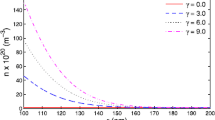
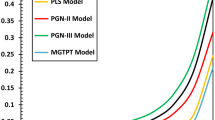
Abstract
Photothermal spectroscopy is a method of measuring the optical absorption and thermal properties of semiconductor materials using high-sensitivity spectroscopic techniques. Heating occurs due to light, which is absorbed but not dissipated by emission. In this paper, a new model is provided that can be used to understand the process of optical thermal transfer and the interaction between elastic plasma waves and heat. The proposed photothermal model is described by the Moore–Gibson–Thompson heat equation. Using the proposed model, the thermal and photoacoustic effects in an infinite isotropic and homogeneous body with a cylindrical cavity of semiconductor material crossed into a fixed magnetic field and subjected to high-intensity laser heat flux were investigated. The inner surface of the cavity is considered to be traction-free, and the carrier density is photogenerated by a laser pulse heat flux that decays exponentially. The numerical calculations for the components of thermal stresses, displacement, temperature field, and carrier density are obtained using the Laplace transform approach. The propagation of heat, elastic, and plasma waves, as well as the distributions of each investigated field, were examined and explained. The comparison is also used to see how different thermal response features, such as thermal relaxation, laser pulse duration, and lifetime, affect the thermoelastic response.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biot, M.A.: Thermoelasticity and irreversible thermodynamics. J. Appl. Phys. 27, 240–253 (1956)
Lord, H.W., Shulman, Y.: A generalized dynamical theory of thermoelasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 15(5), 299–309 (1967)
Green, A.E., Lindsay, K.A.: Thermoelasticity. J. Elast. 2(1), 1–7 (1972)
Green, A.E., Naghdi, P.M.: A re-examination of the basic postulates of thermomechanics. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 432, 171–194 (1991)
Green, A.E., Naghdi, P.M.: On undamped heat waves in an elastic solid. J. Therm. Stress. 15(2), 253–264 (1992)
Green, A.E., Naghdi, P.M.: Thermoelasticity without energy dissipation. J. Elast. 31(3), 189–208 (1993)
Abouelregal, A.E.: Modified fractional thermoelasticity model with multi-relaxation times of higher order: application to spherical cavity exposed to a harmonic varying heat. Waves Random Complex Media (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2019.1628320
Abouelregal, A.E.: Two-temperature thermoelastic model without energy dissipation including higher order time-derivatives and two phase-lags. Mater. Res. Express 6(11), 116535 (2019)
Abouelregal, A.E.: On Green and Naghdi thermoelasticity model without energy dissipation with higher order time differential and phase-lags. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 6(3), 445–456 (2020)
Abouelregal, A.E.: A novel generalized thermoelasticity with higher-order time-derivatives and three-phase lags. Multidiscip. Model. Mater. Struct. 16(4), 689–711 (2019)
Abouelregal, A.E.: Three-phase-lag thermoelastic heat conduction model with higher-order time-fractional derivatives. Indian J. Phys. 94, 1949–1963 (2020)
Abouelregal, A.E., Elhagary, M.A., Soleiman, A., Khalil, K.M.: Generalized thermoelastic-diffusion model with higher-order fractional time-derivatives and four-phase-lags. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/15397734.2020.1730189
Lasiecka, I., Wang, X.: Moore–Gibson–Thompson equation with memory, part II: general decay of energy. J. Diff. Equ. 259, 7610–7635 (2015)
Quintanilla, R.: Moore-Gibson-Thompson thermoelasticity. Math. Mech. Solids 24, 4020–4031 (2019)
Quintanilla, R.: Moore-Gibson-Thompson thermoelasticity with two temperatures. Appl. Eng. Sci. 1, 100006 (2020)
Abouelregal, A.E., Ahmed, I.-E., Nasr, M.E., Khalil, K.M., Zakria, A., Mohammed, F.A.: Thermoelastic processes by a continuous heat source line in an infinite solid via Moore–Gibson–Thompson thermoelasticity. Materials 13(19), 4463 (2020)
