Abstract
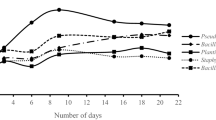
Twenty-four bacteria capable of utilizing naphthalene, as their sole source of carbon and energy for growth were isolated from three different sites in Nsukka, Nigeria. By standard bacteriological methods, these bacteria were characterized taxonomically as belonging to the genus Pseudomonas, Burkholderia or Actinomycetes. Two of the isolates, which showed the highest growth during screening as demonstrated by an increase in their optical densities (OD600) and identified as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia respectively, were also able to grow in anthracene and carbazole, but not very much so in 2,4-dichlorophenol and D-camphor. The isolates showed a concentration-dependent growth in all the compounds they grew in. There were visible changes in the colour of the growth medium of the isolates during their incubation, suggesting the production of different metabolites. There were also changes in their medium pH during growth. These studies demonstrate the possession by the bacterial species of novel degradative systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M., (1999)., Biodegradation and Bioremediation. San Diego, California: Academic Press.
Anonymous, (1983). National Academy of Science, (NAS)., Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Evaluation of Sources and Effects., London: Applied Science Publishers Ltd.
Anonymous, (1984). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency., (EPA)., Creosote — special review. Position document 213. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C.
Autrup, H., (1990)., Carcinogen metabolism in cultured human tissues and cells. Carcinogen., 11, 707–712.
Baron, J. E. and Finegold, S. M., (1990). Methods for testing antimicrobial effectiveness. In C. V. Mosby, ed. Bailey and Scotts Diagnostic Microbiology (8th. ed.) Missouri, USA.
Bauer, J. E. and Capone, D. G., (1985). Degradation and mineralization of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons anthracene and naphthalene in inter tidal marine sediments. Appl. and Environ. Microbiol., 50, 81–90.
Bosch, R., Garcia-Valdes, E. and Moore, E. R. B., (2000). Complete nucleotide sequence and evolutionary significance of a chromosomally encoded naphthalene-degradation lower pathway from Pseudomonas stutzeri AN 10. Gene., 245, 65–74.
Bossert, I., and Bartha, R., (1984). The fate of petroleum in soil ecosystems, In R. M. Atlas (ed.), Petroleum Microbiology. Macmillian Publishing Co., New York, 435–489.
Caterall, F. A., Murray, K. and Williams, P. A., (1971). The configuration of the 1,2-dihydroxy-1, 2-dihydronaphthalene formed by the bacterial metabolism of naphthalene. Biochem. Biophys. Acta., 237, 361–364.
Cerniglia, C. E., (1984). Microbial transformation of polycyclic aromatichydrocarbons. Adv. in Appl. Microbiol., 30, 31–71.
Cerniglia, C. E., and Yang, S. K., (1984). Stereoselective metabolism of anthracene and phenanthrene by the fungus Cunninghamella elegans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 47, 119–124.
Chaudry, R. G., (1994). Biological Degradation and Bioremediation of Toxic Chemicals. London: Chapman and Hall.
Cheesebrough, M., (1998). District laboratory practice in tropical countries, part II (Microbiology). Cambridgeshire Tropical Health Technology, Cambridge, UK.
Cowan, S. T. and Steele, K. J., (1974). Manual for Identification of Medical Bacteria. 2nd. Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Fu, C., Pfanstiel, S., Gao, C., Yan, X., Govind, R. and Tabak, H., (1996). Studies on Contaminant biodegradation in slurryl, water and compacted soil tube reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol., 30, 743–750.
Ghoshal, S., Ramaswami, A. and Luthy, R. G., (1996). Biodegradation of naphthalene from coal tar and heptamethylnonane in mixed batch systems. Environ. Sci. Technol., 30, 1282–1291.
Heitkamp, M. A., Freeman, J. P. and Cerniglia, C. E., (1987). Naphthalene biodegradation in environmental microcosms: estimates of degradation rates and characterization metabolites. Appl. and Environ. Microbiol., 53, 129–136.
Heitkamp, M. A., Franklin, W. and Cerniglia, C. E., (1988). Microbial metabolism of polycyclic aromatic compounds: isolation and characterization of a pyrene-degrading bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 54, 2549–2555.
Jonsen, A. R., Winding, A., Karlson, U. and Roslev, P., (2002)., Linking of microorganisms to phenanthrene metabolism in soil by analysis of 13C-labelled cell-lipids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 68, 6106–6113.
