in the etiopathology of AID. On the other hand, incomplete harmony in the prevalence of AID in identical twins suggests that non-genetic factors may play an important role in determining the disease susceptibility. Besides, epigenetics, which is defined by changes in gene expression without a corresponding change in the DNA sequences, has come in to provide new awareness in the disease etiopathology by bridging the genetic and epigenetic factors. The recent advances in the field of epigenetics provide a new insight into the understanding of the disease mechanisms, development, diagnostic and prognostic approaches, as well as the various treatment methods.
Purpose
This review paper aims to present an overview of epigenetic modifications involved in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and discuss their important roles in clinical and pharmacological settings, including novel and recent therapeutic applications.
Results
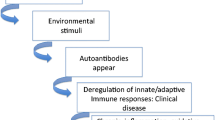
Nowadays, it is believed that autoimmune diseases, such as SLE, begin when genetically susceptible factors associate with environmental triggers. The current therapeutic approaches for SLE treatment have been based on treatments with immunosuppressive drugs, which are linked to various side effects. It is difficult to develop highly effective treatments for SLE patients with minimal or no side effects, mainly due to the disease complexity. The breakthrough of pharmacoepigenetics provides a new approach to solve this problem. Epigenetic modifications can influence the efficacy of drugs by changing the gene expression through modifying chromatin remodeling. In this regard, epigenetic studies in SLE are expected to reveal novel disease biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Conclusions
Accumulating evidence disclosed that epigenetic dysregulations are engaged in SLE pathogenesis and may be exerted as biomarkers to diagnose and as tools to treat these patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waddington CH. Canalization of development and the inheritance of acquired characters. Nature. 1942;150(3811):563–5.
Grolleau-Julius A, Ray D, Yung RL. The role of epigenetics in aging and autoimmunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2010;39(1):42–50.
Brooks WH. X chromosome inactivation and autoimmunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2010;39(1):20–9.
Danchenko N, Satia J, Anthony M. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of worldwide disease burden. Lupus. 2006;15(5):308–18.
Alesaeidi S, Karami J, Mahmoudi M, Akbarian M, Poursani S, Amirzadeh A, et al. Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2) polymorphism in iranian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Inflammation. 2015;38(6):2185–90.
Mahmoudi M, Rezaiemanesh A, Salmaninejad A, Harsini S, Poursani S, Bahrami T, et al. PDCD1 single nucleotide genes polymorphisms confer susceptibility to juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity. 2015;48(7):488–93.
Mirkazemi S, Akbarian M, Jamshidi AR, Mansouri R, Ghoroghi S, Salimi Y, et al. Association of STAT4 rs7574865 with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in Iranian population. Inflammation. 2013;36(6):1548–52.
Tahmasebi Z, Akbarian M, Mirkazemi S, Shahlaee A, Alizadeh Z, Amirzargar AA, et al. Interleukin-1 gene cluster and IL-1 receptor polymorphisms in Iranian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33(10):2591–6.
Xiong W, Lahita RG. Pragmatic approaches to therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(2):97–107.
Eisenberg R. Why can’t we find a new treatment for SLE? J Autoimmun. 2009;32(3):223–30.
Murphy G, Lisnevskaia L, Isenberg D. Systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune rheumatic diseases: challenges to treatment. Lancet. 2013;382(9894):809–18.
Thanou A, Merrill JT. Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: new therapeutic avenues and blind alleys. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(1):23–34.
Zhao S, Long H, Lu Q. Epigenetic perspectives in systemic lupus erythematosus: pathogenesis, biomarkers, and therapeutic potentials. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2010;39(1):3–9.
Selmi C, Lu Q, Humble MC. Heritability versus the role of the environment in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 2012;39(4):249–52.
Germolec D, Kono DH, Pfau JC, Pollard KM. Animal models used to examine the role of the environment in the development of autoimmune disease: findings from an NIEHS Expert Panel Workshop. J Autoimmun. 2012;39(4):285–93.
Ngalamika O, Zhang Y, Yin H, Zhao M, Gershwin ME, Lu Q. Epigenetics, autoimmunity and hematologic malignancies: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2012;39(4):451–65.
Selmi C, Leung PS, Sherr DH, Diaz M, Nyland JF, Monestier M, et al. Mechanisms of environmental influence on human autoimmunity: a national institute of environmental health sciences expert panel workshop. J Autoimmun. 2012;39(4):272–84.
