Abstract
Background
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is unresponsive to conventional therapies. Forced expression of the novel tumor suppressor mda-7 gene in other cell types has resulted in decreased growth and apoptosis. We evaluated cell growth, apoptosis and tumor suppressor characteristics following forced expression of this gene in mesothelioma cell lines.
Methods
MDA-7 expression in human MPM cells at baseline, following pharmacologic differentiation and viral mda-7 transduction (Ad-mda7) were evaluated with Western blot. Cell viability was evaluated with a colorimetric (XTT) assay, and apoptosis with subG1 FACS and Hoescht. Caspase-3 expression was evaluated by functional assay. These parameters were also evaluated in a stable bcl-xl hyper-expressing MPM cell line. Bax mRNA levels were evaluated with realtime PCR.
Results
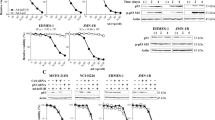
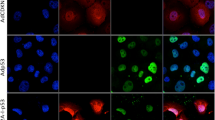
No baseline or differentiated MPM MDA7 expression was found, but was noted following Ad-mda7 exposure. More than 50% of MPM cells were killed at 5 days following Ad-mda7 exposure (p < 0.001). Apoptosis was accompanied by caspase-3 cleavage and increased BAX expression at both the protein (translational) and mRNA (transcriptional) level. These findings were reduced in a bcl-xl hyper-expressing cell line (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
Although mda-7 does not appear to be a MPM suppressor gene, adenoviral-mediated expression in cell lines induces apoptotic cellular death related to BAX upregulation and caspase cleavage. This is supported by abrogation of effect in a bcl-xl hyper-expressing cell line.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ong ST, Vogelzang NJ. (1996) Chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A review. J. Clin. Oncol. 14(3): 1007–1017.
Sahmoud T, Postmus PE, van Pottelsberghe C, et al. (1997) Etoposide in malignant pleural mesothelioma: two phase II trails of the EORTC Lung Cancer cooperative Group. Eur. J. Cancer. 33(13): 2211–2215.
Antman KH. (1989) Natural history and staging of malignant mesothelioma. Chest. 96(1 Suppl): 93S–95S.
Frizelle SP, Rubins JB, Zhou JX, et al. (2000) Gene therapy of established mesothelioma xenografts with recombinant p16INK4a adenovirus. Cancer Gene Ther. 7(11): 1421–1425.
Smythe WR, Hwang HC, Amin KM, et al. (1994) Use of recombinant adenovirus to transfer the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSVtk) gene to thoracic neoplasms: an effective in vitro drug sensitization system. Cancer Res. 54(8): 2055–2059.
Smythe WR, Hwang HC, Elshami AA, et al. (1995) Treatment of experimental human mesothelioma using adenovirus transfer of the herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene. Ann. Surg. 222(1): 78–86.
Pass HI, Robinson BW, Testa JR, Carbone M. (1999) Emerging translational therapies for mesothelioma. Chest. 116(6 Suppl): 455S–460S.
Sterman DH, Treat J, Litzky LA, et al. (1998) Adenovirus-mediated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase/ganciclovir gene therapy in patients with localized malignancy: results of a phase I clinical trial in malignant mesothelioma. Hum. Gene Ther. 9(7): 1083–1092.
Taguchi T, Jhanwar SC, Siegfried JM, et al. (1993) Recurrent deletions of specific chromosomal sites in 1p, 3p, 6q, and 9p in human malignant mesothelioma. Cancer Res. 53(18): 4349–4355.
Mor O, Yaron P, Huszar M, et al. (1997) Absence of p53 mutations in malignant mesotheliomas. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 16(1): 9–13.
Nishiyama Y, Suwa H, Okamoto K, (1995) Low incidence of point mutations in H-, K- and N-ras oncogenes and p53 tumor suppressor gene in renal cell carcinoma and peritoneal mesothelioma of Wistar rats induced by ferric nitrilotriacetate. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 86(12): 1150–1158.
Soini Y, Kinnula V, Kaarteenaho-Wiik R, et al. (1999) Apoptosis and expression of apoptosis regulating proteins bcl-2, mcl-1, bcl-X, and bax in malignant mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 5(11): 3508–3515.
