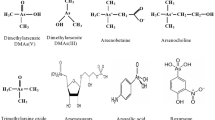
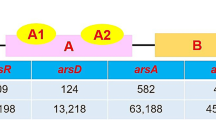
Abstract
Arsenic, distributed pervasively in the natural environment, is an extremely toxic substance which can severely impair the normal functions of living cells. Research on the genetic mechanisms of arsenic metabolism is of great importance for remediating arsenic-contaminated environments. Many organisms, including bacteria, have developed various strategies to tolerate arsenic, by either detoxifying this harmful element or utilizing it for energy generation. This review summarizes arsenic detoxification as well as arsenic respiratory metabolic pathways in bacteria and discusses novel arsenic resistance pathways in various bacterial strains. This knowledge provides insights into the mechanisms of arsenic biotransformation in bacteria. Multiple detoxification strategies among bacteria imply possible functional relationships among different arsenic detoxification/metabolism pathways. In addition, this review sheds light on the bioremediation of arsenic-contaminated environments and prevention of antibiotic resistance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernathy CO, Liu YP, Longfellow D, Aposhian HV, Beck B, Fowler B, Goyer R, Menzer R, Rossman T, Thompson C, Waalkes M (1999) Arsenic: health effects, mechanisms of actions, and research issues. Environ Health Perspect 107:593–597
Abernathy CO, Thomas DJ, Calderon RL (2003) Health effects and risk assessment of arsenic. J Nutr 133:1536S–1538S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/133.5.1536S
Afkar E, Lisak J, Saltikov C, Basu P, Oremland RS, Stolz JF (2003) The respiratory arsenate reductase from Bacillus selenitireducens strain MLS10. FEMS Microbiol Lett 226:107–112
Ahmann D, Roberts AL, Krumholz LR, Morel FM (1994) Microbe grows by reducing arsenic. Nature 371:750. https://doi.org/10.1038/371750a0
Ayyildiz D, Arga KY, Avci FG, Altinisik FE, Gurer C, Gulsoy Toplan G, Kazan D, Wozny K, Brugger B, Mertoglu B, Sariyar Akbulut B (2017) Transcriptomic analysis displays the effect of (−)-roemerine on the motility and nutrient uptake in Escherichia coli. Curr Genet 63:709–722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-016-0673-4
Bhattacharjee H, Rosen BP (1996) Spatial proximity of Cys113, Cys172, and Cys422 in the metalloactivation domain of the ArsA ATPase. J Biol Chem 271:24465–24470
Bhattacharjee H, Li J, Ksenzenko MY, Rosen BP (1995) Role of cysteinyl residues in metalloactivation of the oxyanion-translocating ArsA ATPase. J Biol Chem 270:11245–11250
Cansizoglu MF, Toprak E (2017) Fighting against evolution of antibiotic resistance by utilizing evolvable antimicrobial drugs. Curr Genet 63:973–976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-017-0703-x
Cao B, Chen C, DeMott MS, Cheng Q, Clark TA, Xiong X, Zheng X, Butty V, Levine SS, Yuan G, Boitano M, Luong K, Song Y, Zhou X, Deng Z, Turner SW, Korlach J, You D, Wang L, Chen S, Dedon PC (2014) Genomic mapping of phosphorothioates reveals partial modification of short consensus sequences. Nat Commun 5:3951. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4951
Chen Y, Rosen BP (1997) Metalloregulatory properties of the ArsD repressor. J Biol Chem 272:14257–14262
Chen CM, Misra TK, Silver S, Rosen BP (1986) Nucleotide sequence of the structural genes for an anion pump. The plasmid-encoded arsenical resistance operon. J Biol Chem 261:15030–15038
Chen J, Bhattacharjee H, Rosen BP (2015a) ArsH is an organoarsenical oxidase that confers resistance to trivalent forms of the herbicide monosodium methylarsenate and the poultry growth promoter roxarsone. Mol Microbiol 96:1042–1052. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.12988
Chen J, Madegowda M, Bhattacharjee H, Rosen BP (2015b) ArsP: a methylarsenite efflux permease. Mol Microbiol 98:625–635. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13145
Chen J, Yoshinaga M, Garbinski LD, Rosen BP (2016) Synergistic interaction of glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and ArsJ, a novel organoarsenical efflux permease, confers arsenate resistance. Mol Microbiol 100:945–953. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13371
