Abstract
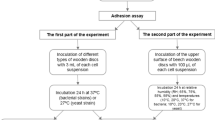
The objective of this study was to investigate Listeria monocytogenes adhesion in new and used polyethylene cutting board surfaces and evaluate its removal using different sanitizers (peracetic acid, chlorhexidine, sodium hypochlorite and organic acids). Results showed that the number of adhered cells increased with time on both surfaces evaluated. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between new and used polyethylene surfaces were observed on the adhesion of microorganism. Treatments with the peracetic acid and sodium hypochlorite sanitizers were very effective to inactivate attached L. monocytogenes on the polyethylene cutting board, avoiding the possible formation of biofilms at all contact times studied. Other sanitizers did not succeed in inhibiting completely the pathogen in the maximum concentration (2.0 %) after 24 h of bacterial growth for both surfaces (chlorohexidine), 3 h of bacterial growth on new and 6 h on used surfaces (organic acid). The results indicate that peracetic acid and a sodium hypochlorite treatment present a better method to remove microbial contamination on the surfaces of cutting boards.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarnisalo K, Lundén J, Korkeala H, Wirtanen G (2007) Susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes strains to disinfectants and chlorinated alkaline cleaners at cold temperatures. LWT Food Sci Technol 40:1041–1048. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2006.07.009
Beltrame CA et al (2013) Comparative lethality kinetic curves and predictive models of F-value for Listeria monocytogenes using different sanitizers. Food Sci Nutr 1:27–31. doi:10.1002/fsn3.5
Beresford MR, Andrew PW, Shama G (2001) Listeria monocytogenes adheres to many materials found in food-processing environments. J Appl Microbiol 90:1000–1005
Bloomfield SF, Scott E (1997) Cross-contamination and infection in the domestic environment and the role of chemical disinfectants. J Appl Microbiol 83:1–9. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1997.00199.x
Boks NP, Norde W, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (2008) Forces involved in bacterial adhesion to hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Microbiology 154:3122–3133. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2008/018622-0
Brilhante São José JF, Dantas Vanetti MC (2012) Effect of ultrasound and commercial sanitizers in removing natural contaminants and Salmonella enterica Typhimurium on cherry tomatoes. Food Control 24:95–99. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.09.008
Briñez WJ, Roig-Sagués AX, Hernández Herrero MM, López-Pedemonte T, Guamis B (2006) Bactericidal efficacy of peracetic acid in combination with hydrogen peroxide against pathogenic and non pathogenic strains of Staphylococcus spp., Listeria spp. and Escherichia coli. Food Control 17:516–521. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2005.02.014
Carpentier B, Cerf O (2011) Review-Persistence of Listeria monocytogenes in food industry equipment and premises. Int J Food Microbiol 145:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.01.005
Gandhi M, Chikindas ML (2007) Listeria: a foodborne pathogen that knows how to survive. Int J Food Microbiol 113:1–15. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.07.008
Kalmokoff ML, Austin JW, Wan XD, Sanders G, Banerjee S, Farber JM (2001) Adsorption, attachment and biofilm formation among isolates of Listeria monocytogenes using model conditions. J Appl Microbiol 91:725–734
Kim H, Bang J, Beuchat LR, Ryu JH (2008) Fate of Enterobacter sakazakii attached to or in biofilms on stainless steel upon exposure to various temperatures or relative humidities. J Food Prot 71:940–945
Martín-Espada MC, D’Ors A, Bartolomé MC, Pereira M, Sánchez-Fortún S (2014) Peracetic acid disinfectant efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms on polystyrene surfaces and comparison between methods to measure it. LWT Food Sci Technol 56:58–61. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2013.11.013
Ölmez H, Temur SD (2010) Effects of different sanitizing treatments on biofilms and attachment of Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes on green leaf lettuce. LWT Food Sci Technol 43:964–970. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2010.02.005
Palmer J, Flint S, Brooks J (2007) Bacterial cell attachment, the beginning of a biofilm. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:577–588. doi:10.1007/s10295-007-0234-4
Parizzi SQF (1999) Adesão bacteriana em diferentes superfícies avaliada pela microscopia de epifluorescência e contagem em placas. Dissertation, Federal University of Viçosa
Riazi S, Matthews KR (2011) Failure of foodborne pathogens to develop resistance to sanitizers following repeated exposure to common sanitizers. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65:374–378. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2010.12.001
Rodriguez A, Autio WR, McLandsborough LA (2008) Effect of surface roughness and stainless steel finish on Listeria monocytogenes attachment and biofilm formation. J Food Prot 71:170–175
Rossoni EMM, Gaylarde CC (2000) Comparison of sodium hypochlorite and peracetic acid as sanitising agents for stainless steel food processing surfaces using epifluorescence microscopy. Int J Food Microbiol 61:81–85. doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(00)00369-X
Sinde E, Carballo J (2000) Attachment of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel, rubber and polytetrafluorethylene: the influence of free energy and the effect of commercial sanitizers. Food Microbiol 17:439–447. doi:10.1006/fmic.2000.0339
Srey S, Jahid IK, Ha SD (2013) Biofilm formation in food industries: a food safety concern. Food Control 31:572–585. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.12.001
Teixeira P, Lima J, Azeredo J, Oliveira RM (2008) Adhesion of Listeria monocytogenes to materials commonly found in domestic kitchens. Int J Food Sci Technol 43:1239–1244
Van Netten P, Huis in’t Veld JH, Mossel DA (1994) The immediate bactericidal effect of lactic acid on meat-borne pathogens. J Appl Bacteriol 77:490–496
Acknowledgments
The authors thank CNPq, CAPES, FAPERGS, Science and Technology Secretary RS and URI-Erechim for the financial support for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beltrame, C.A., Martelo, E.B., Mesquita, R.A. et al. Adhesion of Listeria monocytogenes to cutting board surfaces and removal by different sanitizers. J. Verbr. Lebensm. 10, 41–47 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-014-0923-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-014-0923-7