Abstract
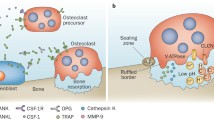
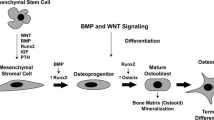
Synovial mesenchymal cells, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and osteoclasts are the three major players directly responsible for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid joint destruction. First, synovial mesenchymal cells, internally driven by a transcription factor c-Fos/AP-1, not only directly invade cartilage and bone as a granulation tissue called “pannus” but also release inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-1β. IL-1β induces MMPs and activates osteoclasts. Synovial cells can also present antigen to T cells to drive antigen-specific immune responses. Second, cartilaginous joint matrix can only be degraded after the first attack of collagen fibrils by MMPs, and importantly, most of the MMPs are under the control of c-Fos/AP-1 and IL-1β as well. Third, differentiation of osteoclast is driven internally by NFATc1, where NFATc1 is under the control of TRAF6, c-Fos/AP-1 and osteoclastogenic signaling complex. IL-1β has been shown to induce osteoclastogenesis directly and also indirectly via signaling through RANKL. Therefore, IL-1β and c-Fos/AP-1 influence each other’s gene expression and activity, resulting in an orchestrated cross-talk that is crucial to arthritic joint destruction, and thus, blockade of IL-1β and/or c-Fos/AP-1 can be most promising as a therapeutic target, and in fact, a selective inhibition of c-Fos/AP-1 does resolve arthritic joint destruction.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens D, Koch AE, Pope RM et al (1996) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (96-kD gelatinase B) in human rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 39:1576–1587
Aikawa Y, Morimoto K, Yamamoto T et al (2008) Treatment of arthritis with a selective inhibitor of c-Fos/activator protein-1. Nat Biotechnol 26:817–823
Angel P, Karin M (1991) The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1072:129–157
Angel P, Imagawa M, Chiu R et al (1987) Phorbol ester inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated transacting factor. Cell 49:729–739
Asagiri M, Hirai T, Kunigami T et al (2008) Cathepsin K-dependent Toll-like receptor 9 signaling revealed in experimental arthritis. Science 319:624–627
Asahara H, Fujisawa K, Kobata T et al (1997) Direct evidence of high DNA binding activity of transcription factor AP-1 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Arthritis Rheum 40:912–918
Athanasou NA, Quinn J, Heryet A et al (1988) The immunohistology of synovial lining cells in normal and inflamed synovium. J Pathol 155:133–142
Barland P, Novikoff AB, Hamerman D (1962) Electron microscopy of the human synovial membrane. J Cell Biol 14:207–220
Beggs S, Salter MW (2008) Taking two cuts at pain. Nat Med 14:243–244
Bondeson J, Foxwell B, Brennan F et al (1999) Defining therapeutic targets by using adenovirus: blocking NF-kappaB inhibits both inflammatory and destructive mechanisms in rheumatoid synovium but spares anti-inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5668–5673
Burrage PS, Mix KS, Brinckerhoff CE (2006) Matrix metalloproteinase: role in arthritis. Front Biosci 11:529–543
Chakraborti S, Mandal M, Das S et al (2003) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: an overview. Mol Cell Biochem 253:269–285
Chikanza IC, Roux-Lombrad P, Dayer JM et al (1995) Dysregulation of the in vivo production of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pathogenetic implications. Arthritis Rheum 38:64–648
Dayer JM (2003) The pivotal role of interleukin-1 in the clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 42(Suppl. 2):ii3–ii10
Dayer JM, Beutler B, Cerami A (1985) Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med 162:2163–2168
Delaisse J, Vaes G (1992) Mechanism of mineral solubilisation and matrix degradation in osteoclastic bone resorption. In: Rifkin BR, Gay CV (eds) Biology and physiology of the osteoclast. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Eastgate JA, Symons JA, Wood NC et al (1988) Correlation of plasma interleukin-1 levels with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2:706–708
Fassbender HG (1975) Pathology of rheumatic diseases. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Fassbender HG (1984) Is pannus a residue of inflammation? Arthritis Rheum 27:956–957
Garnero P, Thompson E, Woodworth T et al (2010) Rapid and sustained improvement in bone and cartilage turnover markers with the anti-interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor tocilizumab plus methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate: results from a substudy of the multicenter double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of tocilizumab in inadequate responders to methotrexate alone. Arthritis Rheum 62:33–43