Feng PH. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1108(1):114–20.
Lu Q. The critical importance of epigenetics in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 2013;41:1–5.
Aslani S, Mahmoudi M, Karami J, Jamshidi AR, Malekshahi Z, Nicknam MH. Epigenetic alterations underlying autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity. 2016;49(2):69–83.
Javierre BM, Fernandez AF, Richter J, Al-Shahrour F, Martin-Subero JI, Rodriguez-Ubreva J, et al. Changes in the pattern of DNA methylation associate with twin discordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Genome Res. 2010;20(2):170–9.
Lei W, Luo Y, Lei W, Luo Y, Yan K, Zhao S, et al. Abnormal DNA methylation in CD4+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, and dermatomyositis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2009;38(5):369–74.
Lu Q, Wu A, Tesmer L, Ray D, Yousif N, Richardson B. Demethylation of CD40LG on the inactive X in T cells from women with lupus. J Immunol. 2007;179(9):6352–8.
Zhou Y, Yuan J, Pan Y, Fei Y, Qiu X, Hu N, et al. T cell CD40LG gene expression and the production of IgG by autologous B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 2009;132(3):362–70.
McCarrey JR. Epigenetic mechanisms regulating gene expression. In: Krawetz SA, Womble DD, editors, Introduction to bioinformatics. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2003.
Quintero-Ronderos P, Montoya-Ortiz G. Epigenetics and autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune Dis. 2012;2012:593720-1–593720-16. doi:10.1155/2012/593720.
Huang K, Fan G. DNA methylation in cell differentiation and reprogramming: an emerging systematic view. Regen Med. 2010;5(4):531–44.
Fan S, Zhang X. CpG island methylation pattern in different human tissues and its correlation with gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;383(4):421–5.
Yun M, Wu J, Workman JL, Li B. Readers of histone modifications. Cell Res. 2011;21(4):564–78.
Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res. 2011;21(3):381–95.
De Ruijter A, Van Gennip A, Caron H, Kemp S, van Kuilenburg A. Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J. 2003;370:737–49.
Scaria V, Hariharan M, Maiti S, Pillai B, Brahmachari SK. Host-virus interaction: a new role for microRNAs. Retrovirology. 2006;3(1):68.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97.
Iezzi G, Sonderegger I, Ampenberger F, Schmitz N, Marsland BJ, Kopf M. CD40–CD40L cross-talk integrates strong antigenic signals and microbial stimuli to induce development of IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106(3):876–81.
Liang J, Zhu X-H, Qin H-H, Lin J-R, Wang D-Q, Huang L, et al. A correlation study on the effects of DNMT1 on methylation levels in CD4+ T cells of SLE patients. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):19701.
Aslani S, Mahmoudi M, Garshasbi M, Jamshidi AR, Karami J, Nicknam MH. Evaluation of DNMT1 gene expression profile and methylation of its promoter region in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35(11):2723–31.
Chung SA, Nititham J, Elboudwarej E, Quach HL, Taylor KE, Barcellos LF, et al. Genome-wide assessment of differential DNA methylation associated with autoantibody production in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0129813.
San Yeung K, Chung BH-Y, Choufani S, Mok MY, Wong WL, Mak CCY, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus identified hypomethylation in genes related to the type I interferon pathway. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0169553.
Zhu H, Mi W, Luo H, Chen T, Liu S, Raman I, et al. Whole-genome transcription and DNA methylation analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells identified aberrant gene regulation pathways in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):162.
Mok A, Solomon O, Nayak RR, Coit P, Quach HL, Nititham J, et al. Genome-wide profiling identifies associations between lupus nephritis and differential methylation of genes regulating tissue hypoxia and type 1 interferon responses. Lupus Sci Med. 2016;3(1):e000183.
Absher DM, Li X, Waite LL, Gibson A, Roberts K, Edberg J, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus reveals persistent hypomethylation of interferon genes and compositional changes to CD4+ T-cell populations. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(8):e1003678.
Coit P, Jeffries M, Altorok N, Dozmorov MG, Koelsch KA, Wren JD, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation study suggests epigenetic accessibility and transcriptional poising of interferon-regulated genes in naive CD4+ T cells from lupus patients. J Autoimmun. 2013;43:78–84.
