Abstract
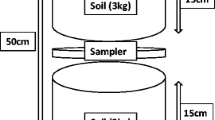
The hydrolysis of surface-applied granular urea (≅ 15 mg of urea/particle) in 14 unsaturated soils as influenced by the amounts and the sequence of additions of urea and water and studied using open and covered soil column systems was in the following order: well-mixed surface-applied surface-applied surface-applied urea, granular urea, granular urea, granular urea, water added > water added > water added ≧ water added before, after, before, before, no drying no drying no drying drying The retarded hydrolysis' of surface-applied granular urea is attributed to retarded soil urease activity. Under the nondrying and drying conditions, the positive effect of increasing amounts of added water on the hydrolysis was less apparent when water was added 24–48 hours before than when it was added immediately after surface application of granular urea. When an increasing number of urea granules were evenly placed on a finite surface of unsaturated soil, the rate of urea application (quantity factor) increased but the percentage of urea hydrolyzed remained practically unchanged. These results suggest that it is necessary to consider ‘effective urea concentration’ and ‘effective urease activity’ for adequate understanding of in situ hydrolysis of broadcast fertilizer urea in unsaturated soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bremner JM and Mulvaney RL (1978) Urease activity in soils. In Burns RG, ed. Soil enzymes, pp 149–196. London: Academic Press
Hauck RD (1984) Significance of nitrogen fertilizer microsite reactions in soil. In Hauck RD, ed. Nitrogen in crop production, pp 507–519. Madison, Wisc.: American Society of Agronomy
Hoare JP and Laidler KJ (1950) The molecular kinetics of the urea-urease system II. The inhibition by product. J Am Chem Soc 72, 2487–2489
Kistiakowsky GB and Rosenberg AJ (1952) The kinetics of urea hydrolysis by urease. J Am Chem Soc 74, 5020–5024
Ladd JN and Jackson RB (1982) Biochemistry of ammonifications. Agronomy 22, 173–228
Martens DA and Bremner JM (1984) Effectiveness of phosphoamides for retardation of urea hydrolysis in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48, 302–305
Sankhayan SD and Shukla UC (1976) Rates of urea hydrolysis in five soils of India. Geoderma 16, 171–178
Savant NK, James AF and McClellan GH (1986) Effect of soil bulk density on hydrolysis of surface-applied urea in unsaturated soils. Fert Res (in press)
Savant NK, James AF and McClellan GH (1983) Hydrolysis of surface-placed granular urea in unsaturated soil. Agronomy Abstracts, pp 160–161
Savant NK, James AF and McClellan GH (1983) Effect of incubation temperature on hydrolysis of surface-placed granular urea in unsaturated soil. Progress Report, Fertilizer Technology Division, International Fertilizer Development Center, Muscle Shoals, Alabama (unpublished)
Singh R and Nye PH (1984) The effect of soil pH and high urea concentrations on urease activity in soil. J Soil Sci 35, 519–527
Singh R and Nye PH (1984) Diffusion of urea, ammonia, and soil alkalinity from surface-applied urea. J Soil Sci 35, 529–538
Technicon (1974) Urea nitrogen. Technicon Method No. SE 40001 FD 4, Technicon Instrument Corporation, Tarrytown, New York
Vlek PLG and Carter MF (1983) The effect of soil environment and fertilizer modifications on the rate of urea hydrolysis. Soil Sci 136, 56–63
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savant, N., James, A. & McClellan, G. Effect of amounts and sequence of additions of urea and water on hydrolysis of surface-applied granular urea in unsaturated soils. Fertilizer Research 11, 231–243 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063320
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063320