Chen C, Wang L, Chen S, Wu X, Gu M, Chen X, Jiang S, Wang Y, Deng Z, Dedon PC, Chen S (2017) Convergence of DNA methylation and phosphorothioation epigenetics in bacterial genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:4501–4506. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1702450114
Dey S, Rosen BP (1995) Dual mode of energy coupling by the oxyanion-translocating ArsB protein. J Bacteriol 177:385–389
Dziarski R, Gupta D (2018) How innate immunity proteins kill bacteria and why they are not prone to resistance. Curr Genet 64:125–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-017-0737-0
Ellis PJ, Conrads T, Hille R, Kuhn P (2001) Crystal structure of the 100 kDa arsenite oxidase from Alcaligenes faecalis in two crystal forms at 1.64 A and 2.03 A. Structure 9:125–132
Endo G, Silver S (1995) CadC, the transcriptional regulatory protein of the cadmium resistance system of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. J Bacteriol 177:4437–4441
Erb TJ, Kiefer P, Hattendorf B, Gunther D, Vorholt JA (2012) GFAJ-1 is an arsenate-resistant, phosphate-dependent organism. Science 337:467–470. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1218455
Erbe JL, Taylor KB, Hall LM (1995) Metalloregulation of the cyanobacterial smt locus: identification of SmtB binding sites and direct interaction with metals. Nucleic Acids Res 23:2472–2478
Fisher E, Dawson AM, Polshyna G, Lisak J, Crable B, Perera E, Ranganathan M, Thangavelu M, Basu P, Stolz JF (2008) Transformation of inorganic and organic arsenic by Alkaliphilus oremlandii sp. nov. strain OhILAs. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1125:230–241. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1419.006
Garbarino JR, Bednar AJ, Rutherford DW, Beyer RS, Wershaw RL (2003) Environmental fate of roxarsone in poultry litter. I. Degradation of roxarsone during composting. Environ Sci Technol 37:1509–1514
Gladysheva TB, Oden KL, Rosen BP (1994) Properties of the arsenate reductase of plasmid R773. Biochemistry 33:7288–7293
Hasegawa H, Rahman MA, Kitahara K, Itaya Y, Maki T, Ueda K (2010) Seasonal changes of arsenic speciation in lake waters in relation to eutrophication. Sci Total Environ 408:1684–1690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.11.062
Hernandez-Maldonado J, Stoneburner B, Boren A, Miller L, Rosen M, Oremland RS, Saltikov CW (2016) Genome sequence of the photoarsenotrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira sp. strain BSL-9, isolated from a hypersaline alkaline arsenic-rich extreme environment. Genome Announc 4(5):e01139–16. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01139-16
Hervas M, Lopez-Maury L, Leon P, Sanchez-Riego AM, Florencio FJ, Navarro JA (2012) ArsH from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 is an efficient NADPH-dependent quinone reductase. Biochemistry 51:1178–1187. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi201904p
Huijbers MM, Montersino S, Westphal AH, Tischler D, van Berkel WJ (2014) Flavin dependent monooxygenases. Arch Biochem Biophys 544:2–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2013.12.005
Ji G, Silver S (1992a) Reduction of arsenate to arsenite by the ArsC protein of the arsenic resistance operon of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9474–9478
Ji G, Silver S (1992b) Regulation and expression of the arsenic resistance operon from Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. J Bacteriol 174:3684–3694
Ji G, Garber EA, Armes LG, Chen CM, Fuchs JA, Silver S (1994) Arsenate reductase of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. Biochemistry 33:7294–7299
Kang YS, Bothner B, Rensing C, McDermott TR (2012) Involvement of RpoN in regulating bacterial arsenite oxidation. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5638–5645. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00238-12
Kapaj S, Peterson H, Liber K, Bhattacharya P (2006) Human health effects from chronic arsenic poisoning—a review. J Environ Sci Health Part A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 41:2399–2428. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520600873571
Kashyap DR, Botero LM, Franck WL, Hassett DJ, McDermott TR (2006) Complex regulation of arsenite oxidation in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 188:1081–1088. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.188.3.1081-1088.2006
