Abstract
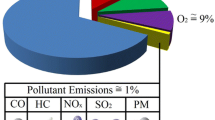
The current paper is an attempt to find a sustainable fuel strategy for passenger cars in Iran. Currently, most of Iran’s passenger cars consume gasoline, a non-renewable fossil fuel. This fuel has well-known environmental impacts, including various kinds of pollutions, as well as the threat of quick running out. These general negative characteristics of gasoline are amplified by the high consumption rate of Iran’s transportation sector, (e.g. about three times more than that of UK). The objective of this paper is firstly selecting possible alternative fuels for Iran’s transportation sector, and then proposing the percent of cars consuming these alternative fuels (along with gasoline). The best strategies are proposed based on environmental and economic considerations, and hence are more sustainable decisions comparing with the other strategies. The best strategies are found using partial order theory and Hasse diagram technique, which is a multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) tool.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asadollah-Fardi, G. R., (2004)., Current situation of air pollution in Tehran with emphasis on district 12. available at: http://www.iges.or.jp/kitakvushu/Meetings/KIN1/Presentations/SessionII/Teheran.pdf.
Anonymous, (1987)., World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED), (1987)., Our Common Future. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Anonymous, (1995)., Australian Petroleum Exploration Association, (APEA), Alternative Transport Fuels. Petroleum Topics. Australian Institute of Petroleum., available at: http://www.appea.com.au/Publications/PetroleumTopics/Alternative_Transport_fuels.pdf. (2004).
Anonymous, (1997)., Institute for Transportation Research and Studies, (ITRS)., Car ownership models (in Persian), Report No. 76-11, Mashad Comprehensive Transportation Plan, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran.
Anonymous, (2004)., Iranian Fuel Consumption Optimizing Organization, (2004)., available at: http://www.ieeo.org. Ministry of Petroleum.
Hardi, P. and Zdan, T., (1997)., Measuring Sustainable Development: Review of Current Practice, International Institute for Sustainable Development. Occasional Paper 17, Canada.
Johnson, C, (2004)., Hydrogen as a Fuel for Automobiles, available at: http://mb-soft.com/public2/hvdrogen.html.
Lerche, D. and Sonersen, P. B., (2003)., Evaluation of the ranking probabilities for partial orders based on random linear extensions, Chemosphere, 53, 981–992.
Moffatt, I., (2001). Measuring and modeling sustainable development, Parthenon Publishing Group, London.
Rassafi, A. A. and Vaziri, M., (2005)., Sustainable transport indicators: Definition and integration. Lint. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 2(1), 83–96.
Vaziri, M. and Rassafi, A. A., (2001)., An appraisal of road transport sustainable development in the Asian and pacific region. Technical Papers of International Seminar on Sustainable Development on Road Transport, New Delhi, India. III39-III46.
Vaziri, M. and Rassafi, A. A., (2003)., Globalization and sustainable development: European experience. Proceedings of “7th International Conference on Global Business and Economic Development”, Bangkok, Thailand. 36–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rassafi, A.A., Vaziri, M. & Azadani, A.N. Strategies for utilizing alternative fuels by Iranian passenger cars. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 3, 59–68 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325908
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325908