Summary
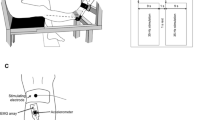
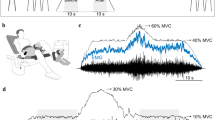
Mechanical and electrical properties were studied for the first dorsal interosseous muscle of the dominant (d-FDI) and non-dominant hand (nd-FDI). Observations were made before, during and after a fatigue test, fatigue being evoked by percutaneous electrical stimulation of the ulnar nerve. The test consisted of 30 Hz bursts of ten supramaximal 0.1 ms pulses, repeated once a second for 5 min. The measurements included the amplitude of the first and fifth compound muscle action potentials (M-waves) within bursts, the peak burst force and the amplitude and time course of single twitches. At the end of the fatigue test, burst force had decreased to about the same extent in the FDI of both hands. The final decline in first M-wave amplitude was, however, significantly more pronounced for the nd-FDI than for the d-FDI. There were no longer any significant discrepancies between the two muscles after a subsequent recovery-period of 15 min. Comparisons among nd-FDI of various individuals demonstrated the presence of significant inter-individual differences in fatigue-related force-drop without any associated differences in M-wave decline. Intra-individual variability was similar for fatigue-related force-drop and M-wave decline.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bigland-Ritchie B, Jones DA, Woods JJ (1979) Excitation frequency and muscle fatigue: electrical responses during human voluntary and stimulated contractions. Exp Neurol 64:414–427
Bigland-Ritchie B, Kukulka CG, Lippold OCJ, Woods JJ (1982) The absence of neuromuscular transmission failure in sustained maximal voluntary contractions. J Physiol (Lond) 330:265–278
Bigland-Ritchie B, Johansson R, Lippold OCJ, Woods JJ (1983) Contractile speed and EMG changes during fatigue of sustained maximal voluntary contractions. J Neurophysiol 50:313–324
Burke D, Skuse NF, Lethlean AK (1974) Isometric contraction of the abductor digiti minimi muscle in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 37:825–834
Cooper RG, Edwards RHT, Gibson H, Stokes MJ (1988) Human muscle fatigue: frequency dependence of excitation and force generation. J Physiol (Lond) 397:585–599
De Luca CJ, Sabbahi MA, Roy SH (1986) Median frequency of the myoelectric signal. Effects of hand dominance. Eur J Appl Physiol 55:457–464
Duchateau J, Hainaut K (1984) Training effects on muscle fatigue in man. For J Appl Physiol 53:248–252
Duchateau J, Hainaut K (1985) Electrical and mechanical failures during sustained and intermittent contractions in humans. J Appl Physiol 58:942–947
Edström L, Grimby L (1986) Effect of exercise on the motor unit. Muscle Nerve 9:104–126
Gandevia SC, McKenzie DK (1988) Activation of human muscles at short muscle lengths during maximal static efforts. J Physiol (Lond) 407:599–613
Hultman E, Sjöholm H (1983) Electromyogram, force and relaxation time during and after continuous electrical stimulation of human skeletal muscle in situ. J Physiol (Lond) 339:33–40
Jones DA, Bigland-Ritchie B, Edwards RHT (1979) Excitation frequency and muscle fatigue: mechnical responses during voluntary and stimulated contractions. Exp Neurol 64:401–413
Kernell D, Donselaar Y, Eerbeek O (1987) Effects of physiological amounts of high- and low-rate chronic stimulation on fasttwitch muscle of the cat hindlimb. II. Endurance-related properties. J Neurophysiol 58:614–627
Merton PA (1954) Voluntary strength and fatigue. J Physiol (Lond) 123:553–564
Milner-Brown HS, Miller RG (1986) Muscle membrane excitation and impulse propagation velocity are reduced during muscle fatigue. Muscle Nerve 9:367–374
Naess K, Storm-Mathisen A (1955) Fatigue of sustained tetanic contractions. Acta Physiol Scand 34:351–366
Rutherford OM, Jones DA (1988) Contractile properties and fatiguability of the human adductor pollicis and first dorsal interosseus: a comparison of the effects of two chronic stimulation patterns. J Neurol Sci 85:319–331
Stephens JA, Taylor A (1972) Fatigue of maintained voluntary muscle contraction in man. J Physiol (Lond) 220:1–18
Tanaka M, McDonagh MJN, Davies CTM (1984) A comparison of the mechanical properties of the first dorsal interosseous in the dominant and non-dominant hand. Eur J Appl Physiol 53:17–20
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zijdewind, C., Bosch, W., Goessens, L. et al. Electromyogram and force during stimulated fatigue tests of muscles in dominant and non-dominant hands. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 60, 127–132 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00846032
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00846032