Summary
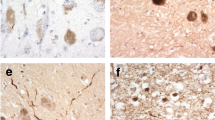
The distribution and severity of the neuropathological changes in 57 cases of Alzheimer's disease, and 11 patients with Down's syndrome were investigated with reference to the cerebellum: A modified silver stain and a monoclonal antibody raised against amyloid β-protein were used to identify amyloid plaques. The highest incidence of amyloid plaques in the cerebellum (93%) was found in the group of patients who developed dementia before 65 years of age. This figure dropped to 56% in those patients with dementia beginning after 75 years. In 37 of these cases the distribution of the pathological changes of the disease were also examined in the brain stem. The severity of the pathological changes in the cerebellum corresponded to the involvement of the brain stem nuclei with connections to the cerebellar cortex. The possibility that the disease process spreads to the cerebellum by involving the fibres from the brain stem is discussed with reference to previous anatomical and neurochemical studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas JE, Brodal P (1988a) Demonstration of a mamilloponto-cerebellar pathway. A multi tracer study in the cat. Eur J Neurosci 1:61–74
Allsop D, Landon M, Kidd M, Lowe JS, Reynolds GP, Gardner A (1986) Monoclonal antibodies raised against a subsequence of cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 68:252–256
Barcikowska M, Wisniewski HM, Bancher C, Grundke-Iqbal I (1989) About the presence of paired helical filaments in dystrophic neurites participating in the plaque formation. Acta Neuropathol 78:225–231
Bloom FE, Hoffer BJ, Siggins GR (1971) Studies on norepinephrine-containing afferents to Purkinje cells of rat cerebellum. I. Localisation of the fibres and their synapses. Brain Res 25:501–521
Bondareff W, Mountjoy Q, Roth M, Rossor M, Iversen L, Reynolds G (1987) Age and histopathologic heterogeneity in Alzheimer's disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 44:412–417
Braak H, Braak E, Boh J, Lang W (1989) Alzheimer's disease: amyloid plaques in the cerebellum. J Neurol Sci 93:277–287
Brodal A (1981) Neurological anatomy in relation to clinical medicine. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 294–393
Brodal P (1979) The pontocerebellar projection in the Rhesus monkey: an experimental study with retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. Neuroscience 4:193–208
Brodal P (1980) The projection from the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis to the cerebellum in the Rhesus monkey. Exp Brain Res. 38:29–36
Brodal P (1982) The cerebro-ponto-cerebellar pathway: salient features of its organisation. Exp Brain Res [Suppl] 6:108–133
Brun A, Gustafson L (1976) Distribution of cerebral degeneration in Alzheimer's disease a clinico-pathological study Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci 223:15–33
Bugiani O, Giaccone G, Frangione B, Ghetti B, Tagliavini F (1989) Alzheimer's patients: pre-amyloid deposits are more widely distributed than senile plaques throughout the central nervous system. Neurosci Lett 103:263–268
Cole G, Williams P, Alldrick D, Singhrao S (1989) Amyloid plaques in the cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease. Clin Neuropathol 4:188–191
Cross RB (1982) Demonstration of neurofibrillary tangles in paraffin sections. A quick and simple method using Palmgren's method. Med Lab Sci 39:67–69
Curcio C, Kemper T (1984) Nucleus raphe dorsalis in dementia of the Alzheimer's type: neurofibrillary changes and neuronal packing density. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43:359–368
Dewar D, Chalmers D, Shand A, Graham D, McCulloch J (1990) Selective Reduction of Quisqualate (AMPA) receptors in Alzheimer cerebellum. Ann Neurol 28:805–810
Esiri MM, Wilcock GK (1986) Cerebral Amyloid angiopathy in dementia and old age. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:1221–1226
Esiri MM, Pearson RCA, Steele J, Bowen D, Powell TPS (1990) A Quantitative study of the neurofibrillary tangles and the choline acetyl transferase activity in the cerebral cortex and amygdala in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53:161–165
Fuxe K (1965) Evidence for the existence of monoamine neurons in the central nervous system. IV. Distribution of monoamine terminals in the central nervous system. Acta Physiol Scand 64:37–85
Geinisman Y, Bondareff W, Telstar A (1979) Transport of [3H] fucose-labelled glycoproteins in the septo-hippocampal pathway of young adult and senescent rats. Brain Res 125:182–186
Gilman S, Bloedel J, Lechtenberg R (1981) Disorders of the cerebellum. In: Contemporary neurology series. FAD Avis Company, Philadelphia, pp 63–70
Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer's disease. Initial report of the purification and characterisation of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120:885–890
Haga C, Yamaguchi, Ikeda K, Kossa KAK (1989) PAM modified methenamine silver stain for senile plaques-comparison with β-protein immunostaining. Dementia 3:417–422
