Summary
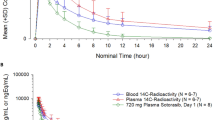
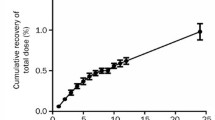
The pharmacokinetics of gold sodium thiomalate (GST) and triethylphosphine gold (auranofin; AF) are different. Gold sodium thiomalate (GST) is completely bioavailable while only 15–25% of auranofin (AF) is absorbed. Protein binding of AF occurs to a larger extent to macroglobulins than does GST and total body retention of GST is much greater than AF at six months (30% versus approximately 1%). While terminal serum half-lives are approximately equal, total body half-lives are 250 days for GST and 69 days for AF. In addition, excretory pathways contrast markedly, with 85% of AF appearing in the feces while only 30% of GST is excreted by this route; 15% of AF gold appears in the urine and approximately 70% of GST gold is excreted via this route. With all the above differences one would expect that organ and cellular distribution of these compounds would differ. While gold from both drugs is concentrated in kidney, the percent of the dose found in the kidneys is less for AF than GST, at least in animals (0.4% vs 4.8%). Minute quantities are found in other organs but more study is needed to more clearly define organ distribution of these gold compounds, particularly in man.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furst, D.E. Single dose pharmacokinetics of gold compounds. Rheumatol 1983, 8, 40–51.
Blocka, K.L., Furst, D.E., Landaw, E.M., Dromgoole, S.H., Blumberg, A., Paulus, H.E. Single dose pharmacokinetics of auranofin in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol, 1982, 9(8), 110–119.
Furst, D.E., Landaw, E.M. Unpublished data.
Blan, S.P.L. Metabolism of hold during lactation. Arthritis Rheum, 1973, 16, 777–778.
Schattenkirchner, M. Die goldbehandlung der chronishen polyarthritis. In: Compendia Rheumatologica, Editors: Mathies, Wagenhauser, Eular, Basel, 1977, 5–113.
Jeffrey, M.R., Freundlich, H.F., Bailey, D.M. Distribution and excretion of radiogold in animals. Ann Rheum Dis, 1958, 17, 52–60.
Rubinstein, H.M., Dietz, A.A., Albert, A. Serum gold levels in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis, 1973, 32, 128–131.
Intoccia, A.P., Flanagan, T.L., Walz, D.T., et al. Pharmacokinetics of Auranofin in animals. J Rheumatol, 1982, 9(8), 90–98.
Lorber, A., Jackson, W.H., Simon, TM. Effects of chrysotherapy on cell-mediated immune response. J Rheumatol, 1982, 9(8), 37–45.
Herrlinger, J.D., Alssen, C, Berens, R., Hecker, U., Weikert, W. Distribution of gold in serum erythrocytes and white blood cells after in vitro incubation and during chrysotherapy with different gold compounds. J Rheumatol, 1982, 9(8), 81–89.
Gottlieb, N.L. Comparative pharmacokinetics of parenteral and oral gold compounds. J Rheumatol, 1982, 99-111.
Gerber, R.C., Paulus, H.E., Bluestone, R., Lederer, M. Kinetics of aurthiomalate in serum and synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum, 1972, 15, 625–629.
Grahame, R., Billings, R., Laurence, M. Tissue gold levels after chrysotherapy. Ann Rheum Dis, 1973, 33, 536–539.
Vernon-Roberts, B., Dore, J.L., Jessop, J.D., Henderson, W.J. Selective concentration and localization of gold in macrophages of synovial and other tissues during and after chrysotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum, 1972, 15, 16–22.
Smith Kline Laboratories (In House Data).
Gottlieb, N.L., Smith, P.M., Smith, E.M. Tissue gold concentrations in a rheumatoid arthritic receiving chrysotherapy, Arthritis Rheum, 1972, 15, 16–22.
Dromgoole, S.H., Sarkissian, E., Furst, D.E., Blocka, K.N., Neville, M.E., Paulus, H.E. Distribution of gold in the cellular elements of blood of rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving chronic auranofin therapy (In preparation), 1983.
Ghadially, F.N. The technique of electron probe X-ray analysis and the atomic composition of aurosomes. J Rheumatol, 1979, 5, 25–30.
Thomas, L., Ghadially, F.N. Aurosomes produced in the synovial membrane by the oral administration of a gold compound. SK&F, 36914, Virchows Arch Abt B Zellpath, 1977, 26, 105–109.
Gerber, R.C., Paulus, H.E., Hennrick, R.L., Lederer, M., Bluestone, R., Blacker, W.H., Pearson, C.M. Gold kinetics following aurothiomalate therapy: use of whole body radiation counter. J Lab Clin Med, 1974, 83, 778–789.
Gottlieb, N.L., Smith, P.M., Smith, E.M. Pharmacodynamics of 197Au and 195Au-labelled aurothiomalate in blood. Arthritis Rheum, 1974, 17, 171–183.
Furst, D.E., Levine, S., Srinvasan, R., Paulus, H.E. A double-blind trial of high versus conventional dosages of gold salts for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum, 1977, 20, 1473–1480.
Weisman, M.H., Hardison, W.G.M., Walz, D.T. Studies of the intestinal metabolism of oral gold. J Rheumatol, 1980, 7, 633–638.
Jessop, J.D., Johns, R.G.S. Serum gold determinations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving socium aurothiomalate. Ann Rheum Dis, 1973, 32, 228–232.
Mascarhenas, B.R., Granda, J.L., Freyberg, R.H. Gold metabolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with gold compounds - reinvestigated. Arthritis Rheum, 1972, 15, 391–402.
Payne, B.J., Saunders, L.Z. Heavy metal nephropathy of rodents. Vet Path, 1978, 15(5), 51–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furst, D.E., Dromgoole, S.H. Comparative pharmacokinetics of triethylphosphine gold (Auranofin) and gold sodium thiomalate (GST). Clin Rheumatol 3 (Suppl 1), 17–24 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03342618
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03342618