Abstract
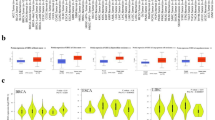
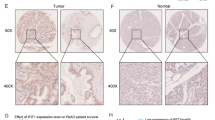
The transcriptional factor Forkhead box protein C2 (FOXC2) was recently demonstrated to be up-regulated in various cancer types. However, its expression profile and the biological functions in pancreatic cancer remain unknown. In this study, we examined the expression pattern of FOXC2 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tissues and investigated the functions of FOXC2 in the progression of PDAC. It was found that the expression of FOXC2 was up-regulated in PDAC samples. Forced expression of FOXC2 promoted the growth and migration of the PDAC cells, while knocking down the expression of FOXC2 inhibited the growth and migration of the PDAC cells. Moreover, FOXC2 was found to interact with beta-catenin and promote cell growth by activating beta-catenin/TCF signaling. Taken together, this study demonstrated the oncogenic roles of FOXC2 in PDAC, and FOXC2 might be a therapeutic target for PDAC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Lam EW, Brosens JJ, Gomes AR, Koo CY. Forkhead box proteins: tuning forks for transcriptional harmony. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:482–95.
Kume T. The cooperative roles of Foxc1 and Foxc2 in cardiovascular development. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;665:63–77.
Ren YH, Liu KJ, Wang M, et al. De-SUMOylation of FOXC2 by SENP3 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2014;5:7093–104.
Hollier BG, Tinnirello AA, Werden SJ, et al. FOXC2 expression links epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73:1981–92.
Hayashi H, Sano H, Seo S, Kume T. The Foxc2 transcription factor regulates angiogenesis via induction of integrin beta3 expression. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:23791–800.
Mortazavi F, An J, Dubinett S, Rettig M. p120-catenin is transcriptionally downregulated by FOXC2 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8:762–74.
Seo S, Fujita H, Nakano A, Kang M, Duarte A, Kume T. The forkhead transcription factors, Foxc1 and Foxc2, are required for arterial specification and lymphatic sprouting during vascular development. Dev Biol. 2006;294:458–70.
Sano H, Leboeuf JP, Novitskiy SV, et al. The Foxc2 transcription factor regulates tumor angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;392:201–6.
Liu B, Han SM, Tang XY, Han L, Li CZ. Overexpressed FOXC2 in ovarian cancer enhances the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and invasion of ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2014;31:2545–54.
Zheng CH, Quan Y, Li YY, Deng WG, Shao WJ, Fu Y. Expression of transcription factor FOXC2 in cervical cancer and effects of silencing on cervical cancer cell proliferation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:1589–95.
Jiang S, Zhu L, Tang H, et al. Ape1 regulates WNT/beta-catenin signaling through its redox functional domain in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2015;47:610–20.
Cui J, Jiang W, Wang S, Wang L, Xie K. Role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in drug resistance of pancreatic cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18:2464–71.
Zeng G, Germinaro M, Micsenyi A, et al. Aberrant Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia. 2006;8:279–89.
Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149:1192–205.
Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–80.
You W, Fan L, Duan D, et al. Foxc2 over-expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells stimulates osteogenic differentiation and inhibits adipogenic differentiation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;386:125–34.
Savage J, Voronova A, Mehta V, Sendi-Mukasa F, Skerjanc IS. Canonical Wnt signaling regulates Foxc1/2 expression in P19 cells. Differentiation. 2010;79:31–40.
Jho EH, Zhang T, Domon C, Joo CK, Freund JN, Costantini F. Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:1172–83.
Behrens J, Jerchow BA, Wurtele M, et al. Functional interaction of an axin homolog, conductin, with beta-catenin, APC, and GSK3beta. Science. 1998;280:596–9.
Deng YZ, Chen PP, Wang Y, et al. Connective tissue growth factor is overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and promotes tumorigenicity through beta-catenin-T-cell factor/Lef signaling. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:36571–81.
Jiang J, Tian S, Yu C, Chen M, Sun C. TRIM37 promoted the growth and migration of the pancreatic cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4078-7.
Endo H, Watanabe T, Sugioka Y, Niioka M, Inagaki Y, Okazaki I. Activation of two distinct MAPK pathways governs constitutive expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 2009;35:1237–45.
Ma J, Sawai H, Ochi N, et al. PTEN regulates angiogenesis through PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009;331:161–71.
Cui YM, Jiang D, Zhang SH, et al. FOXC2 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation through inhibition of FOXO3a and activation of MAPK and AKT signaling pathways. Cancer Lett. 2014;353:87–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Lei Cui and Shengchun Dang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, L., Dang, S., Qu, J. et al. FOXC2 is up-regulated in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and promotes the growth and migration of cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37, 8579–8585 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4607-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4607-4