Abouelregal, A.E., Ahmad, H., Nofal, T.A., Abu-Zinadah, H.: Moore–Gibson–Thompson thermoelasticity model with temperature-dependent properties for thermo-viscoelastic orthotropic solid cylinder of infinite length under a temperature pulse. Phys. Scr. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/abfd63
Aboueregal, A.E., Sedighi, H.M.: The effect of variable properties and rotation in a visco-thermoelastic orthotropic annular cylinder under the Moore Gibson Thompson heat conduction model. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 235(5), 1004–1020 (2021)
Aboueregal, A.E., Sedighi, H.M., Shirazi, A.H., Malikan, M., Eremeyev, V.A.: Computational analysis of an infinite magneto-thermoelastic solid periodically dispersed with varying heat flow based on non-local Moore–Gibson–Thompson approach. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-021-00998-1
Abouelregal, A.E., Ersoy, H., Civalek, Ö.: Solution of Moore–Gibson–Thompson equation of an unbounded medium with a cylindrical hole. Mathematics 9(13), 1536 (2021)
Kaltenbacher, B., Lasiecka, I., Marchand, R.: Wellposedness and exponential decay rates for the Moore–Gibson–Thompson equation arising in high intensity ultrasound. Control Cybern. 40, 971–988 (2011)
Bazarra, N., Fernández, J.R., Quintanilla, R.: Analysis of a Moore-Gibson-Thompson thermoelastic problem. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 382(15), 113058 (2021)
Lotfy, K.: The elastic wave motions for a photothermal medium of a dual-phase-lag model with an internal heat source and gravitational field. Can. J. Phys. 94, 400–409 (2016)
Gordon, J.P., Leite, R.C.C., Moore, R.S., et al.: Long- transient effects in lasers with inserted liquid samples. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. 119, 501 (1964)
Todorovic, D.M., Nikolic, P.M., Bojicic, A.I.: Photoacoustic frequency transmission technique: electronic deformation mechanism in semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 85, 7716 (1999)
Song, Y.Q., Todorovic, D.M., Cretin, B., Vairac, P.: Study on the generalized thermoelastic vibration of the optically excited semiconducting microcantilevers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 47, 1871 (2010)
Lotfy, K., Abo-Dahab, S.M.: Two-dimensional problem of two temperature generalized thermoelasticity with normal mode analysis under thermal shock problem. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 12(8), 1709–1719 (2015)
Othman, M.I.A., Lotfy, K.: The influence of gravity on 2-D problem of two temperature generalized thermoelastic medium with thermal relaxation. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 12(9), 2587–2600 (2015)
Lotfy, K., Othman, M.I.A.: Effect of rotation on plane waves in generalized thermo-microstretch elastic solid with a relaxation time. Meccanica 47(6), 1467–1486 (2012)
Lotfy, K.: Effect of variable thermal conductivity during the photothermal diffusion process of semiconductor medium. Silicon 11, 1863–1873 (2019)
Youssef, H.M., El-Bary, A.A.: Generalized thermoelastic infinite layer subjected to ramp-type thermal and mechanical loading under three theories—state space approach. J. Therm. Stress. 32(12), 1293–1309 (2009)
Ezzat, M., El-Bary, A.A., Ezzat, S.: Combined heat and mass transfer for unsteady MHD flow of perfect conducting micropolar fluid with thermal relaxation. Energy Convers. Manag. 52(2), 934–945 (2011)
Ezzat, M.A., El-Bary, A.A.: MHD free convection flow with fractional heat conduction law. Magnetohydrodynamics 48(4), 503–522 (2012)
Ezzat, M.A., El-Bary, A.A.: Magneto-thermoelectric viscoelastic materials with memory-dependent derivative involving two-temperature. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 50(4), 549–567 (2016)
Song, Y.Q., Bai, J.T., Ren, Z.Y.: Study on the reflection of photothermal waves in a semiconducting medium under generalized thermoelastic theory. Acta Mech. 223, 1545–1557 (2012)
Othman, M.I.A., Marin, M.: Effect of thermal loading due to laser pulse on thermoelastic porous medium under G-N theory. Results Phys. 7, 3863–3872 (2017)
Rekhi, S., Tempere, J., Silvera, I.F.: Temperature determination for nanosecond pulsed laser heating. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74(8), 3820–3825 (2003)
