Abstract
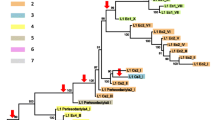
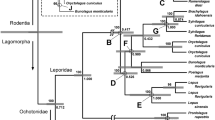
We determined ∼215 bp of DNA sequence from the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) of 240 cloned L1 (LINE-1) elements isolated from 22 species of Rattus sensu lato and Rattus sensu stricto murine rodents. The sequences were sorted into different L1 subfamilies, and oligonucleotides cognate to them were hybridized to genomic DNA of various taxa. From the distribution of the L1 subfamilies in the various species, we inferred the partial phylogeny of Rattus sensu lato. The four Maxomys species comprise a well-defined clade separate from a monophyletic cluster that contains the two Leopoldamys and four Niviventer species. The Niviventer/ Leopoldamys clade, in turn, shares a node with the clade that contains Berylmys, Sundamys, Bandicota, and Rattus sensu stricto. The evolutionary relationships that we deduced agree with and significantly extend the phylogeny of Rattus sensu lato established by other molecular criteria. Furthermore, the L1 amplification events scored here produced a unique phylogenetic tree, that is, in no case did a character (a given L1 amplification event) appear on more than one branch. The lack of homoplasy found in this study supports the robustness of L1 amplification events as phylogenetic markers for the study of mammalian evolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA (1989) Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Buluwela L, Forster A, Boehm T, Rabbitts TH (1989) A rapid procedure for colony screening using nylon filters. Nucleic Acids Res 17: 452
Burton FH, Loeb DD, Voliva CF, Martin SL, Edgell MH, Hutchison III CA (1986) Conservation throughout mammalia and extensive protein-encoding capacity of the highly repeated DNA long interspersed sequence one. J Mol Biol 187: 291–304
Carleton MD, Musser GG (1984) Muroid rodents. Orders and families of Recent mammals of the world. Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 289–379
Casavant NC, Hardies SC (1994) The dynamics of murine LINE-1 subfamily amplification. J Mol Biol 241: 390–397
Catzeflis F (1991) Animal tissue collections for molecular genetics and systematics. Trends Ecol Evol 6: 168
Chan KL, Dhaliwal SS, Yong HS (1979) Protein variation and systematics of three subgenera of malayan rats (Rodentia: Muridae, genus Rattus Fisher). Comp Biochem and Physiol 64B: 329–337
Chevret P (1994) Etude évolutive des Murinae (Rongeurs: Mammifères) africains par hybridations ADN/ADN. Comparisons avec les approches morphologiques et paléontologiques. Montpellier II
Chevret P(submitted) Relationships of seven genera of the Rattus group (Rodentia: Murinae) deduced from DNA/DNA hybridization. J Mammalogy
Chevret P, Denys C, Jaeger J-J, Michaux J, Catzeflis FM (1993) Molecular evidence that the spiny mouse (Acomys) is more closely related to gerbils (Gerbillinae) than to true mice (Murinae). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 3433–3436
Denys C, Michaux J (1992) La troisième molaire supérieure chez les Muridae d’Afrique tropicale et le cas des genres Acomys, Uranomys, et Lophuromys. Bonn Zool Beitr 43: 367–382
Ellerman JR (1941) The families and genera of living rodents. British Museum (Natural History), London
Ellerman JR (1947-1948) Notes on some Asiatic rodents in the British Museum. Proc Zool Soc London 117: 259–271
Ellerman JR (1949) The families and genera of living rodents. Vol III, Appendix II (Notes on the rodents from Madagascar in the British Museum, and on a collection from the island obtained by Mr. C. S. Webb). London, British Museum (Natural History)
Fanning TG (1983) Size and structure of the highly repetitive BAM HI element in mice. Nucleic Acids Res 11: 5073–5091
Furano AV, Hayward BE, Chevret P, Catzeflis F, Usdin K (1994) Amplification of the ancient murine Lx family of long interspersed repeated DNA occurred during the murine radiation. J Mol Evol 38: 18–27
Furano AV, Robb SM, Robb FT (1988) The structure of the regulatory region of the rat L1 (L1Rn, long interspersed repeated) DNA family of transposable elements. Nucleic Acids Res 16: 9215–9231
Furano AV, Usdin K (1995) DNA fossils and phylogenetic analysis. Using L1 (LINE-1, long interspersed repeated) DNA to determine the evolutionary history of mammals. J Biol Chem 270: 25301–25304
Gadi IK, Sharma T (1983) Cytogenetic relationships in Rattus, Cremnomys, Millardia, Nesokia, and Bandicota. Genetica 61: 21–40
Gemmeke H, Niethammer J (1984) Zur Taxonomie der Gattung Rattus (Rodentia, Muridae). Z Säugetierkunde 49: 104–116
Hänni C, Laudet V, Barriel V, Catzeflis FM (1995) Evolutionary relationships of Acomys and other murids (Rodentia, Mammalia) based on complete 12s rRNA mitochondrial gene sequences. Israel J Zool 41: 131–146
Hardison R, Miller W (1993) Use of long sequence alignments to study the evolution and regulation of mammalian globin gene clusters. Mol Biol Evol 10: 73–102
Hayward BE, Zavanelli M, Furano AV (1997) Recombination creates novel L1 (LINE-1) elements in Rattus norvegicus. Genetics 146: 641–654