Koechler S, Cleiss-Arnold J, Proux C, Sismeiro O, Dillies MA, Goulhen-Chollet F, Hommais F, Lievremont D, Arsene-Ploetze F, Coppee JY, Bertin PN (2010) Multiple controls affect arsenite oxidase gene expression in Herminiimonas arsenicoxydans. BMC Microbiol 10:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-10-53
Krafft T, Macy JM (1998) Purification and characterization of the respiratory arsenate reductase of Chrysiogenes arsenatis. Eur J Biochem 255:647–653
Kuroda M, Dey S, Sanders OI, Rosen BP (1997) Alternate energy coupling of ArsB, the membrane subunit of the Ars anion-translocating ATPase. J Biol Chem 272:326–331
Laverman AM, Blum JS, Schaefer JK, Phillips E, Lovley DR, Oremland RS (1995) Growth of strain SES-3 with arsenate and other diverse electron acceptors. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3556–3561
Lin YF, Walmsley AR, Rosen BP (2006) An arsenic metallochaperone for an arsenic detoxification pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15617–15622. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603974103
Lin YF, Yang J, Rosen BP (2007) ArsD: an As(III) metallochaperone for the ArsAB As(III)-translocating ATPase. J Bioenerg Biomembr 39:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-007-9113-y
Liu G, Liu M, Kim EH, Maaty WS, Bothner B, Lei B, Rensing C, Wang G, McDermott TR (2012) A periplasmic arsenite-binding protein involved in regulating arsenite oxidation. Environ Microbiol 14:1624–1634. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02672.x
Malasarn D, Keeffe JR, Newman DK (2008) Characterization of the arsenate respiratory reductase from Shewanella sp. strain ANA-3. J Bacteriol 190:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01110-07
Meng YL, Liu Z, Rosen BP (2004) As(III) and Sb(III) uptake by GlpF and efflux by ArsB in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 279:18334–18341. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M400037200
Muller D, Lievremont D, Simeonova DD, Hubert JC, Lett MC (2003) Arsenite oxidase aox genes from a metal-resistant beta-proteobacterium. J Bacteriol 185:135–141
Murphy JN, Saltikov CW (2007) The cymA gene, encoding a tetraheme c-type cytochrome, is required for arsenate respiration in Shewanella species. J Bacteriol 189:2283–2290. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01698-06
Nadar SV, Yoshinaga M, Kandavelu P, Sankaran B, Rosen BP (2014) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of the ArsI C-As lyase from Thermomonospora curvata. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Commun 70:761–764. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X14008814
Newman DK, Kennedy EK, Coates JD, Ahmann D, Ellis DJ, Lovley DR, Morel FM (1997) Dissimilatory arsenate and sulfate reduction in Desulfotomaculum auripigmentum sp. nov. Arch Microbiol 168:380–388
Nordstrom DK (2002) Public health. Worldwide occurrences of arsenic in ground water. Science 296:2143–2145. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1072375
Qin J, Rosen BP, Zhang Y, Wang G, Franke S, Rensing C (2006) Arsenic detoxification and evolution of trimethylarsine gas by a microbial arsenite S-adenosylmethionine methyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2075–2080. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506836103
Rahman M, Tondel M, Ahmad SA, Axelson O (1998) Diabetes mellitus associated with arsenic exposure in Bangladesh. Am J Epidemiol 148:198–203
Reaves ML, Sinha S, Rabinowitz JD, Kruglyak L, Redfield RJ (2012) Absence of detectable arsenate in DNA from arsenate-grown GFAJ-1 cells. Science 337:470–473. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1219861
Rosen BP (2002) Biochemistry of arsenic detoxification. FEBS Lett 529:86–92
Rosen BP, Liu Z (2009) Transport pathways for arsenic and selenium: a minireview. Environ Int 35:512–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2008.07.023
Rosen BP, Hsu CM, Karkaria CE, Owolabi JB, Tisa LS (1990) Molecular analysis of an ATP-dependent anion pump. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 326:455–463
