Abstract
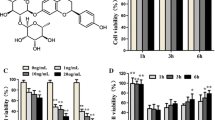
Curcumin plays an important role in inflammation regulation. This study aimed to investigate the effect of curcumin on vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and its mechanism. VSMCs were treated with different concentrations of curcumin (0, 50, 100 and 150 μg/mL). MTT assay and flow cytometry were used to analyze the effects of curcumin on LPS-induced VSMCs viability and apoptosis. The expression and release of inflammatory cytokines in VSMCs were detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Moreover, the proteins expressions of NF-κB and JNK signaling pathways were analyzed by western blot. Interestingly, the results showed that curcumin could reduce LPS induced inflammatory injury by increasing VSMC’s viability, reducing apoptosis and inhibiting the release of inflammatory cytokines. In addition, curcumin increased the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in LPS treated VSMCs. Mechanistically, we found that curcumin attenuated LPS-induced cell damage in VSMCs via inhibition of NF-κB and the JNK signal pathway. Curcumin can protect VSMCs from LPS induced inflammatory damage, which may be related to the blocking of NF-κB and the JNK signaling pathway. Herewith, curcumin could be potential therapeutics for the treatment of atherosclerosis.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams S, Haylett WL, Johnson G, Carr JA, Bardien S (2019) Antioxidant effects of curcumin in models of neurodegeneration, aging, oxidative and nitrosative stress: a review. Neuroscience 406:1–21
Farhood B, Mortezaee K, Goradel NH, Khanlarkhani N, Salehi E, Nashtaei MS, Najafi M, Sahebkar A (2019) Curcumin as an anti-inflammatory agent: implications to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. J Cell Physiol 234(5):5728–5740
Han X, Zhang L, Liu Y, Wu M, Li X, Zhang ZT, Li T (2020) Resveratrol protects H9c2 cells against hypoxia-induced apoptosis through miR-30d-5p/SIRT1/NF-κB axis. J Biosci 45(1):1–10
Han Y, Chen R, Lin Q, Liu Y, Ge W, Cao H, Li J (2021) Curcumin improves memory deficits by inhibiting HMGB1-RAGE/TLR4-NF-κB signalling pathway in APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice hippocampus. J Cell Mol Med 25(18):8947–8956
Kattoor AJ, Pothineni NVK, Palagiri D, Mehta JL (2017) Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 19(11):1–11
Kong Q, Ma X, Lyu J-X, Wang C, Du X-Y, Guan Y-Q (2020) Plasma RANTES level is correlated with cardio-cerebral atherosclerosis burden in patients with ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Chron Dis Transl Med 6(1):46–54
Li Y, Tian L, Sun D, Yin D (2019) Curcumin ameliorates atherosclerosis through upregulation of miR-126. J Cell Physiol 234(11):21049–21059. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28708. Retraction in: J Cell Physiol. 2021, 236(12):8258
Lin X, Bai D, Wei Z, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Deng H, Huang X (2019) Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress in RAW264. 7 cells by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. PLOS ONE 14(5):e0216711
Liu T, Han C, Sun L, Ding Z, Shi F, Wang R, Wang W, Shan W, Zhang Y, Hu N (2019) Association between new circulating proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory adipocytokines with coronary artery disease. Coron Artery Dis 30(7):528
Lu Z, Li Y, Syn W-K, Wang Z, Lopes-Virella MF, Lyons TJ, Huang Y (2020) Amitriptyline inhibits nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and atherosclerosis induced by high-fat diet and LPS through modulation of sphingolipid metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 318(2):E131–E144
Meng Z, Yan C, Deng Q, Gao D-F, Niu X-L (2013) Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro via ROS-relative TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34(7):901–911
Mollazadeh H, Cicero AF, Blesso CN, Pirro M, Majeed M, Sahebkar A (2019) Immune modulation by curcumin: the role of interleukin-10. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59(1):89–101
Morita S-Y (2016) Metabolism and modification of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins involved in dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. Biol Pharm Bull 39(1):1–24
Ozawa-Umeta H, Kishimoto A, Imaizumi A, Hashimoto T, Asakura T, Kakeya H, Kanai M (2020) Curcumin β-D-glucuronide exhibits anti–tumor effects on oxaliplatin-resistant colon cancer with less toxicity in vivo. Cancer Sci 111(5):1785
