Abstract
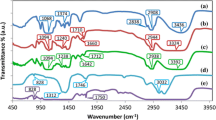
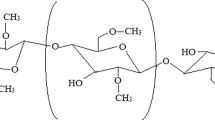
The present study illustrates cadmium chloride (CdCl2)-doped hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) polymer electrolyte films. Solution cast method is employed to prepare polymer electrolyte samples of HPMC complexed with various concentrations of CdCl2 (1–4 %, wt.%). Structural and thermal studies of these polymer samples were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). XRD results showed that the amorphous domains of HPMC polymer matrix were increased with increase in CdCl2 salt concentration. DSC results revealed that the presence of CdCl2 in the polymer matrix increases the melting temperature; however, it is observed that the heat of fusion (ΔH f ) is high for pure HPMC films. The variation in the film morphology was examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Direct current (dc) conductivity was measured in the temperature range 313–383 K. The magnitude of electrical conductivity was found to be increased with increasing salt concentration and temperature. The activation energy region data (region I and region II) indicated the dominance of ion-type charge transport in these polymer electrolyte films. HPMC polymer electrolytes with 4 % CdCl2 salt concentration exhibit the least crystallinity and the highest conductivity 1.01 × 10−6 Scm−1 at 313 K.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armand MB (1993) J Solid State Ionics 9/10:745
Papke BL, Ratner MA, Shriver DF (1992) J Electrochem Soc 129:1694
Berthier C, Gorecki W, Miner M, Amand MB, Chabagno JM, Riguad P (1983) J Solid State Ionics 11:91
Armand MB (1986) Annu Rev Mater Sci 16:245–261
Chaubey A, Gerard M, Singhal R, Singh VS, Malhotra BD (2000) J Electrochim Acta 46:723
Lascaud S, Perrier M, Vallee A, Besner S, Prud home J, Armand M (1994) J Macromol 27:7469
Balaki Bhargav P, Madhu Mohan V, Sharma AK, Rao VVRN (2007) J Ionics 13(3):173–178
Subramanya Kilarkaje V, Manjunatha S, Raghu MVN, Prasad A, Devendrappa H (2011) J Phys D: Appl Phys 44:105403
Subramanya K, Raghu S, Devendrappa H (2012) AIP Conf Proc Vol., 1447 , 965
Nanda Prakash MB, Manjunath A, Somashekar R (2013) J Adv Condens Matter Phys 35:1–6
Rotta J, Minatti E, Barret PLM (2011) J Cienc Tecnol Aliment Campinas 31(2):450–455
Honary S, Ebrahimi P, Emrani N (2010) J Pharma Bio Sci V1(2):1–8
Hardy IJ, Cook WG, Melia CD (2006) J Pharma Bio Sci 311(1–2):26–32
Bruce PG, Vincent CA (1993) J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 89:3187–3203
Colin, Durizot E (1994) J Mater Sci 9:8
Liu B, Xu GQ, Gan LM, Chew CH, Li WS, Shen ZX (2001) J Appl Phys 89:1059
Yukoh S, Sumihiro S, Makoto O (2006) Int J Pharm 317(2):120–126
Madhu Mohan V, Raja V, Sharma AK, Narasimha Rao VVRN (2004) J Mater Chem Phys 94:177
Bhargav PB, Mohan VM, Sharma AK, Rao VVRN (2009) J Curr Appl Phys 9:165–171
Malathi J, Kumaravadivel M, Brahmanandhan GM, Hema M, Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S (2010) J Non-Cryst Solids 356:2277–2281
Hermans PH, Weidinger A (1961) J Macromol Chem 24:44
Sangappa D et al (2008) J Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res 266:3975–3980
Zhang S, Lee JY, Hong L (2004) J Power Sources 126(1–2):125–133
Chu PP, Reddy MJ (2003) J Power Sources 115:288
Karmakar A, Ghosh A (2011) J Nanoparticle Res 13:2989–2996
Subba R, Sharma AK, Narasimha Rao VVR (2006) J Polym Sci 47:1318
HiranKumar G, Selvasekarapandian S, Kuwata N, Kawamura J, Hattori T (2005) J Power Sources 144:262
Chakraborty G et al (2011) J Solid State Commun 151:754–758
Janaki Rami Reddy T, Achari VBS, Sharma AK, Rao VVRN (2007) J Ionics 13:435–439
Omed Gh A, Tahir DA, Ahmad SS, Ahmad HT (2013) IOSR-JAP 4:52–57
Devendrappa H, Subba Rao UV, Ambika Prasad MVN (2006) J Power Sources 155(2):368
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge all the support and the useful discussion by Professor Srikantaiah, retired Scientist, BARC, Mumbai. Thanks to the technical staff at SID and Material Science Department, IISc, Bangalore for DSC and SEM analysis. We thank Grian Technologies Pvt. Limited, Bangalore for their support in electrical conductivity studies. A special thanks to Dr Shibu M Eappen, Scientist in charge, SAIF Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin, for XRD measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rani, N.S., Sannappa, J., Demappa, T. et al. Effects of CdCl2 concentration on the structural, thermal and ionic conductivity properties of HPMC polymer electrolyte films. Ionics 21, 133–140 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1151-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1151-y