Rosenberg H, Gerdes RG, Chegwidden K (1977) Two systems for the uptake of phosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 131:505–511
Saltikov CW, Newman DK (2003) Genetic identification of a respiratory arsenate reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10983–10988. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1834303100
Santini JM, vanden Hoven RN (2004) Molybdenum-containing arsenite oxidase of the chemolithoautotrophic arsenite oxidizer NT-26. J Bacteriol 186:1614–1619
Sato T, Kobayashi Y (1998) The ars operon in the skin element of Bacillus subtilis confers resistance to arsenate and arsenite. J Bacteriol 180:1655–1661
Sharma VK, Sohn M (2009) Aquatic arsenic: toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environ Int 35:743–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2009.01.005
Shen Z, Luangtongkum T, Qiang Z, Jeon B, Wang L, Zhang Q (2014) Identification of a novel membrane transporter mediating resistance to organic arsenic in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:2021–2029. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02137-13
Shi J, Vlamis-Gardikas A, Aslund F, Holmgren A, Rosen BP (1999) Reactivity of glutaredoxins 1, 2, and 3 from Escherichia coli shows that glutaredoxin 2 is the primary hydrogen donor to ArsC-catalyzed arsenate reduction. J Biol Chem 274:36039–36042
Sofia HJ, Burland V, Daniels DL, Plunkett G III, Blattner FR (1994) Analysis of the Escherichia coli genome. V. DNA sequence of the region from 76.0 to 81.5 minutes. Nucleic Acids Res 22:2576–2586
Tchounwou PB, Patlolla AK, Centeno JA (2003) Carcinogenic and systemic health effects associated with arsenic exposure—a critical review. Toxicol Pathol 31:575–588. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230390242007
Tisa LS, Rosen BP (1990) Molecular characterization of an anion pump. The ArsB protein is the membrane anchor for the ArsA protein. J Biol Chem 265:190–194
Tong T, Chen S, Wang L, Tang Y, Ryu JY, Jiang S, Wu X, Chen C, Luo J, Deng Z, Li Z, Lee SY, Chen S (2018) Occurrence, evolution, and functions of DNA phosphorothioate epigenetics in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E2988–E2996. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1721916115
Walker JE, Saraste M, Runswick MJ, Gay NJ (1982) Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J 1:945–951
Wang G, Kennedy SP, Fasiludeen S, Rensing C, DasSarma S (2004) Arsenic resistance in Halobacterium sp. strain NRC-1 examined by using an improved gene knockout system. J Bacteriol 186:3187–3194
Wang L, Chen S, Xiao X, Huang X, You D, Zhou X, Deng Z (2006) arsRBOCT arsenic resistance system encoded by linear plasmid pHZ227 in Streptomyces sp. strain FR-008. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3738–3742. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.5.3738-3742.2006
Wang L, Chen S, Xu T, Taghizadeh K, Wishnok JS, Zhou X, You D, Deng Z, Dedon PC (2007) Phosphorothioation of DNA in bacteria by dnd genes. Nat Chem Biol 3:709–710. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2007.39
Wang L, Chen S, Vergin KL, Giovannoni SJ, Chan SW, DeMott MS, Taghizadeh K, Cordero OX, Cutler M, Timberlake S, Alm EJ, Polz MF, Pinhassi J, Deng Z, Dedon PC (2011) DNA phosphorothioation is widespread and quantized in bacterial genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:2963–2968. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1017261108
Wang L, Jiang S, Chen C, He W, Wu X, Wang F, Tong T, Zou X, Li Z, Luo J, Deng Z, Chen S (2018a) Synthetic genomes: from DNA synthesis to genome design. Angew Chemie Int Ed 57:2–11
Wang L, Jiang S, Deng Z, Dedon PC, Chen S (2018b) DNA phosphorothioate modification—a new multi-functional epigenetic system in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuy036
Willsky GR, Malamy MH (1980a) Characterization of two genetically separable inorganic phosphate transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 144:356–365
Willsky GR, Malamy MH (1980b) Effect of arsenate on inorganic phosphate transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 144:366–374
Wolfe-Simon F, Switzer Blum J, Kulp TR, Gordon GW, Hoeft SE, Pett-Ridge J, Stolz JF, Webb SM, Weber PK, Davies PC, Anbar AD, Oremland RS (2011) A bacterium that can grow by using arsenic instead of phosphorus. Science 332:1163–1166. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1197258