Qu R, Qu W (2019) Metformin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response in VSMCs by regulating TLR4 and PPAR-gamma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(11):4988–4995
Sitia S, Tomasoni L, Atzeni F, Ambrosio G, Cordiano C, Catapano A, Tramontana S, Perticone F, Naccarato P, Camici P (2010) From endothelial dysfunction to atherosclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 9(12):830–834
Srisook K, Mankhong S, Chiranthanut N, Kongsamak K, Kitwiwat N-T, Tongjurai P, Aramsangtienchai P (2019) Anti-inflammatory effect of trans-4-methoxycinnamaldehyde from Etlingera pavieana in LPS-stimulated macrophages mediated through inactivation of NF-κB and JNK/c-Jun signaling pathways and in rat models of acute inflammation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 371:3–11
Strela FB, Brun BF, Berger RC, Melo S, de Oliveira EM, Barauna VG, Vassallo PF (2020) Lipopolysaccharide exposure modulates the contractile and migratory phenotypes of vascular smooth muscle cells. Life sciences 241:117098
Wang Y, Zhou S, Sun W, McClung K, Pan Y, Liang G, Tan Y, Zhao Y, Liu Q, Sun J (2014) Inhibition of JNK by novel curcumin analog C66 prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy with a preservation of cardiac metallothionein expression. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 306(11):E1239–E1247
Wang C, Niimi M, Watanabe T, Wang Y, Liang J, Fan J (2018) Treatment of atherosclerosis by traditional Chinese medicine: questions and quandaries. Atherosclerosis 277:136–144
Yu M-H, Li X, Li Q, Mo S-J, Ni Y, Han F, Wang Y-B, Tu Y-X (2019) SAA1 increases NOX4/ROS production to promote LPS-induced inflammation in vascular smooth muscle cells through activating p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway. BMC Mol Cell Biol 20(1):1–11
Zhang S, Zou J, Li P, Zheng X, Feng D (2018) Curcumin protects against atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice by inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 expression. J Agric Food Chem 66(2):449–456
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Luo Y, Du Y, Zhang X, Fu J (2019) Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation by promoting microglial M2 polarization via TREM2/TLR4/NF-κB pathways in BV2 cells. Mol Immunol 116:29–37
Zhang M, Li Y, Xie H, Chen J, Liu S (2020) Curcumin inhibits proliferation, migration and neointimal formation of vascular smooth muscle via activating miR-22. Pharm Biol 58(1):610–619
Zhao X, Ma L, Dai L, Zuo D, Li X, Zhu H, Xu F (2020) TNF-α promotes the malignant transformation of intestinal stem cells through the NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Oncol Rep 44(2):577–588
Zhong Y, Liu T, Guo Z (2012) Curcumin inhibits ox-LDL-induced MCP-1 expression by suppressing the p38MAPK and NF-κB pathways in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Inflamm Res 61(1):61–67
Zhong Y, Feng J, Li J, Fan Z (2017) Curcumin prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity via the Ras/MEK1/2 signaling pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Med Rep 16(4):4315–4319
Zhou T, Wang Y, Liu M, Huang Y, Shi J, Dong N, Xu K (2020) Curcumin inhibits calcification of human aortic valve interstitial cells by interfering NF-κB, AKT, and ERK pathways. Phytother Res 34(8):2074–2081
Zhu Y, Xian X, Wang Z, Bi Y, Chen Q, Han X, Tang D, Chen R (2018) Research progress on the relationship between atherosclerosis and inflammation. Biomolecules 8(3):80
Funding
This work has funded by key R & D project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of science and technology (No. 20161bg70078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HR designed, resources and performed the experiments. QH provided support for data analysis and writing the manuscript and BW and MY provided, resources, discussion, design and peer review process. All the authors have seen and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed to publish this manuscript in Inflammopharmacology.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, H., Huang, Q., Wan, B. et al. Curcumin alleviates lipopolysaccharides-induced inflammation and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells via inhibition of the NF-κB and JNK signaling pathways. Inflammopharmacol 30, 517–525 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-021-00912-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-021-00912-w