Renauer P, Coit P, Jeffries MA, Merrill JT, McCune WJ, Maksimowicz-McKinnon K, et al. DNA methylation patterns in naïve CD4+ T cells identify epigenetic susceptibility loci for malar rash and discoid rash in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci Med. 2015;2(1):e000101.
Pastor WA, Aravind L, Rao A. TETonic shift: biological roles of TET proteins in DNA demethylation and transcription. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(6):341–56.
Zhao M, Wang J, Liao W, Li D, Li M, Wu H, et al. Increased 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in CD4+ T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2016;69:64–73.
Barreto G, Schäfer A, Marhold J, Stach D, Swaminathan SK, Handa V, et al. Gadd45a promotes epigenetic gene activation by repair-mediated DNA demethylation. Nature. 2007;445(7128):671–5.
Li Y, Zhao M, Yin H, Gao F, Wu X, Luo Y, et al. Overexpression of the growth arrest and DNA damage-induced 45α gene contributes to autoimmunity by promoting DNA demethylation in lupus T cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(5):1438–47.
Li Y, Huang C, Zhao M, Liang G, Xiao R, Yung S et al. A possible role of HMGB1 in DNA demethylation in CD4+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:206298-1–206298-5. doi:10.1155/2013/206298.
Luo Y, Zhao M, Lu Q. Demethylation of promoter regulatory elements contributes to CD70 overexpression in CD4+ T cells from patients with subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(4):425–30.
Zhao M, Sun Y, Gao F, Wu X, Tang J, Yin H, et al. Epigenetics and SLE: RFX1 downregulation causes CD11a and CD70 overexpression by altering epigenetic modifications in lupus CD4+ T cells. J Autoimmun. 2010;35(1):58–69.
He X-J, Ding Y, Xiang W, Dang X-Q. Roles of 1,25(OH)2D3 and vitamin D receptor in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus by regulating the activation of CD4+ T cells and the PKCδ/ERK signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(3–4):743–56.
Hong K-M, Kim H-K, Park S-Y, Poojan S, Kim M-K, Sung J et al. CD3Z hypermethylation is associated with severe clinical manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus and reduces CD3ζ-chain expression in T cells. Rheumatology. 2017;56(3):467–76.
Richardson B. Effect of an inhibitor of DNA methylation on T cells. II. 5-Azacytidine induces self-reactivity in antigen-specific T4+ cells. Hum Immunol. 1986;17(4):456–70.
Quddus J, Johnson K, Gavalchin J, Amento E, Chrisp C, Yung R, et al. Treating activated CD4+ T cells with either of two distinct DNA methyltransferase inhibitors, 5-azacytidine or procainamide, is sufficient to cause a lupus-like disease in syngeneic mice. J Clin Investig. 1993;92(1):38.
Yung RL, Quddus J, Chrisp CE, Johnson KJ, Richardson BC. Mechanism of drug-induced lupus. I. Cloned Th2 cells modified with DNA methylation inhibitors in vitro cause autoimmunity in vivo. J Immunol. 1995;154(6):3025–35.
Kaplan MJ, Lu Q, Wu A, Attwood J, Richardson B. Demethylation of promoter regulatory elements contributes to perforin overexpression in CD4+ lupus T cells. J Immunol. 2004;172(6):3652–61.
Garaud S, Le Dantec C, Jousse-Joulin S, Hanrotel-Saliou C, Saraux A, Mageed RA, et al. IL-6 modulates CD5 expression in B cells from patients with lupus by regulating DNA methylation. J Immunol. 2009;182(9):5623–32.
Fali T, Le Dantec C, Thabet Y, Jousse S, Hanrotel C, Youinou P, et al. DNA methylation modulates HRES1/p28 expression in B cells from patients with Lupus. Autoimmunity. 2014;47(4):265–71.
Dean GS, Tyrrell-Price J, Crawley E, Isenberg DA. Cytokines and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(4):243–51.
Zhao M, Tang J, Gao F, Wu X, Liang Y, Yin H et al. Hypomethylation of IL10 and IL13 promoters in CD4+ T cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:931018-1–931018-9. doi:10.1155/2010/931018.
Zhao M, Liu S, Luo S, Wu H, Tang M, Cheng W, et al. DNA methylation and mRNA and microRNA expression of SLE CD4+ T cells correlate with disease phenotype. J Autoimmun. 2014;54:127–36.