Gravallese EM, Goldring SR (2000) Cellular mechanisms and the role of cytokines in bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:2143–2151
Gutman A, Wasylyk B (1990) The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J 9:2241–2246
Hembry RM, Bagga MR, Reynolds JJ et al (1995) Immunolocalisation studies on six matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in synovia from patients with osteo- and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 54:25–32
Henderson B, Pettipher ER (1989) Arthritogenic actions of recombinant IL-1 and TNF in the rabbit: evidence for synergistic interactions between cytokines in vivo. Clin Exp Immunol 75:306–310
Hess J, Porte D, Munz C et al (2001) AP-1 and Cbfa/Runt physically interact and regulate parathyroid hormone-dependent MMP13 expression in osteoblasts through a new osteoblast-specific element 2/AP-1 composite element. J Biol Chem 276:20029–20038
Horai R, Saijo S, Tanioka H et al (2000) Development of chronic inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in IL-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J Exp Med 191:313–320
Jiang Y, Genant HK, Watt I et al (2000) A multicenter, double-blind, dose-ranging, randomized, placebo-controlled study of recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: radiologic progression and correlation of Genant and Larsen scores. Arthritis Rheum 43:1001–1009
Jimenez MJ, Balbin M, Lopez JM et al (1999) Collagenase 3 is a target of Cbfa1, a transcription factor of the runt gene family involved in bone formation. Mol Cell Biol 19:4431–4442
Joosten LA (2010) Excessive interleukin-1 signaling determines the development of Th1 and Th17 responses in chronic inflammation. Arthritis Rheum 62:320–322
Joosten LA, Helsen MM, Saxne T et al (1999) IL-1 alpha beta blockade prevents cartilage and bone destruction in murine type II collagen-induced arthritis, whereas TNF-alpha blockade only ameliorates joint destruction. J Immunol 163:5049–5055
Kahle P, Saal JG, Schaudt K et al (1992) Determination of cytokines in synovial fluids: correlation with diagnosis and histomorphological characteristics of synovial fluid. Ann Rheum Dis 51:731–734
Karin M, Liu Z, Zandi E (1997) AP-1 function and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:240–246
Kawasaki H, Komai K, Ouyang Z et al (2001) c-Fos/activator protein-1 transactivates wee1 kinase at G1/S to inhibit premature mitosis in antigen-specific Th1 cells. EMBO J 20:4618–4627
Kawasaki H, Komai K, Nakamura M et al (2003) Human wee1 kinase is directly transactivated by and increased in association with c-Fos/AP-1: rheumatoid synovial cells overexpressing these genes go into aberrant mitosis. Oncogene 22:6839–6844
Kawasaki Y, Xu ZZ, Wang X et al (2008) Distinct roles of matrix metalloproteinases in the early- and late-phase development of neuropathic pain. Nat Med 14:331–336
Kimura H, Tateishi H, Ziff M (1977) Surface ultrastructure of rheumatoid articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum 20:1085–1098
Klareskog L, Forsum U, Kabelitz D et al (1982) Immune functions of human synovial cells: phenotypic and T cell regulatory properties of macrophage-like cells that express HLA-DR. Arthritis Rheum 25:488–501
Kobayashi K, Takahashi N, Jimi E et al (2000) Tumor necrosis factor stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a mechanism independent of the ODF/RANKL-RANK interaction. J Exp Med 191:275–286
Koch AE, Kunkel SL, Chensue SW et al (1992) Expression of interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist by human rheumatoid synovial tissue macrophages. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 65:23–29
Koga T, Inui M, Inoue K et al (2004) Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with RANKL for bone homeostasis. Nature 428:758–763
Koga K, Takaesu G, Yoshida R et al (2009) Cyclic adenosine monophosphate suppresses the transcription of proinflammatory cytokines via the phosphorylated c-Fos protein. Immunity 30:372–383
Kuroki Y, Shiozawa S, Sugimoto T et al (1992) Constitutive expression of c-fos gene inhibits type 1 collagen synthesis in transfected osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 182:1389–1394
Kuroki Y, Shiozawa S, Yoshihara R et al (1993) The contribution of human c-fos DNA to cultured synovial cells: a transfection study. J Rheumatol 20:422–428
Lindhout E, van Eijk M, van Pel M et al (1999) Fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients have intrinsic properties of follicular dendritic cells. J Immunol 162:5949–5956
Lohmander LS, Neame PJ, Sandy JD (1993) The structure of aggrecan fragments in human synovial fluid. Evidence that aggrecanase mediates cartilage degradation in inflammatory joint disease, joint injury, and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 36:1214–1222