Narasimhan SR, Yang L, Gerwin BI, Broaddus VC. (1998) Resistance of pleural mesothelioma cell lines to apoptosis: relation to expression of Bcl-2 and Bax. Am. J. Physiol. 275(1 Pt 1): L165–L171.
Jiang H, Lin J, Su Z-Z, et al. (1995) Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene. 11: 2477–2486.
Madireddi MT, Dent P, Fisher PB. (2000) Regulation of mda-7 gene expression during human melanoma differentiation. Oncogene. 19(10): 1362–1368.
Ekmekcioglu S, Ellerhorst J, Mhashilkar AM, et al. (2001) Down-regulated melanoma differentiation associated gene (mda-7) expression in human melanomas. Intl. J. Cancer. 94(1): 54–59.
Jiang H, Su Z-Z, Lin JJ, et al. (1996) The Melanoma Differentiation Associated Gene MDA-7 Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93: 9160–9165.
Su ZZ, Madireddi MT, Lin JJ, et al. (1998) The cancer growth suppressor gene mda-7 selectively induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in nude mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95(24): 14400–14405.
Saeki T, Mhashilkar A, Chada S, et al. (2000) Tumor-suppressive effects by adenovirus-mediated mda-7 gene transfer in non-small cell lung cancer in vitro. Gene Ther. 7: 2051–2057.
Madireddi MT, Su ZZ, Young CS, et al. (2000) Mda-7, a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene with promise for cancer gene therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 465: 239–261.
Mhashilkar AM, Schrock RD, Hindi M, et al. (2001) Melanoma differentiation associated gene (mda-7): a novel anti-tumor gene for cancer gene therapy. Mol. Med. 7(4): 271–282.
Cao XX, Mohiuddin I, Ece F, et al. (2001) Histone deacetylase inhibitor down-regulation of bcl-xl gene expression leads to apoptotic cell death in mesothelioma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 25(5): 562–568.
Korsmeyer SJ. (1999) BCL-2 gene family and the regulation of programmed cell death. Cancer Res. 59(7 Suppl): 1693s–1700s.
Nasreen N, Mohammed KA, Dowling PA, et al. (2000) Talc induces apoptosis in human malignant mesothelioma cells in vitro. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 161(2 Pt 1): 595–600.
Rubins JB, Greatens T, Kratzke RA, et al. (1998) Lovastatin induces apoptosis in malignant mesothelioma cells. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 157(5 Pt 1): 1616–1622.
Broaddus VC, Yang L, Scavo LM, et al. (1996) Asbestos induces apoptosis of human and rabbit pleural mesothelial cells via reactive oxygen species. J. Clin. Invest. 98(9): 2050–2059.
Marklund L, Henriksson R, Grankvist K. (2000) Amphotericin B-induced apoptosis and cytotoxicity is prevented by the Na+, K+, 2Cl(-)-cotransport blocker bumetanide. Life Sci. 66(23): L319–L324.
Su Z, Madireddi M, Lin J, et al. (1998) The cancer growth suppressor gene mda-7 selectively induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in nude mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95: 14400–14405.
Mohiuddin I, Cao X, Fang B, et al. (2001) Significant augmentation of pro-apoptotic gene therapy by pharmacologic bcl-xl down-regulation in mesothelioma. Cancer Gene Ther. 8: 547–554.
Shimizu S, Shinohara Y, Tsujimoto Y. (2000) Bax and Bcl-xL independently regulate apoptotic changes of yeast mitochondria that require VDAC but not adenine nucleotide translocator. Oncogene. 19(38): 4309–4318.
Kim CN, Wang X, Huang Y, et al. (1997) Overexpression of Bcl-X(L) inhibits Ara-C-induced mitochondrial loss of cytochrome c and other perturbations that activate the molecular cascade of apoptosis. Cancer Res. 57(15): 3115–3120.
Gottlieb E, Vander Heiden MG, Thompson CB. (2000) Bcl-x(L) prevents the initial decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential and subsequent reactive oxygen species production during tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis. Mol. Cell Biol. 20(15): 5680–5689.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X.X., Mohuiddin, I., Chada, S. et al. Adenoviral Transfer of mda-7 Leads to BAX Up-regulation and Apoptosis in Mesothelioma Cells, and is Abrogated by Over-expression of BCL-XL. Mol Med 8, 869–876 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03402093
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03402093