Hewlins MJE, Weeks I, Jasani B (1984) Non-deleterious dinitrophenyl (DNP) hapten labelling of antibody protein. J Immunol Methods 70:111–118
Hirani N, Onodera S, Kawamura K (1982) Cerebellotectal projections studied in cats with horseradish peroxidase or tritiated amino acid axonal transport. Exp Brain Res 48:1–12
Hokefelt T, Fuxe K (1969) Cerebellar monoamine terminals: a new type of afferent fibre to the cortex cerebelli. Exp Brain Res 9:63–72
Hopkins DA, Holstege (1978) Amygdaloid projections to the mesencephalon, pons and medulla oblongata in the cat. Exp Brain Res 32:529–547
Isekii E, Matsushita M, Kosaka K, Kondo H, Ishii T, Amano N (1989) Distribution and Morphology of brain stem plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 78:131–136
Jacobs BL, Foote SL, Bloom FE (1978) Differential projections of neurons within the dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat: a horseradish peroxidase study. Brain Res 147:149–153
Joachim CL, Morris JH, Selkoe D (1989) Diffuse senile plaques occur commonly in the cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Clin Pathol 135:309–319
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42:1097–1105
Mann DMA, Yates PO (1983) Serotonin nerve cells in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46:96
Mann DMA, Yates PO, Marcyniuk B, Ravindera CR (1986) The topography of plaques and tangles in Down's syndrome patients of different ages. Neuropathol Appl Neuropathol 12:427–437
Mann DMA, Jones D, Prinja D, Purkiss MS (1990) The prevalence of amyloid (A4) protein deposits within the cerebral and cerebellar cortex in Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 80:318–327
Marcyniuk B, Mann DMA, Yates PO (1986) Loss of nerve cells from locus coeruleus in Alzheimer's disease is topographically arranged. Neurosci Lett 64:247–252
Ogomori K, Kitamoto T, Tateishii J, Sato Y, Suetsugu M, Abe M (1989) β-protein amyloid is widely distributed in the central nervous system of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 134:243–251
Oliver C, Holland AJ (1986) Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease: a review. Psychol Med 16:307–322
Olszewski J, Baxter D (1954) Cytoarchitecture of the human brain stem. Karger, New York
Pearson RCA, Powell TPS (1990) The neuroanatomy of Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurosci 2:101–122
Pearson RCA, Esiri MM, Hirons RW, Wilcock GK, Powell TPS (1985) Anatomical correlates of the distribution of the pathological changes in the neocortex in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4531–4534
Perry TL, Currier RD, Hansen S (1977) Aspartate taurine imbalance in dominantly inherited olivo-ponto-cerebellar atrophy. Neurology 27:257–267
Pickel VM, Segal M, Bloom F (1974) A radio-autographic study of the efferent pathways of the locus coeruleus. J Comp Neurol 155:15–42
Pro JD, Smith CH, Sumi M (1980) Presenile Alzheimer's disease. Amyloid plaques in the cerebellum. Neurology 30:820–825
Probst A, Brun N, Schweiler H, Lauten Schlager (1981) A special type of senile plaque, possibly an initial stage. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74:133–141
Ross CA, Bredt D, Synder SH (1990) Messenger molecules in the cerebellum. Trends Neurosci 13:216–222
Rossor MN, Iversen LL, Reynolds GP, Mountjoy CQ, Roth M (1984) Neurochemical characteristics of early and late onset types of Alzheimer's disease. Br Med J 288:961–964
Saper CB, Wainer BH, German DC (1987) Axonal and transneuronal transport in the transmission of neurological disease: potential role in system degenerations, including Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience 23:389–398
Shinnar S, Maciewicz RJ, Shofer RJ (1975) A raphe projection of the cat cerebellar cortex. Brain Res 97:139–143
Suenaga T, Hirano A, LLena J, Ksieza K, Reding H, Yen SH, Dickson D (1990) Modified Bielchwsky and immunocytochemical studies on cerebellar plaques in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 49:31–40
Tomlinson BE, Corsellis JAN (1984) Ageing and the dementias In: Adams HJ, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 4th edn. Edward Arnold, London, pp 951–1025
Wisniewski KE, Wisniewski HM, Wen GY (1985) Occurrence of neuropathological changes and dementia of Alzheimer's disease in Down's syndrome. Ann Neurol 17:278–282
Yamaguchi H, Hirani S, Morimatsu M, Shoji M, Ihara Y (1988) A variety of cerebral amyloid deposits in the brains of Alzheimer's type dementia demonstrated by β-protein immunostaining. Acta Neuropathol 76:541–549
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cole, G., Neal, J.W., Singhrao, S.K. et al. The distribution of amyloid plaques in the cerebellum and brain stem in Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease: a light microscopical analysis. Acta Neuropathol 85, 542–552 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230495
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230495