Wu J, Rosen BP (1991) The ArsR protein is a trans-acting regulatory protein. Mol Microbiol 5:1331–1336
Wu J, Rosen BP (1993) The arsD gene encodes a second trans-acting regulatory protein of the plasmid-encoded arsenical resistance operon. Mol Microbiol 8:615–623
Wu S, Wang L, Gan R, Tong T, Bian H, Li Z, Du S, Deng Z, Chen S (2018) Signature arsenic detoxification pathways in Halomonas sp. strain GFAJ-1. mBio 9:e00515-8
Xu C, Zhou T, Kuroda M, Rosen BP (1998) Metalloid resistance mechanisms in prokaryotes. J Biochem 123:16–23
Xue XM, Yan Y, Xu HJ, Wang N, Zhang X, Ye J (2014) ArsH from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 reduces chromate and ferric iron. FEMS Microbiol Lett 356:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12481
Yang HC, Cheng J, Finan TM, Rosen BP, Bhattacharjee H (2005) Novel pathway for arsenic detoxification in the legume symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 187:6991–6997. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.20.6991-6997.2005
Yang J, Rawat S, Stemmler TL, Rosen BP (2010) Arsenic binding and transfer by the ArsD As(III) metallochaperone. Biochemistry 49:3658–3666. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi100026a
Ye J, Yang HC, Rosen BP, Bhattacharjee H (2007) Crystal structure of the flavoprotein ArsH from Sinorhizobium meliloti. FEBS Lett 581:3996–4000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2007.07.039
Yoshinaga M, Rosen BP (2014) A CAs lyase for degradation of environmental organoarsenical herbicides and animal husbandry growth promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:7701–7706. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1403057111
Yuan C, Lu X, Qin J, Rosen BP, Le XC (2008) Volatile arsenic species released from Escherichia coli expressing the AsIII S-adenosylmethionine methyltransferase gene. Environ Sci Technol 42:3201–3206
Zargar K, Hoeft S, Oremland R, Saltikov CW (2010) Identification of a novel arsenite oxidase gene, arxA, in the haloalkaliphilic, arsenite-oxidizing bacterium Alkalilimnicola ehrlichii strain MLHE-1. J Bacteriol 192:3755–3762. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00244-10
Zargar K, Conrad A, Bernick DL, Lowe TM, Stolc V, Hoeft S, Oremland RS, Stolz J, Saltikov CW (2012) ArxA, a new clade of arsenite oxidase within the DMSO reductase family of molybdenum oxidoreductases. Environ Microbiol 14:1635–1645. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02722.x
Zhou T, Radaev S, Rosen BP, Gatti DL (2000) Structure of the ArsA ATPase: the catalytic subunit of a heavy metal resistance pump. EMBO J 19:4838–4845. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.17.4838
Zhu YG, Johnson TA, Su JQ, Qiao M, Guo GX, Stedtfeld RD, Hashsham SA, Tiedje JM (2013) Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes in Chinese swine farms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:3435–3440. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1222743110
Zhu YG, Yoshinaga M, Zhao FJ, Rosen BP (2014) Earth abides arsenic biotransformations. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 42:443–467. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-054942
Zou X, Wang L, Li Z, Luo J, Wang Y, Deng Z, Du S, Chen S (2018) Genome engineering and modification toward synthetic biology for the production of antibiotics. Med Res Rev 38:229–260. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21439
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the National Science Foundation of China (31720103906, 31520103902, 31670072, 31670086, and 31170070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This work does not contain any research with human participants and/or animals.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all the authors included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kupiec.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, G., Chen, X., Du, S. et al. Genetic mechanisms of arsenic detoxification and metabolism in bacteria. Curr Genet 65, 329–338 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-018-0894-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-018-0894-9