Mengshol JA, Vincenti MP, Brinckerhoff CE (2001) IL-1 induces collagenase-3 (MMP-13) promoter activity in stably transfected chondrocyotic cells: requirement for Runx-2 and activation by p38 MAPK and JNK pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4361–4372
Milner JM, Patel A, Rowan AD (2008) Emerging roles of serine proteinases in tissue turnover in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:3644–3656
Miyauchi A, Kuroki Y, Fukase M et al (1994) Persistent expression of proto-oncogene c-fos stimulates osteoclast differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 205:1547–1555
Mudgett JS, Hutchinson NI, Chartrain NA et al (1998) Susceptibility of stromelysin 1-deficient mice to collagen-induced arthritis and cartilage destruction. Arthritis Rheum 41:110–121
Murphy G, Willenbrock F (1995) Tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloendopeptidases. Methods Enzymol 248:496–510
Okada Y (2000) Matrix-degrading metalloproteinases and their roles in joint destruction. Mod Rheumatol 10:121–128
Okada Y, Takeuchi N, Tomita K et al (1989) Immunolocalization of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) in rheumatoid synovioblasts (B cells): correlation with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 48:645–653
Okada Y, Gonoji Y, Nakanishi I et al (1990) Immunohitochemical demonstration of collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) in synovial lining cells of rheumatoid synovium. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Pathol 59:305–312
Okada Y, Naka K, Kawamura K et al (1995) Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (92-kilodalton gelatinase/type IV collagenase = gelatinase B) in Osteoclasts: implications for bone resorption. Lab Invest 72:311–322
Pap T, Shigeyama Y, Kuchen S et al (2000) Differential expression pattern of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:1226–1232
Pap T, Gay S, Schett G (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases. In: Smolen JS, Lipsky PE (eds) Biological therapies in rheumatology. Taylor & Francis Ltd, London
Porter S, Clark IM, Kevorkian L et al (2004) The ADAMTS metalloproteinases. Biochem J 386(Pt 1):15–27
Poulter LW, Duke O, Hobbs S et al (1982) Histochemical discrimination of HLA-DR positive cell populations in the normal and arthritic synovial lining. Clin Exp Immunol 48:381–388
Probert L, Plows D, Kontogeorgos G et al (1995) The type I interleukin-1 receptor acts in series with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) to induce arthritis in TNF-transgenic mice. Eur J Immunol 25:1794–1797
Ray A, Bal BS, Ray BK (2005) Transcriptional induction of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in the chondrocyte and synoviocyte cells is regulated via a novel mechanism: evidence for functional cooperation between serum amyloid A-activating factor-1 and AP-1. J Immunol 175:4039–4048
Redlich K, Hayer S, Ricci R et al (2002) Osteoclasts are essential for TNF-mediated joint destruction. J Clin Invest 110:1419–1427
Reunanan N, Li SP, Ahonen M et al (2002) Activation of p38 alpha MAPK enhances collagenase-1 (matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1) and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) expression by mRNA stabilization. J Biol Chem 277:32360–32368
Rooney M, Symons JA, Duff GW (1990) Interleukin-1 beta in synovial fluid is related to local disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 10:217–219
Schett G, Stach C, Zwerina J et al (2008) How antirheumatic drugs protect joints from damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:2936–2948
Schonthal A, Herrlich P, Rahmsdorf HJ et al (1988) Requirement for fos gene expression in the transcriptional activation of collagenase by other oncogenes and phorbol esters. Cell 54:325–334
Schumacher HR (1973) Fate of particular material arriving at the synovium via the circulation. An ultrastructural study. Ann Rheum Dis 32:212–218
Scott DL, Kingsley GH (2006) Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 355:704–712
Shimizu S, Shiozawa S, Shiozawa K et al (1985) Quantitative histologic studies on the pathogenesis of periarticular osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 28:25–31
Shimizu S, Shiozawa S, Shiozawa K et al (1988) The restoration of proliferation and differentiation of peripheral blood mononuclear non-adherent cells into immunoglobulin-secreting cells by autologous synovial adherent cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol 54:350–356
Shimizu K, Kawasaki H, Morisawa T et al (2000) Spontaneous and cytokine regulated c-fos gene expression in rheumatoid synovial cells. Ann Rheum Dis 59:636–640
Shinohara M, Koga T, Okamoto K et al (2008) Tyrosine kinases Btk and Tec regulate osteoclast differentiation by linking RANK and ITAM signals. Cell 132:794–806
