Abstract
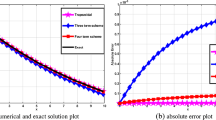
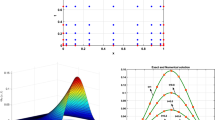
In this paper, we will develop a four-stage high algebraic order symmetric two-step method with vanished phase-lag and its first up to the fourth derivative. For the proposed method, we will study the following: the phase-lag analysis of the new method; the development of the new method; the local truncation error analysis which is based on the radial Schrödinger equation; the stability and the interval of periodicity analysis which is based on a scalar test equation with frequency different than the frequency of the scalar test equation used for the phase-lag analysis; the error estimation procedure which is based on the algebraic order; and the numerical results from our numerical tests for the examination of the efficiency of the new obtained method. The numerical tests are based on the numerical solution of the Schrödinger equation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastassi Z.A., Simos T.E.: A parametric symmetric linear four-step method for the efficient integration of the Schrödinger equation and related oscillatory problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 236, 3880–3889 (2012)
Raptis A.D., Simos T.E.: A four-step phase-fitted method for the numerical integration of second order initial-value problem. BIT. 31, 160–168 (1991)
Lambert, J.D.: Numerical Methods for Ordinary Differential Systems, The Initial Value Problem, pp. 104–107. Wiley, New York (1991)
Simos J.D., Williams J.D.: A finite-difference method for the numerical solution of the Schrödinger equation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 79, 189–205 (1997)
Thomas R.M.: Phase properties of high order almost P-stable formulae. BIT. 24, 225–238 (1984)
Lambert J.D., Watson I.A.: Symmetric multistep methods for periodic initial values problems. J. Inst. Math. Appl. 18, 189–202 (1976)
Franco J.M., Palacios M.: High-order P-stable multistep method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 30, 1–10 (1990)
Chawla M.M., Neta B.: Families of two-step fourth order P-stable methods for second order differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 15, 213–223 (1986)
Anastassi Z.A., Simos T.E.: An optimized Runge–Kutta method for the solution of orbital problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 175(1), 1–9 (2005)
Papadopoulos D.F., Simos D.F.: A modified Runge–Kutta–Nyström method using phase lag properties for the numerical solution of orbital problems. Appl. Math. Inform. Sci. 7(2), 433–437 (2013)
ThMonovasilis D.F., Kalogiratou Z., Simos T.E.: Exponentially fitted symplectic Runge–Kutta–Nyström methods. Appl. Math. Inform. Sci. 7(1), 81–85 (2013)
Panopoulos T.E., Simos T.E.: An optimized symmetric 8-step semi-embedded predictor-corrector method for ivps with oscillating solutions. Appl. Math. Inform. Sci. 7(1), 73–80 (2013)
Kalogiratou Z., Monovasilis T., Ramos H., Simos T.E.: A new approach on the construction of trigonometrically fitted two step hybrid methods. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 303, 146–155 (2016)
Dormand J.R., Prince P.J.: A family of embedded RungeKutta formulae. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 6, 19–26 (1980)
Raptis A.D., Allison A.C.: Exponential-fitting methods for the numerical solution of the Schrödinger equation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 14, 1–5 (1978)
Raptis A.D., Cash J.R.: A variable step method for the numerical integration of the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 36, 113–119 (1985)
Allison J.R.: The numerical solution of coupled differential equations arising from the Schrödinger equation. J. Comput. Phys. 6, 378–391 (1970)
Allison A.C., Dalgarno A.: The rotational excitation of molecular hydrogen. Proc. Phys. Soc. 90(3), 609–614 (1967)
Bernstein R.B., Dalgarno A., Massey H., Percival I.C.: Thermal scattering of atoms by homonuclear diatomic molecules. Proc. Roy. Soc. Ser. A. 274, 427–442 (1963)
Bernstein R.B.: Quantum mechanical (phase shift) analysis of differential elastic scattering of molecular beams. J. Chem. Phys. 33, 795–804 (1960)
Simos T.E.: Exponentially fitted Runge–Kutta methods for the numerical solution of the Schrödinger equation and related problems. Comput. Mater. Sci. 18, 315–332 (2000)
Dormand J.R., Prince J.R.: A family of embedded Runge–Kutta formula. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 6, 19–26 (1980)
Brugnano, L., Iavernaro, F.: Line Integral Methods for Conservative Problems, Series: Monographs and Research Notes in Mathematics. Chapman and Hall/CRC (2016). ISBN 978 – 1 – 4822 – 6384 – 8 (print), ISBN 978 – 1 – 4822 – 6385 – 5 (eBook)
Mu K., Simos T.E.: A RungeKutta type implicit high algebraic order two-step method with vanished phase-lag and its first, second, third and fourth derivatives for the numerical solution of coupled differential equations arising from the Schrödinger equation. J. Math. Chem. 53, 1239–1256 (2015)
Liang M., Simos T.E.: A new four stages symmetric two-step method with vanished phase-lag and its first derivative for the numerical integration of the Schrödinger equation. J. Math. Chem. 54, 1187–1211 (2016)
Hui F., Simos T.E.: Hybrid high algebraic order two-step method with vanished phase-lag and its first and second derivatives. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 73, 619–648 (2015)
Xi, X., Simos, T.E.: A new high algebraic order four stages symmetric two-step method with vanished phase-lag and its first and second derivatives for the numerical solution of the Schrödinger equation and related problems. J. Math. Chem. (in press)
Zhou Z., Simos T.E.: A new two stage symmetric two-step method with vanished phase-lag and its first, second, third and fourth derivatives for the numerical solution of the radial Schrödinger equation. J. Math. Chem. 54, 442–465 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highly Cited Researcher (http://highlycited.com/), Active member of the European Academy of Sciences. Active member of the European Academy of Sciences and Arts. Corresponding Member of the of European Academy of Arts, Sciences and Humanities.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Simos, T.E. A High-Order Two-Step Phase-Fitted Method for the Numerical Solution of the Schrödinger Equation. Mediterr. J. Math. 13, 5177–5194 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00009-016-0800-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00009-016-0800-y