Abstract.
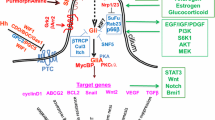
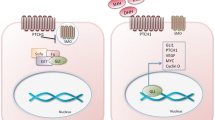
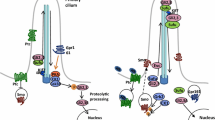
Hedgehog signalling is a key regulator of embryonic development controlling proliferation and/or cell fate determination. With identification of the Hedgehog receptor PTCH1 as a tumour suppressor gene that underlies the human nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS), the Hedgehog signalling pathway was firmly linked to cancer. It now appears that constitutive activation of Hedgehog signalling, by inactivating mutations in PTCH1 or activating mutations in the coreceptor SMOH, is required and possibly sufficient for basal cell carcinoma development and also contributes to the formation of a variety of other tumour types, including medulloblastoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. Several lines of evidence, including transgenic mice experiments, suggest that the critical cellular effect is stimulation of proliferation mediated by the transcriptional effector GLI1. Additional components of the signal transduction machinery as well as essential target genes remain to be identified, and involvement of the Hedgehog signalling pathway in other tumour types and/or hereditary cancer predisposition syndromes is to be expected.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toftgård, R. Hedgehog signalling in cancer . CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 57, 1720–1731 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000654
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000654