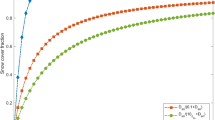
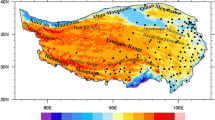
Abstract
In order to develop a seasonal snow model of land surface process as accurately as possible for climatic study, it is necessary to fully understand the effects of important snow internal processes and interaction with air and to get an insight into influence of several relevant parameterization schemes with parameters’ uncertainty to some degree. Using the snow model (SAST) developed by first author and other one and some useful field observation data, this paper has conducted a series of sensitivity studies on the parameterization schemes. They are relative to compaction process, snow thermal conduction, methodology of layering snow pack and to key parameters such as snow albedo, water holding capacity. Then, based on the results from the sensitivity studies, some useful conclusions for snow cover model improvement are obtained from the analysis of the results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, E. A., 1976: A point energy and mass balance model of a snow cover. NOAA Technical Report NWS, 19, Office of Hydrology, National Weather Service, Silver Spring, MD.
Barnett, T. P., L. Dumenil, U. Schlese, E. Roeckner, and M. Latif, 1989: The effect of Eurasian snow cover on regional and global climate variations. Journal of Atmospheric Science, 46, 661–685.
Cohen, J., and D. Rind, 1991: The effect of snow cover on the climate. Journal of Climate, 4, 689–706.
Dewey, K. F., 1997: Daily minimun, and maximun temperature forecast and the influence of snow cover. Mon. Weat. Rev., 105, 1594–1598.
Gray, D. M., and P. G. Landine, 1987: Albedo model for shallow prairie snow covers. Canadian Journal of Earth Science, 24, 1760–1768.
Hahn, D. G., and J. Shukla, 1976: An apparent relation between Eurasian snow cover and India monsoon rainfall. Journal of Atmospheric Science, 33, 2461–2462.
Jin, J. M., X. Gao, Z. L. Yang, R. C. Bales, S. Sorooshian, R. E. Dickinson, S. F. Sun, and G. X. Wu, 1999: Comparative analyses of physically based snowmelt models for climate simulations. Journal of Climate, 12, 2643–2657.
Jordan, R., 1991: A one-dimensional Temperature Model for a Snow Cover. CRREL, Special Report, 91–lb.
Kondo, J., and T. Yamazaki, 1990: A prediction model for snowmelt, snow surface temperature and freezing depth using a heat balance method. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 29, 375–384.
Kukla, G., 1981: Climate role of snow cover, in Allison, A. (ed.), Sea Level, Ice and Climatic Change, International Association of Hydrological Sciences Publication 131, Washington DC, 79–107.
Loth, B., and H. F. Graf, 1993: Snow cover model for global climate simulation. Journal of Geophysical Research, 98(D6), 10451–10464.
Loth, B., and H.F. Graf, 1996: Modeling the snow cover for climate studies. Report No. 190, Max-Planck-Institute fur Meteorologie, 1–30.
Loth, B., and H.F. Graf, 1998: Modeling the snow cover in climate studies, I. Long term integration under different climatic conditions using a multilayered snow-cover model. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103(D10), 11313–11327.
Lynch-Stieglitz, M. 1994: The development and validation of a simple snow model for the GISS GCM. Journal of Climate, 7, 1842–1855.
Roeckner, E., K. Arpe, L. Bengtsson, S. Brinkop, L. Domenil, M. Esch, E. Kirk, F. Lunkeit, M. Ponater, B. Rockel, R. Sausen, U. Schlese, S. Schubert, M. Windelband, 1992: Simulation of the present -day climate with the ECHMA model: Impact of model physics and resolution, Max-planket-Institute fur Meteorologie, Report No. 93.
Siemer, A. H., 1988: One dimensional EBM of a snow cover taking into account liquid water transmission, Ber. Inst. Meteorol, Klimatol, Univ. Hannover, 34, 126.
Slater, A. G., A. J. Pitman, and C. E. Desborough, 1998: The validation of a snow parameterization designed for use in General Circulation Models. International Journal of Climatology, 8, 595–617.
Sturm, M., J. Holmgren, M. Konig, and K. Morris, 1987: The thermal conductivity of seasonal snow. Journal of Glaciology, 43(143), 26–42.
Sud Y. C., and D. M. Mocko, 1998: Development and evaluation of a new snow-physics model to complement SSIB (Part I), Accepted by Journal of Meteorology Society of Japan.
Sun, S. F., J. Jin, and Y. K. Xue, 1999: A simple snow-atmosphere-soil transfer model. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104(D16), 19587–19597.
Sun, S. F., and Y. K. Xue, 2001: Implementing a new snow scheme in Simplified Simple Biosphere Model. Advances in Atmosphric Sciences, 18(3), 335–354.
Vernekar, A. D., J. Zhou, and J. Shukla, 1995: The effect of Eurasian snow cover on the Indian monsoon. Journal of Climate, 8, 248–266.
Verseghy, D. L., 1991: Class a Canadian land surface scheme for GCMS, I. Soil model. International Journal of Climate, 11, 111–133.
Wagner, A. J., 1973: The influence of average snow depth on monthly mean temperature anomaly. Monthly Weather Review, 101, 626–636.
Walsh, J. E., W. H. Jasperson, and B. Ross, 1985: Influence of snow cover and soil moisture on monthly air temperature. Monthly Weather Review, 113, 756–768.
Wiliams, J., 1975: The influences of snow cover on the atmospheric circulation and its role in climate change: An analysis based on results from the NCAR global circulation model. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 14, 137–152.
Yeh, T. C., R. T. Wetherald, and S. Manabe, 1983: A model study of the short-term climate and hydrologic effect of sudden-snow-cover removal. Monthly Weather Review, 111, 1013–1024.
Yen, Y. C., 1981: Review of thermal properties of snow, ice and sea ice., CRREL Report 81-10, USA Cold Regions and Engineering Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
CDThis work is financially supported by I) National Key Programme for Developing Basic Sciences: Gl998040900-Part I, 2) NSF (key project: 49835010 D0501F, 3) NSF project: 40075019, 4) LASO 49823002, 5) National key project studies on short-range climate prediction system in China (NO. 96-908-02-02-04), 6) National key project-B: Second scientific research and experiment on Tibetan Plateau-TIPEX.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shufen, S., Jingyang, L. A Sensitivity Study on Parameterization Scheme of Snow Internal and Interfacial Processes in Snow Model. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 18, 910–928 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03403512
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03403512