Abstract.
Objective and design:
The Macrophage-derived Neutrophil Chemotactic Factor (MNCF) has been characterized as a dexamethasone-resistant neutrophil chemotactic lectin produced by rat macrophages. This study was undertaken to evaluate different MNCF cellular sources and investigate the mechanisms by which MNCF overcomes the anti-inflammatory actions of dexamethasone.
Material and methods:
The mouse macrophage-like cell line P388D1 and thioglycollate-elicited mouse macrophages were studied regarding their capacity to release MNCF. Neutrophil migration assays were performed in vivo and in vitro, in either the presence or absence of extracellular matrix glycoproteins (ECM).
Results:
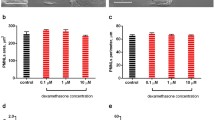
Mouse and P388D1 macrophages release a lectin that reproduces the activities of rat MNCF. The ability of MNCF to induce neutrophil adhesion and haptotaxis is enhanced through its interaction with laminin and fibronectin. These properties are not inhibited by dexamethasone.
Conclusions:
Together, our results suggest that dexamethasone-resistant neutrophil migration induced by MNCF occurs probably because of its interactions with ECM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 27 September 2006; returned for revision 6 February 2007; accepted by M. Katori 23 April 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Toledo, K.A., Bernardes, E.S., Baruffi, M.D. et al. Neutrophil haptotaxis induced by mouse MNCF: interactions with extracellular matrix glycoproteins probably contribute to overcoming the anti-inflammatory action of dexamethasone. Inflamm. res. 56, 368–376 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-007-6159-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-007-6159-6