Zhang Z, Song L, Maurer K, Petri MA, Sullivan KE. Global H4 acetylation analysis by ChIP-chip in systemic lupus erythematosus monocytes. Genes Immun. 2010;11(2):124–33.
Zhang Z, Shi L, Dawany N, Kelsen J, Petri MA, Sullivan KE. H3K4 tri-methylation breadth at transcription start sites impacts the transcriptome of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Epigenet. 2016;8(1):14.
Hu N, Qiu X, Luo Y, Yuan J, Li Y, Lei W, et al. Abnormal histone modification patterns in lupus CD4+ T cells. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(5):804–10.
Hu N, Long H, Zhao M, Yin H, Lu Q. Aberrant expression pattern of histone acetylation modifiers and mitigation of lupus by SIRT1-siRNA in MRL/lpr mice. Scand J Rheumatol. 2009;38(6):464–71.
Long H, Huang W, Yin H, Zhao S, Zhao M, Lu Q. Abnormal expression pattern of histone demethylases in CD4+ T cells of MRL/lpr lupus-like mice. Lupus. 2009;18:1327–8.
Zhao M, Wu X, Zhang Q, Luo S, Liang G, Su Y, et al. RFX1 regulates CD70 and CD11a expression in lupus T cells by recruiting the histone methyltransferase SUV39H1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6):1.
Zhou Y, Qiu X, Luo Y, Yuan J, Li Y, Zhong Q, et al. Histone modifications and methyl-CpG-binding domain protein levels at the TNFSF7 (CD70) promoter in SLE CD4+ T cells. Lupus. 2011;20(13):1365–71.
Zhang Q, Liao J, Zhao M, Liang G, Wu X, Zhang P, et al. Inhibited expression of hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 associated with loss of jumonji domain containing 3 promoter binding contributes to autoimmunity in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2011;37(3):180–9.
Liu Y, Liao J, Zhao M, Wu H, Yung S, Chan TM, et al. Increased expression of TLR2 in CD4+ T cells from SLE patients enhances immune reactivity and promotes IL-17 expression through histone modifications. Eur J Immunol. 2015;45(9):2683–93.
Leung YT, Shi L, Maurer K, Song L, Zhang Z, Petri M, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 1 and histone H4 acetylation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Epigenetics. 2015;10(3):191–9.
Zhang Q, Ding S, Zhang H, Long H, Wu H, Zhao M, et al. Increased Set1 binding at the promoter induces aberrant epigenetic alterations and up-regulates cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate response element modulator alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Epigenet. 2016;8(1):126.
Fang TJ, Lin YZ, Liu CC, Lin CH, Li RN, Wu CC, et al. Methylation and gene expression of histone deacetylases 6 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(10):968–73.
Shen N, Liang D, Tang Y, De Vries N, Tak P-P. MicroRNAs—novel regulators of systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(12):701–9.
Smith S, Fernando T, Wu PW, Seo J, Gabhann JN, Piskareva O, et al. MicroRNA-302d targets IRF9 to regulate the IFN-induced gene expression in SLE. J Autoimmun. 2017;79:105–11.
Katsuyama E, Yan M, Watanabe KS, Matsushima S, Yamamura Y, Hiramatsu S, et al. Downregulation of miR-200a-3p, targeting CtBP2 complex, is involved in the hypoproduction of IL-2 in systemic lupus erythematosus-derived T cells. J Immunol. 2017;198(11):4268–76.
Cheng J, Wu R, Long L, Su J, Liu J, Wu X-D, et al. miRNA-451a targets IFN regulatory factor 8 for the progression of systemic lupus erythematosus. Inflammation. 2017;40(2):676–87.
Hedrich CM, Tsokos GC. Epigenetic mechanisms in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Trends Mol Med. 2011;17(12):714–24.
Pan Y, Sawalha AH. Epigenetic regulation and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Transl Res. 2009;153(1):4–10.
Zhao S, Wang Y, Liang Y, Zhao M, Long H, Ding S, et al. MicroRNA-126 regulates DNA methylation in CD4+ T cells and contributes to systemic lupus erythematosus by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(5):1376–86.
Ding S, Liang Y, Zhao M, Liang G, Long H, Zhao S, et al. Decreased microRNA-142-3p/5p expression causes CD4+ T cell activation and B cell hyperstimulation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(9):2953–63.
