Abstract
Objective
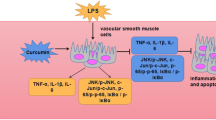
This study was designed to identify the inhibitory effect of curcumin on ox-LDL-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) production and investigated whether the effects are mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and NF-κB pathways in rat vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs).
Methods
The VSMCs cells were pretreated with curcumin, before stimulation with ox-LDL. The ox-LDL-induced MCP-1 expression was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Intracellular signaling was investigated by Western blot.
Results
The concentrations of MCP-1 in cell supernatant and were upregulated by ox-LDL in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Additionally, curcumin decreased the expression of MCP-1 in a dose-dependent manner under treatment with ox-LDL (100 μg/ml). Signal transduction studies indicated that the ox-LDL-induced MCP-1 expression in VSMCs could be partly reversed by the inhibitor of p38 MAPK (SB203580) and NF-κB (BAY11-7082), whereas the ERK inhibitor (PD98059) and the JNK inhibitor (SP600125) had no effect. Western blot revealed that curcumin reduced ox-LDL- induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation and nuclear NF-κB p65 protein at the indicated concentration.
Conclusion
Curcumin suppresses ox-LDL-induced MCP-1 expression in VSMCs via the p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways, which suggests that the anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin is related to the down-regulation of MCP-1 expression and offers a new theoretical basis in the anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goel A, Kunnumakkara AB, Aggarwal BB. Curcumin as “Curecumin”: from kitchen to clinic. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;75(4):787–809.
Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis. Nature. 2000;407(6801):233–41.
Chobanian AV. Single risk factor intervention may be inadequate to inhibit atherosclerosis progression when hypertension and hypercholesterolemia co-exist. Hypertension. 1991;18(2):130–1.
Fogelman A, Schechter I, Seager J, Hokom M, Child JS, Edwards PA. Malondialdehyde alteration of low density lipoproteins leads to cholesteryl ester accumulation in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1980;77(4):2214–8.
Reckless J, Rubin E, Verstuyft J, Metcalfe JC, Grainger DJ. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, but not tumor necrosis factor is correlated with monocyte infiltration in mouse lipid lesions. Circulation. 1999;99(17):2310–6.
Wang GP, Deng ZD, Ni J, Qu ZL. Oxidized low density lipoprotein and very low density lipoprotein enhance expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in rabbit peritoneal exudate macrophages. Atherosclerosis. 1997;133(1):31–6.
Clarke MC, Talib S, Figg NL, Bennett MR. Vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis induces interleukin-1-directed inflammation: effects of hyperlipidemia-mediated inhibition of phagocytosis. Circ Res. 2010;106(2):363–72.
Navab M, Imes SS, Hama SY, Hough GP, Ross LA, Bork RW, Valente AJ, et al. Monocyte transmigration induced by modification of low density lipoprotein in cocultures of human aortic wall cells is due to induction of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 synthesis and is abolished by high density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1991;88(6):2039–46.
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Okamoto Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Hotta K, et al. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-kappa B signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. Circulation. 2000;102(11):1296–301.
Egashira K. Clinical importance of endothelial function in arteriosclerosis and ischemic heart disease. Circ J. 2002;66(6):529–33.
Usui M, Egashira K, Ohtani K, Kataoka C, Ishibashi M, Hiasa K, Katoh M, et al. Anti-monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene therapy inhibits restenotic changes (neointimal hyperplasia) after balloon injury in rats and monkeys. FASEB J. 2002;16(13):1838–40.
Egashira K, Zhao Q, Kataoka C, Ohtani K, Usui M, Charo IF, et al. Importance of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 pathway in neointimal hyperplasia after periarterial injury in mice and monkeys. Circ Res. 2002;90(11):1167–72.
Hokimoto S, Oike Y, Saito T, Kitaoka M, Oshima S, Noda K, et al. Increased expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in atherectomy specimens from patients with restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circ J. 2002;66(1):114–6.
Kamimura M, Bea F, Akizawa T, Katus HA, Kreuzer J, Viedt C. Platelet-derived growth factor induces tissue factor expression in vascular smooth muscle cells via activation of Egr-1. Hypertension. 2004;44(6):944–51.
Wallenfeldt K, Fagerberg B, Wikstrand J, Hulthe J. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein in plasma is a prognostic marker of subclinical atherosclerosis development in clinically healthy men. J Intern Med. 2004;256(5):413–20.
Gonçalves I, Gronholdt ML, Söderberg I, Ares MP, Nordestgaard BG, Bentzon JF, et al. Humoral immune response against defined oxidized low-density lipoprotein antigens reflects structure and disease activity of carotid plaques. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25(6):1250–5.
Steinberg D. Low density lipoprotein oxidation and its pathobiological significance. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(34):20963–6.
Rong JX, Berman JW, Taubman MB, Fisher EA. Lysophosphatidylcholine stimulates monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene expression in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22(10):1617–23.
Geng H, Wang A, Rong G, Zhu B, Deng Y, Chen J, et al. The effects of ox-LDL in human atherosclerosis may be mediated in part via the toll-like receptor 4 pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;342(1–2):201–6.
Jing Q, Xin SM, Cheng ZJ, Zhang WB, Zhang R, Qin YW, et al. Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by oxidized LDL in vascular smooth muscle cells: mediation via pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins and association with oxidized LDL-induced cytotoxicity. Circ Res. 1999;84(7):831–9.
Wang WY, Li J, Yang D, Xu W, Zha RP, et al. Ox-LDL stimulates lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 expression in THP-1 monocytes via PI3 K and p38 MAPK pathways. Circ Res. 2010;85(4):845–52.
Sun Y, Chen X (2010) Ox-LDL-induced LOX-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells: role of reactive oxygen species. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. doi:10.1111/j.1472-8206.2010.00885.x (Epub ahead of print).
Hong MH, Kim MH, Chang HJ, Kim NH, Shin BA, Ahn BW, et al. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression in endothelial cells via blocking NF-kappaB signaling. Life Sci. 2007;80(21):1957–65.
Takaya K, Koya D, Isono M, Sugimoto T, Sugaya T, Kashiwagi A, et al. Involvement of ERK pathway in albumin-induced MCP-1 expression in mouse proximal tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;284(5):1037–45.
Lim JH, Kwon TK. Curcumin inhibits phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)-induced MCP-1 expression by inhibiting ERK and NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48(1):47–52.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Feng jian for their excellent suggestions for this experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Liwu Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Y., Liu, T. & Guo, Z. Curcumin inhibits ox-LDL-induced MCP-1 expression by suppressing the p38MAPK and NF-κB pathways in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Inflamm. Res. 61, 61–67 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0389-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0389-3