Abstract
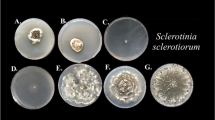
Silicon (Si) can reduce the severity of fungal diseases in field crops, but the mechanism by which Si protects plants from fungal diseases is not well understood. This study investigated the effect of potassium silicate on the growth of five soilborne phytopathogenic fungi in vitro. Results showed that the growth of four of the fungal isolates (Rhizoctonia solani, Pestalotiopsis clavispora, Fusarium oxysporum and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. fragariae) was signficantly (P < 0.05) inhibited on potassium silicate amended PDA plates. However, when the pH of potassium silicate amended PDA was reduced so that it was equivalent to unamended PDA (control), there was no difference in fungal growth between the two treatments. This indicated that the inhibition of fungal growth on potassium silicate amended PDA was due to a pH effect. Our results imply that reductions in fungal disease after field plants are treated with low concentrations of Si are probably not due to fungistatic effects of Si, but rather due to other mechanisms such as Si acting as a physical barrier against pathogen penetration or Si-induced defense response in plants.
Zusammenfassung
Silizium (Si) kann die Befallsstärke pilzlicher Krankheitserreger in Feldfrüchten vermindern, aber der Wirkungsmechanismus von Si wurde bisher nur unzureichend geklärt. In dieser Studie wurde der Einfluss von Kaliumsilikat auf das Wachstum von fünf bodenbürtigen pflanzenpathofgenen Pilzen in vitro untersucht. Die Eregebnisse zeigten, dass das Wachstum von vier Pilzisolaten (Rhizoctonia solani, Pestalotiopsis clavispora, Fusarium. oxysporum and Fusarium. oxysporum f. sp. fragariae) auf PDA-Petrischalen in Gegenwart von Kaliumsilikat signifikant (P < 0.05) vermindert war. Sank dagegen der pH des PDA-Kaliumsilikat-Mediums auf den Wert der PDA-Kontrolle, unterschied sich das Pilzwachstum der beiden Varianten nicht. Dies deutet darauf hin, dass die Wachstumsbeeinträchtigung auf Kaliumsilikat-PDA auf einem pHEffekt beruht. Die Ergebnisse implizieren, dass die Hemmwirkung geringer Si-Konzentrationen auf Pilzkrankheiten von Feldfrüchten wahrscheinlich nicht auf einer fungistatischen Wirkung, sondern eher auf anderen Mechanismen wie der Wirkung als physikalische Penetrationsbarriere oder einer Auslösung pflanzlicher Abwehrmechanismen durch das Si beruht.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bélanger, R.R., P.A. Bowen, D.L. Ehret, J.G. Menzies, 1995: Soluble silicon-its role in crop and disease management of greenhouse crops. Plant Dis. 79, 329–336.
Bekker, T.F., C. Kaiser, N. Labuschagne, 2009: The antifungal activity of potassium silicate and the role of pH against selected plant pathogenic fungi in vitro. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 26, 55–57.
Bekker, T.F., C. Kaiser, R. Van Der Merwe, N. Labuschagne, 2006: In-vitro inhibition of mycelial growth of several phytopathogenic fungi by soluble potassium silicate. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 23, 169–172.
Bi, Y., S.P. Tian, Y.R. Guo, Y.H. Ge, G.Z. Qin, 2006: Sodium silicate reduces postharvest decay on Hami melons: Induced resistance and fungistatic effects. Plant Dis. 90, 279–283.
Fawe, A., M. Abou-Zaid, J.G. Menzies, R.R. Bélanger, 1998: Silicon-mediated accumulation of flavonoid phytoalexins in cucumber. Phytopathology 88, 396–401.
Guevel, M.H., J.G. Menzies, R.R. Bélanger, 2007: Effect of root and foliar applications of soluble silicon on powdery mildew control and growth of wheat plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 119, 429–436.
Ingold, C.T., 1973: The Biology of Fungi. Hutchinson & Co. Ltd., London.
Kanto, T., K. Maekawa, M. Aino, 2007: Suppression of conidial germination and appressorial formation by silicate treatment in powdery mildew of strawberry. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 73, 1–7.
Kanto, T., A. Miyoshi, T. Ogawa, K. Maekawa, M. Aino, 2004: Suppressive effect of potassium silicate on powdery mildew of strawberry in hydroponics. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 70, 207–211.
Kanto, T., A. Miyoshi, T. Ogawa, K. Maekawa, M. Aino, 2006: Suppressive effect of liquid potassium silicate on powdery mildew of strawberry in soil. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 72, 137–142.
Li, Y.C., Y. Bi, Y.H. Ge, X.J. Sun, Y. Wang, 2009: Antifungal activity of sodium silicate on Fusarium sulphureum and its effect on dry rot of potato tubers. J. Food Sci. 74, M213–M218.
Liang, Y.C., W.C. Sun, J. Si, V. Romheld, 2005: Effects of foliarand root-applied silicon on the enhancement of induced resistance to powdery mildew in Cucumis sativus. Plant Pathol. 54, 678–685.
Ma, J.F., N. Yamaji, 2008: Functions and transport of silicon in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 3049–3057.
Maekawa, K., K. Watanabe, T. Kanto, M. Aino, M. Saigusa, 2003: Effect of soluble silicic acid on suppression of rice leaf blast. Jpn. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 74, 293–299.
Qin, G.Z., S.P. Tian, 2005: Enhancement of biocontrol activity of Cryptococcus laurentii by silicon and the possible mechanisms involved. Phytopathology 95, 69–75.
Remus-Borel, W., J.G. Menzies, R.R. Bélanger, 2005: Silicon induces antifungal compounds in powdery mildew-infected wheat. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 66, 108–115.
Wainwright, M., K. Al-Wajeeh, S.J. Grayston, 1997: Effect of silicic acid and other silicon compounds on fungal growth in oligotrophic and nutrient-rich media. Mycol. Res. 101, 933–938.
Wang, L.J., T.L. Hu, L.J. Ji, K.Q. Cao, 2007: Inhibitory efficacy of calcium cyanamide on the pathogens of replant diseases in strawberry. Front. Agric. China. 1, 183–187.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, GH., Xue, QH., Tang, M. et al. Inhibitory effects of potassium silicate on five soil-borne phytopathogenic fungi in vitro. J Plant Dis Prot 117, 180–184 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356358
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356358