Wang Y, Liang J, Qin H, Ge Y, Du J, Lin J, et al. Elevated expression of miR-142-3p is related to the pro-inflammatory function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells in SLE. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):263.
Luo S, Liu Y, Liang G, Zhao M, Wu H, Liang Y, et al. The role of microRNA-1246 in the regulation of B cell activation and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Epigenet. 2015;7(1):1.
Sourour SK, Aboelenein HR, Elemam NM, Abdelhamid AK, Salah S, Abdelaziz AI. Unraveling the expression of microRNA-27a* & NKG2D in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and natural killer cells of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.13099.
Furukawa H, Oka S, Matsui T, Hashimoto A, Arinuma Y, Komiya A, et al. Genome, epigenome and transcriptome analyses of a pair of monozygotic twins discordant for systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Immunol. 2013;74(2):170–5.
Zhu X, Liang J, Li F, Yang Y, Xiang L, Xu J. Analysis of associations between the patterns of global DNA hypomethylation and expression of DNA methyltransferase in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Dermatol. 2011;50(6):697–704.
Qin HH, Zhu XH, Liang J, Yang YS, Wang SS, Shi WM, et al. Associations between aberrant DNA methylation and transcript levels of DNMT1 and MBD2 in CD4+ T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Australas J Dermatol. 2013;54(2):90–5.
Nakkuntod J, Sukkapan P, Avihingsanon Y, Mutirangura A, Hirankarn N. DNA methylation of human endogenous retrovirus in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Hum Genet. 2013;58(5):241–9.
Lin S, Hsieh S, Lin Y, Lee C, Tsai M, Lai L, et al. A whole genome methylation analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus: hypomethylation of the IL10 and IL1R2 promoters is associated with disease activity. Genes Immun. 2012;13(3):214–20.
Nielsen CT, Østergaard O, Johnsen C, Jacobsen S, Heegaard NH. Distinct features of circulating microparticles and their relationship to clinical manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(10):3067–77.
Ullal AJ, Reich CF, Clowse M, Criscione-Schreiber LG, Tochacek M, Monestier M, et al. Microparticles as antigenic targets of antibodies to DNA and nucleosomes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2011;36(3):173–80.
Stagakis E, Bertsias G, Verginis P, Nakou M, Hatziapostolou M, Kritikos H, et al. Identification of novel microRNA signatures linked to human lupus disease activity and pathogenesis: miR-21 regulates aberrant T cell responses through regulation of PDCD4 expression. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(8):1496–506.
Fan W, Liang D, Tang Y, Qu B, Cui H, Luo X, et al. Identification of microRNA-31 as a novel regulator contributing to impaired interleukin-2 production in T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(11):3715–25.
Motawi TK, Mohsen DA, El-Maraghy SA, Kortam MA. MicroRNA-21, microRNA-181a and microRNA-196a as potential biomarkers in adult Egyptian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chem Biol Interact. 2016;260:110–6.
Wang H, Peng W, Ouyang X, Li W, Dai Y. Circulating microRNAs as candidate biomarkers in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Transl Res. 2012;160(3):198–206.
Carlsen AL, Schetter AJ, Nielsen CT, Lood C, Knudsen S, Voss A, et al. Circulating microRNA expression profiles associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(5):1324–34.
Paz Z, Tsokos GC. New therapeutics in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013;25(3):297–303.
Merrill JT, Ginzler EM, Wallace DJ, McKay JD, Lisse JR, Aranow C, et al. Long-term safety profile of belimumab plus standard therapy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(10):3364–73.
Ding HJ, Gordon C. New biologic therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013;13(3):405–12.
Dawson MA, Kouzarides T. Cancer epigenetics: from mechanism to therapy. Cell. 2012;150(1):12–27.
Højfeldt JW, Agger K, Helin K. Histone lysine demethylases as targets for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(12):917–30.
Helin K, Dhanak D. Chromatin proteins and modifications as drug targets. Nature. 2013;502(7472):480–8.
Nicodeme E, Jeffrey KL, Schaefer U, Beinke S, Dewell S, C-w Chung, et al. Suppression of inflammation by a synthetic histone mimic. Nature. 2010;468(7327):1119–23.
