Abstract
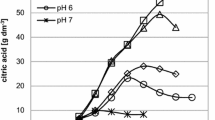
Oxalic acid is the predominant by-product formed in the scleroglucan production process with Sclerotium rolfsii, representing an additional cost factor for the subsequent downstream processing. In this study, the formation of oxalic acid was substantially reduced using a low initial pH and oxygen limitation during batch cultivation. At an initial pH of 2.0 only traces of oxalic acid were determined in the culture medium (end concentration <0.5 g l−1) while the scleroglucan production remained unaffected. In addition, it was observed that oxalic acid formation ceased under oxygen limitation. This is due to a not yet described oxalic acid synthetic enzyme named glycolate oxidase (EC 1.1.3.15) which was identified in cell-free extracts of Sclerotium rolfsii and further characterized. The influence of the dissolved oxygen tension (DOT) on oxalic acid synthesis by the fungus was studied in continuous culture. The steady-state oxalic acid concentration in the culture medium increased with a rise in DOT.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 February 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schilling, B., Henning, A. & Rau, U. Repression of oxalic acid biosynthesis in the unsterile scleroglucan production process with Sclerotium rolfsii ATCC 15205. Bioprocess Engineering 22, 51–55 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009101
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009101