Shiozawa S, Kuroki Y (1994) Osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis: a molecular biological aspect of connective tissue gene activation. Tohoku J Exp Med 173:189–198
Shiozawa S, Tokuhisa T (1992) Contribution of synovial mesenchymal cells to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 21:267–273
Shiozawa S, Tsumiyama K (2009) Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and c-Fos/AP-1. Cell Cycle 8:1539–1543
Shiozawa S, Shiozawa K, Fujita T (1983a) Morphologic observation in the early phase of the cartilage-pannus junction: light and electron microscopic studies of active cellular pannus. Arthritis Rheum 26:472–478
Shiozawa S, Shiozawa K, Fujita T (1983b) Presence of HLA-DR antigen on synovial type A and B cells: an immunoelectron microscopic study in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and normal traumatic joints. Immunology 50:587–594
Shiozawa S, Tanaka Y, Fujita T et al (1992) Destructive arthritis without lymphocyte infiltration in H2-c-fos transgenic mice. J Immunol 148:3100–3104
Shiozawa S, Shimizu S, Tanaka K et al (1997) Studies on the contribution of c-fos/AP-1 to arthritic joint destruction. J Clin Invest 99:1210–1216
Sirum-Connolly K, Brinckerhoff C (1991) Interleukin-1 or phorbol induction of the stromelysin promoter requires an element that cooperates with AP-1. Nucleic Acids Res 19:335–341
Sun Y, Wenger L, Brinckerhoff CE et al (2002) Basic calcium phosphate crystals induce matrix metalloproteinase-1 through the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase/c-Fos/AP-1 metalloproteinase 1 pathway. J Biol Chem 277:1544–1552
Takayanagi H (2007) Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol 7:292–304
Teitelbaum SL (2004) RANKing c-Jun in osteoclast development. J Clin Invest 114:463–465
Theill LE, Boyle WJ, Penninger JM (2002) RANK-L and RANK: T cells, bone loss, and mammalian evolution. Annu Rev Immunol 20:795–823
Thornton S, Duwel LE, Boivin GP et al (1999) Association of the course of collagen-induced arthritis with distinct patterns of cytokine and chemokine messenger RNA expression. Arthritis Rheum 42:1109–1118
Tiku ML, Theodorescu M, Skosey JL (1985) Immunobiological function of normal rabbit synovial cells. Cell Immunol 91:415–424
Tolboom TC, n Mil AH, Nelissen RG et al (2005) Invasiveness of fibroblast-like synoviocytes is an individual patient characteristic associated with the rate of joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 52:1999–2002
Trabandt A, Aicher WK, Gay RE et al (1992) Spontaneous expression of immediately-early response genes c-fos and egr-1 in collagenase-producing rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Rheumatol Int 12:53–59
Tran CN, Davis MJ, Tesmer LA et al (2007) Presentation of arthritogenic peptide to antigen-specific T cells by fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum 56:1497–1506
van de Loo AA, van den Berg WB (1990) Effects of murine recombinant IL-1 on synovial joints in mice: measurement of patellar cartilage metabolism and joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis 49:238–245
van den Berg WB (2001) Anti-cytokine therapy in chronic destructive arthritis. Arthritis Res 3:18–26
van den Berg WB (2002) Lessons from animal models of arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 4:232–239
van den Steen PE, Dubois B, Nelissen I et al (2002) Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 37:375–536
Vincenti MP, Coon CI, Brinckerhoff CE (1998) Nuclear factor kappaB/p50 activates an element in the distal matrix metalloproteinase 1 promoter in interleukin-1 beta-stimulated synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 41:1987–1994
Walsh MC, Kim N, Kadono Y et al (2006) Osteoimmunology: interplay between the immune system and bone metabolism. Annu Rev Immunol 24:33–63
Whitmarsh AJ, Shore P, Sharrocks AD et al (1995) Integration of MAP kinase signal transduction pathways at the serum response element. Science 269:403–407
Will H, Atkinson SJ, Butler GS et al (1996) The soluble catalytic domain of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves the propeptide of progelatinase A and intiates autoproteolytic activation. Regulation by TIMP-2 and TIMP-3. J Biol Chem 271:17119–17123
Yan C, Boyd D (2007) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. J Cell Physiol 211:19–26
Yoshihara Y, Nakamura H, Obata K et al (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 59:455–461
Zwerina J, Redlich K, Polzer K et al (2007) TNF-induced structural joint damage is mediated by interleukin-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11742–11747
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shiozawa, S., Tsumiyama, K., Yoshida, K. et al. Pathogenesis of Joint Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 59, 89–95 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-011-0116-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-011-0116-3