Lewis EC, Blaabjerg L, Størling J, Ronn SG, Mascagni P, Dinarello CA et al. The oral histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 reduces cytokines and protects islet β cells in vivo and in vitro. Mol Med. 2011;17(5–6):369–77.
Munro S, Mitchell M, Ponnampalam A. Histone deacetylase inhibition by trichostatin A mitigates LPS induced TNFα and IL-10 production in human placental explants. Placenta. 2013;34(7):567–73.
Grabiec AM, Korchynskyi O, Tak PP, Reedquist KA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte and macrophage IL-6 production by accelerating mRNA decay. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(3):424–31.
Grabiec AM, Krausz S, de Jager W, Burakowski T, Groot D, Sanders ME, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress inflammatory activation of rheumatoid arthritis patient synovial macrophages and tissue. J Immunol. 2010;184(5):2718–28.
Mishra N, Reilly CM, Brown DR, Ruiz P, Gilkeson GS. Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate renal disease in the MRL-lpr/lpr mouse. J Clin Investig. 2003;111(4):539–52.
Salvi V, Bosisio D, Mitola S, Andreoli L, Tincani A, Sozzani S. Trichostatin A blocks type I interferon production by activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Immunobiology. 2010;215(9):756–61.
Cornacchia E, Golbus J, Maybaum J, Strahler J, Hanash S, Richardson B. Hydralazine and procainamide inhibit T cell DNA methylation and induce autoreactivity. J Immunol. 1988;140(7):2197–200.
Luo Y, Zhang X, Zhao M, Lu Q. DNA demethylation of the perforin promoter in CD4+ T cells from patients with subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Dermatol Sci. 2009;56(1):33–6.
Tao R, de Zoeten EF, Özkaynak E, Chen C, Wang L, Porrett PM, et al. Deacetylase inhibition promotes the generation and function of regulatory T cells. Nat Med. 2007;13(11):1299–307.
Liu Z, Zhang C, Sun J. Deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A down-regulates Foxp3 expression and reduces CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;400(3):409–12.
Li N, Zhao D, Kirschbaum M, Zhang C, Lin C-L, Todorov I, et al. HDAC inhibitor reduces cytokine storm and facilitates induction of chimerism that reverses lupus in anti-CD3 conditioning regimen. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008;105(12):4796–801.
Vojinovic J, Damjanov N, D’Urzo C, Furlan A, Susic G, Pasic S, et al. Safety and efficacy of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(5):1452–8.
Furlan A, Monzani V, Reznikov LL, Leoni F, Fossati G, Modena D et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety and inducible cytokine responses during a phase 1 trial of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 (givinostat). Mol Med. 2011;17(5–6):353–62.
Glauben R, Sonnenberg E, Wetzel M, Mascagni P, Siegmund B. Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate interleukin 6-dependent CD4+ T cell polarization in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(9):6142–51.
Bodar EJ, Simon A, van der Meer JW. Effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 in autoinflammatory syndromes. Mol Med. 2011;17(5–6):363–8.
Regna NL, Chafin CB, Hammond SE, Puthiyaveetil AG, Caudell DL, Reilly CM. Class I and II histone deacetylase inhibition by ITF2357 reduces SLE pathogenesis in vivo. Clin Immunol. 2014;151(1):29–42.
Krützfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M, et al. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature. 2005;438(7068):685–9.
Esau C, Davis S, Murray SF, Yu XX, Pandey SK, Pear M, et al. miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 2006;3(2):87–98.
Velagapudi SP, Gallo SM, Disney MD. Sequence-based design of bioactive small molecules that target precursor microRNAs. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10(4):291–7.
Thai T-H, Patterson HC, Pham D-H, Kis-Toth K, Kaminski DA, Tsokos GC. Deletion of microRNA-155 reduces autoantibody responses and alleviates lupus-like disease in the Faslpr mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2013;110(50):20194–9.
Pan Y, Jia T, Zhang Y, Zhang K, Zhang R, Li J, et al. MS2 VLP-based delivery of microRNA-146a inhibits autoantibody production in lupus-prone mice. Int J Nanomed. 2012;7:5957–67.
Wang G, Tam L-S, Li EK-M, Kwan BC-H, Chow K-M, Luk CC-W, et al. Serum and urinary cell-free MiR-146a and MiR-155 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2010;37(12):2516–22.