Anzellini, S., Boccato, S.: A practical review of the laser-heated diamond anvil cell for university laboratories and synchrotron applications. Crystals 10(6), 459 (2020)
Pasternak, S., Aquilanti, G., Pascarelli, S., Poloni, R., Canny, B., Coulet, M.-V., Zhang, L.: A diamond anvil cell with resistive heating for high pressure and high temperature x-ray diffraction and absorption studies. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79(8), 085103 (2008)
Yilbas, B.S., Al-Dweik, A.Y., Al-Aqeeli, N., Al-Qahtani, H.M.: Laser Pulse Heating of Surfaces and Thermal Stress Analysis. Verlag: Springer International Publishing, Heidelberg (2014)
Todorovic, D.M.: Plasma, thermal, and elastic waves in semiconductors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74, 582 (2003)
Vasilev, A.N., Sandomirskii, V.B.: Photoacoustic effects in finite semiconductors. Sov. Phys. Semicond. 18, 1095 (1984)
Cattaneo, C.: A form of heat-conduction equations which eliminates the paradox of instantaneous propagation. C. R. 247, 431–433 (1958)
Vernotte, P.: Les paradoxes de la theorie continue de l’equation de lachaleur. C. R. 246, 3154–3155 (1958)
Vernotte, P.: Some possible complications in the phenomena of thermal conduction. C. R. 252, 2190–2191 (1961)
Abouelregal, A.E.: Two-temperature thermoelastic model without energy dissipation including higher order time-derivatives and two phase-lags. Mater. Res. Express 6, 116535 (2019)
Zenkour, A.M., Abouelregal, A.E.: Effect of temperature dependency on constrained orthotropic unbounded body with a cylindrical cavity due to pulse heat flux. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 10(1), JTST0019–JTST0019 (2015)
Honig, G., Hirdes, U.: A method for the numerical inversion of Laplace transform. J. Comp. Appl. Math. 10, 113–132 (1984)
Tzou, D.Y.: Macro-To Micro-Scale Heat Transfer: The Lagging Behavior. Taylor & Francis, Abingdon (1997)
Abbas, I.A., Aly, K.A.: A study on photothermal waves in a semiconductor material photogenerated by a focused laser beam. J. Mol. Eng. Mater. 04(02), 1650003 (2016)
Lotfy, K., Hassan, W., El-Bary, A.A., Kadry, M.A.: Response of electromagnetic and Thomson effect of semiconductor medium due to laser pulses and thermal memories during photothermal excitation. Results Phys. 16, 102877 (2020)
Khamis, A.K., El-Bary, A.A., Lotfy, K., Bakali, A.: Photothermal excitation processes with refined multi dual phase-lags theory for semiconductor elastic medium. Alex. Eng. J. 59(1), 1–9 (2020)
Abouelregal, A.E.: Magnetophotothermal interaction in a rotating solid cylinder of semiconductor silicone material with time dependent heat flow. Appl. Math. Mech. Engl. Ed. 42, 39–52 (2021)
Alharbi, A.M., Bayones, F.S.: Generalized magneto-thermo-viscoelastic problem in an infinite circular cylinder in two models subjected to rotation and initial stress. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 12(5), 1055–1066 (2018)
Soleiman, A., Abouelregal, A.E., Ahmad, H., Thounthong, P.: Generalized thermoviscoelastic model with memory dependent derivatives and multi-phase delay for an excited spherical cavity. Phys. Scr. 95(11), 115708 (2020)
Trajkovski, D., Čukić, R.: A coupled problem of thermoelastic vibrations of a circular plate with exact boundary conditions. Mech. Res. Commun. 26(2), 217–224 (1999)
Wang, X., Xu, X.: Thermoelastic wave in metal induced by ultrafast laser pulses. J. Therm. Stress. 25(5), 457–473 (2002)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Deanship of Scientific Research at Jouf University for funding this work through research Grant No. (DSR-2021-03-03177). We would also like to extend our sincere thanks to the College of Science and Arts in Al-Qurayyat for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors discussed the results, reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasr, M.E., Abouelregal, A.E. Light absorption process in a semiconductor infinite body with a cylindrical cavity via a novel photo-thermoelastic MGT model. Arch Appl Mech 92, 1529–1549 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02128-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02128-y