Misonne X (1969) African and Indo-Australian Muridae: Evolutionary trends. Annales du Musée Royal d’Afrique Centrale, Tervuuren 172: 1–219
Modi WS (1996) Phylogenetic history of LINE-1 among arvicolid rodents. Mol Biol Evol 13: 633–641
Musser GG (1969) Results of the Archbold Expeditions. No. 91. A new genus and species of murid rodent from Celebes, with a discussion of its relationships. Amer Mus Novitates 2384: 1–41
Musser GG (1970) Rattus masaretes: a synonym of Rattus rattus moluccarius. J Mammalogy 51: 606–609
Musser GG (1981) Results of the Archbold Expeditions. N∘ 105. Notes on systematics of Indo-Malayan murid rodents, and descriptions of new genera and species from Ceylon, Sulawesi, and the Philippines. Bull Amer Mus Nat Hist 168: 225–334
Musser GG, Carleton MD (1993) Family Muridae. Mammal species of the world. A taxonomic and geographic reference. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington and London, pp 501–755
Musser GG, Heaney LR (1992) A review of the Philippine Muridae. Bull Amer Mus Nat Hist 211: 1–138
Musser GG, Holden HE (1991) Sulawesi rodents (Muridae: Murinae): morphological and geographical boundaries of species in the Rattus hoffmanni group and a new species form Pulua Peleng. Bull Amer Mus Nat Hist 206: 322–413
Musser GG, Marshall JT, Boeadi (1979) Definition and contents of the Sundaic genus Maxomys (Rodentia, Muridae). J Mammalogy 60: 592–606
Musser GG, Newcomb C (1983) Malaysian murids and the giant rat of Sumatra. Bull Amer Mus Nat Hist 174: 327–598
Niethammer J (1977) Versuch der Rekonstruktion der phylogenetischen Beziehungen zwischen einigen zentralasiatischen Muriden. Bonn Zool Beitr 28: 236–247
Padgett RW, Hutchison III CA, Edgell MH (1988) The F-type 5′ motif of mouse L1 elements: a major class of L1 termini similar to the A-type in organization but unrelated in sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 16: 739–749
Pascale E, Liu C, Valle E, Usdin K, Furano AV (1993) The evolution of long interspersed repeated DNA (L1, LINE 1) as revealed by the analysis of an ancient rodent L1 DNA family. J Mol Evol 36: 9–20
Pascale E, Valle E, Furano AV (1990) Amplification of an ancestral mammalian L1 family of long interspersed repeated DNA occurred just before the murine radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 9481–9485
Philippe H (1993) MUST, a computer package for management utilitarians for sequences and trees. Nucleic Acids Res 21: 5264–5272
Rickart EA, Musser GG (1993) Philippine rodents: chromosomal characteristics and their significance for phylogenetic inference among 13 species (Rodentia: Muridae: Murinae). Amer Mus Novitates 3064: 1–34
Rikke BA, Hardies SC (1991) LINE-1 repetitive DNA probes for species-specific cloning from Mus spretus and Mus domesticus genomes. Genomics 11: 895–904
Ruedas LA, Kirsch JAW (1997) Systematics of Maxomys Sody, 1936 (Rodentia: Muridae: Murinae): DNA/DNA hybridization studies of some Borneo-Javan species and allied Sundaic and Australo-Papuan genera. Biol J Linn Soc London 61: 385–408
Rychlik W, Rhoads RE (1989) A computer program for choosing optimal oligonucleotides for filter hybridization, sequencing, and in vitro amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 17: 8543–8551
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4: 406–425
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chainterminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467
Scott AF, Schmeckpeper BJ, Abdelrazik M, Comey CT, O’Hara B, Rossiter JP, Cooley T, Heath P, Smith KD, Margolet L (1987) Origin of the human L1 elements: proposed progenitor genes deduced from a consensus DNA sequence. Genomics 1: 113–125
Simpson GG (1945) The principles of classification and a classification of mammals. Bull Amer Mus Nat Hist 85: 1–350
Smit AFA, Tóth G, Riggs AD, Jurka J (1995) Ancestral, mammalianwide subfamilies of LINE-1 repetitive sequences. J Mol Biol 246: 401–417
Usdin K, Chevret P, Catzeflis FM, Verona R, Furano AV (1995) L1 (LINE-1) retrotransposable elements provide a fossil record of the phylogenetic history of murid rodents. Mol Biol Evol 12: 73–82
Voliva CF, Jahn CL, Comer MB, Hutchison III CA, Edgell MH (1983) The L1Md long interspersed repeat family in the mouse: almost all examples are truncated at one end. Nucleic Acids Res 11: 8847–8859
Watts CHS, Baverstock PR (1994) Evolution in some South-East Asian Murinae (Rodentia), as assessed by microcomplement fixation of albumin, and their relationship to Australian murines. Aust J Zool 42: 711–722
Watts CHS, Baverstock PR (1995) Evolution in some African Murinae (Rodentia) assessed by microcomplement fixation of albumin. J African Zool 109: 423–433
Yosida TH (1980) Cytogenetics of the black rat. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verneau, O., Catzeflis, F. & Furano, A.V. Determination of the evolutionary relationships in Rattus sensu lato (Rodentia : Muridae) using L1 (LINE-1) amplification events. J Mol Evol 45, 424–436 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006247
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006247