Wang G, Tam L-S, Kwan BC-H, Li EK-M, Chow K-M, Luk CC-W, et al. Expression of miR-146a and miR-155 in the urinary sediment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31(3):435–40.
Wen Z, Xu L, Chen X, Xu W, Yin Z, Gao X, et al. Autoantibody induction by DNA-containing immune complexes requires HMGB1 with the TLR2/microRNA-155 pathway. J Immunol. 2013;190(11):5411–22.
Boldin M, Chang K. NF-kappaB dependent induction of microRNA miR-146. An inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(33):12481–6.
Pan Y, Zhang Y, Jia T, Zhang K, Li J, Wang L. Development of a microRNA delivery system based on bacteriophage MS2 virus-like particles. FEBS J. 2012;279(7):1198–208.
Nozaki Y, Yamagata T, Yoo BS, Sugiyama M, Ikoma S, Kinoshita K, et al. The beneficial effects of treatment with all-trans-retinoic acid plus corticosteroid on autoimmune nephritis in NZB/WF1 mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005;139(1):74–83.
Ma J, Liu Y, Li Y, Gu J, Liu J, Tang J, et al. Differential role of all-trans retinoic acid in promoting the development of CD4+ and CD8+ regulatory T cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2014;95(2):275–83.
Kinoshita K, Yoo B-S, Nozaki Y, Sugiyama M, Ikoma S, Ohno M, et al. Retinoic acid reduces autoimmune renal injury and increases survival in NZB/W F1 mice. J Immunol. 2003;170(11):5793–8.
Lu L, Ma J, Li Z, Lan Q, Chen M, Liu Y, et al. All-trans retinoic acid promotes TGF-β-induced Tregs via histone modification but not DNA demethylation on Foxp3 gene locus. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24590.
X-x Xu, Qi X-M, Zhang W, Zhang C-Q, Wu X-X, Wu Y-G, et al. Effects of total glucosides of paeony on immune regulatory toll-like receptors TLR2 and 4 in the kidney from diabetic rats. Phytomedicine. 2014;21(6):815–23.
Zhang H, Xiao W, Hou P. Clinical study of total glucosides of paeony in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi (Chinese journal of integrated traditional and Western medicine/Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he xue hui, Zhongguo Zhong yi yan jiu yuan zhu ban). 2011;31(4):476–9.
Lin J, Xiao L, Ouyang G, Shen Y, Huo R, Zhou Z, et al. Total glucosides of paeony inhibits Th1/Th17 cells via decreasing dendritic cells activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Immunol. 2012;280(2):156–63.
Dolff S, Bijl M, Huitema MG, Limburg PC, Kallenberg CG, Abdulahad WH. Disturbed Th1, Th2, Th17 and T reg balance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 2011;141(2):197–204.
Cao T, Wenzel SE, Faubion WA, Harriman G, Li L. Enhanced suppressive function of regulatory T cells from patients with immune-mediated diseases following successful ex vivo expansion. Clin Immunol. 2010;136(3):329–37.
Zhao M, G-p Liang, M-n Tang, S-y Luo, Zhang J, W-j Cheng, et al. Total glucosides of paeony induces regulatory CD4+ CD25+ T cells by increasing Foxp3 demethylation in lupus CD4+ T cells. Clin Immunol. 2012;143(2):180–7.
Sfikakis P, Souliotis VL, Fragiadaki K, Moutsopoulos H, Boletis J, Theofilopoulos A. Increased expression of the FoxP3 functional marker of regulatory T cells following B cell depletion with rituximab in patients with lupus nephritis. Clin Immunol. 2007;123(1):66–73.
Aslani S, Jafari N, Javan MR, Karami J, Ahmadi M, Jafarnejad M. Epigenetic modifications and therapy in multiple sclerosis. Neuromol Med. 2016;19:1–13.
Mahmoudi M, Aslani S, Nicknam MH, Karami J, Jamshidi AR. New insights toward the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis; genetic variations and epigenetic modifications. Modern Rheumatol. 2016;27:1–12.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by a grant from the Deputy of Research, Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 94-03-41-30371).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foma, A.M., Aslani, S., Karami, J. et al. Epigenetic involvement in etiopathogenesis and implications in treatment of systemic lupus erythematous. Inflamm. Res. 66, 1057–1073 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-017-1082-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-017-1082-y