Abstract
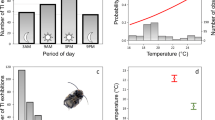
Tonic immobility (TI) is an unlearned behavioral response characterized by a state of immobility and torpor. Effect of inter-trial interval on duration of tonic immobility was assessed in thirty, juvenile lemon sharks (Negaprion brevirostris). Regression analyses showed that massed trials of 12 per session increased the average duration of tonic immobility by 475 sec compared to spaced trials of 1 per session. Each experiment was composed of 24 trials. TI is stable and durations much longer in the lemon shark than for other sharks. These findings have enabled us to develop a quantitative bioassay for use in testing chemical shark repellents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Chertok, L. 1968. Animal hypnosis. In Abnormal Behavior in Animals. pp. 129–158. Edited by M.W. Fox, W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia.
Crawford, F.T. 1977. Induction and duration of tonic immobility. Psychol. Rec. 1: 89–107.
Gallup, G.G. Jr. 1974. Animal hypnosis: Factual status of a fictional concept. Psychol. Bull. 81: 836–853.
Gallup, G.G. Jr. Boren, J.C., Suarez, S.D., Wallnau, L.B. and Gagliardi, G.L. 1980. Evidence for the integrity of central processing during tonic immobility. Physiol. Behav. 23: 189–194.
Gallup, G.G. Jr., Ledbetter, D.H. and Maser, J.D. 1976. Strained differences among chickens in immobility. J. Comp. Physiol. 90: 1075–1081.
Gruber, S.H. 1980. Keeping sharks in captivity. J. Aquaricult. 1: 6–14.
Gruber, S.H. and Zlotkin, E. 1982. Bioassay of surfactants as shark repellants. Nav. Res. Rev. 2: 18–27.
Hennig, C.W. 1978. Tonic immobility in the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). Primates 19: 333–342.
Hennig, C.W. 1979. Biphasic effects of serotonin on tonic immobility in domestic fowl. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 12: 519–523.
Karmanova, I.G., Churnosov, E.V. and Popova, D.I. 1976. Differences in the diurnal form of rest of the brown bullhead (Ictalurus nebulosis) and frog (Rana temporaria). Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 12: 572–578.
Lefebure, L. and Sabourin, M. 1977. Effects of spaced and massed repeated elicitation on tonic immobility in the goldfish (Carassius auratus). Behav. Biol. 211: 300–305.
Nash, R.F. and Gallup, G.G. Jr. 1976. Habituation and tonic immobility in domestic chickens. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 90: 870–876.
Ratner, S.L. 1977. Immobility of invertebrates: What can we learn? Psychol. Rec. 1: 1–13.
Ternes, J.W. 1977. Circadian susceptibility to animal hypnosis. Psychol. Rec. 1: 15–19.
Thompson, R.F. and Spencer, W.A. 1966. Habituation: A model phenomenon for the study of neuronal substrates of behavior. Psychol. Rev. 73: 16–43.
Whitman, P.A., Marshall, J.A. and Keller, E.L. 1986. Tonic immobility in the smooth dogfish shark, Mustelus canis Copeia 1986: 829–832.
Zlotkin E. and Gruber, S.H. 1984. Synthetic surfactants: A new approach to the development of shark repellants. Arch. Toxicol. 56: 55–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watsky, M.A., Gruber, S.H. Induction and duration of tonic immobility in the lemon shark, Negaprion brevirostris . Fish Physiol Biochem 8, 207–210 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004459
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004459