Jonsen, R. J. and Karlson, U., (2004). Evaluation of bacterial strategies to promote the bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Appl. Microbiol. Biot., 63, 452–459.
Jonsen, R. J., Lucas, Y. W. and Harms, H., (2005). Principles of microbial PAH-degradation in soil. Environ. Poll., 133, 71–84.
Kastner, M., Breuer-Jammali, M. and Mahro, B., (1994). Enumeration and characterisation of the soil microflora from hydrocarbon-contaminated soil sites able to mineralise polycyclic hydrocarbons (PAH). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 41, 267–273.
Kiyohara, H. K., Nagao, K., Kuono, K. and K. Yano., (1982). Phenanthrene-degrading phenotype of Alkaligenes fecalis AFK2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 43, 458–461.
Klaasen, C. D., (2001). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Krieg, N. R., Holt, J. G., Bergy, D. and Sneath P. H. A., (1993). Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology 9th. ed., Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore, USA.
Laflamme, R. E., and Hite, R. A., (1978). The global distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in recent sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 42, 289–303.
Lee, C. M., (1998). Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Properties and Environmental Fate. An exams model simulation. Lecture notes on EE&S (Environmental Engineering Chemistry II: Environmental Organic Chemistry. Clemson University, USA.
Levinson, W. E., Stormo, K. E., Tao, H. L. and Crawford, R. L., (1994). Hazardous waste clean-up and treatment with encapsulated or entrapped microorganisms In: G. R. Chaudry, ed., Biological Degradation and Bioremediation of Toxic Chemicals, London: Chapman and Hall., 455–469.
Lewis, D. L., Hodson, R. E. and Freeman. L. F., (1984). Effects of microbial community interactions on transformation rates of xenobiotic chemicals. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 48, 561–565.
Mitchell, J. A. and Cain, R. B., (1996). Pesticides Sci., 48, 1–11.
Miller, E. C. and Miller, J. A., (1974). Biochemical mechanisms of chemical carcinogenesis. In H. Busch, ed. The Molecular Biology of Cancer, New York: Academic Press, 377–403.
Moore, M. N., Livingstone, D. R. and Widdows, J. (1989). Hydrocarbons in marine ollusks: biological effects and ecological consequences, 291–328. In U. Varanasi (ed.) Metabolism of PAHs in the Aquatic Environment. CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, Fla.
Mueller, J. G., Chapman, P. J., Blattman, B. O. and Pritchard, P. H. (1990). Isolation and characterization of a fluoranthene-utilizing strain of Pseudomonas paucimobilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 56, 1079–1086.
Mueller, J. G., Devereux, R., Santavy, D. L., Lantz, S. E., Willis, S. E. and Pritchard, S. G., (1997). Phylogenic and physiological comparisons of PAH-degrading bacteria from geographically diverse soils. Antonie van Leeuwenhock, 71, 329–343.
Obi, I. U. (1990). Statistical methods for detecting differences between treatment means and research methodology issues in laboratory and field experiments. Nsukka: AP Express Publishers Ltd, Nigeria.
Obrigawitch, T., Martin, A. R. and Roteth. F. W., (1983). Degradation of thiocarbamate herbicides in soil exhibiting rapid EPTC breakdown. Weed Sci., 31, 187–192.
Ornston, L. N. and Yeh, W. K. (1982). Recurring themes and repeated sequences in metabolic evolution. In A. M. Chakrabarty, Ed. Biodegradation and Detoxification of Environmental Pollutants. CRC Press, Miami.
Pothuluri, J. V. and Cerniglia, C. E., (1994). Microbial metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. In G. R. Chaudry, ed. Biological Degradation and Bioremediation Toxic Chemicals. London: Chapman and Hall., 92–124.
Prantera, M. T., Drozdowicz, A., Leite S. G. and Rosado A. S., (2002). Degradation of gasoline aromatic hydrocarbons by two N2-fixing soil bacteria. Biotechnol. Lett., 24, 85–89.
Soulas, G., Codaccioni, P. and Fournier J. C., (1983). Chemosphere, 12, 1101–1106.
Spain, J. C., Pritchard, P. H. and Bourquin A. W., (1980). Effects of adaptation on biodegradation rates in sediment/ water cores for estuarine and freshwater environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 40, 726–734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nnamchi, C.I., Obeta, J.A.N. & Ezeogu, L.I. Isolation and characterization of some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacteria from Nsukka soils in Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 3, 181–190 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325924
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325924